Question
(a) White light passes through a cloud of cool low-pressure gas, as illustrated in Fig. 10.1.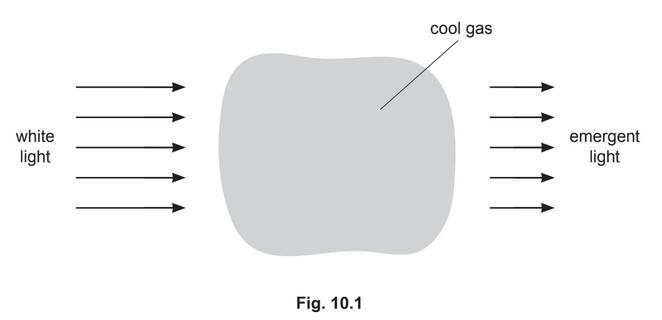
For light that has passed through the gas, its continuous spectrum is seen to contain a
number of darker lines.
Use the concept of discrete electron energy levels to explain the existence of these darker
lines.
(b) The uppermost electron energy bands in a solid are illustrated in Fig. 10.2.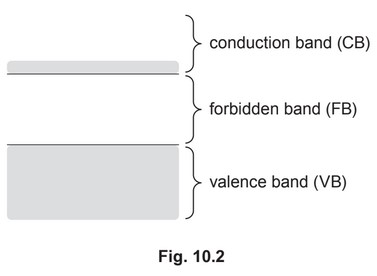
Use band theory to explain the dependence on light intensity of the resistance of a
light-dependent resistor (LDR).
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) • photon gives energy to electron (in an inner shell) or electron (in an inner shell) absorbs a photon
• electron moves (from lower) to higher energy level
• energy (of photon) is equal to difference in energy levels
• electron de-excites giving off photon (of same energy)
• photons emitted in all directions
(b) (in light) photons gives energy to electrons in VB
or
(in light) electrons in VB absorb photons
electron crosses FB/jumps to CB
(positive) holes left/created in VB
low intensity: few electrons in CB/most electrons in VB
or
high intensity: more photons so more electrons in CB
or
electron-hole pairs are charge carriers
Question
(a) (i) Explain what is meant by a photon.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
(ii) By reference to intensity of light, state one piece of evidence provided by the photoelectric
effect for a particulate nature of light.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
(b) Some electron energy levels in a solid are illustrated in Fig. 11.1.
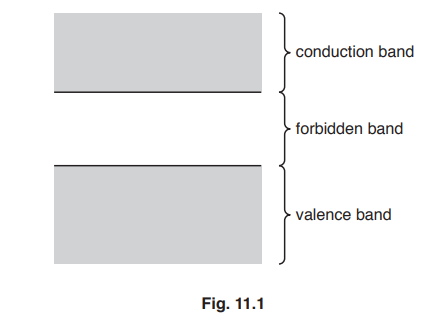
A semiconductor material has a very high resistance in darkness.
Light incident on the semiconductor material causes its resistance to decrease.
Explain the resistance of the semiconductor material in different light conditions.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[5]
Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) packet/quantum/discrete amount of energy
of electromagnetic radiation
(a)(ii) (maximum) energy of emitted electrons is independent of intensity
or
no emission of electrons below the threshold frequency regardless of intensity
or
no emission of electrons when photon energy is less than work function (energy) regardless of intensity
(b) in darkness: conduction band empty so high resistance
in daylight: electrons in valence band absorb photons
in daylight: electrons ‘jump’ to conduction band
this leaves holes in valence band
