Question
A child moves down a long slide, as shown in Fig. 4.1.
The child moves from rest at the top end X of the slide. An average resistive force of 76N opposes the motion of the child as they move to the lower end Y of the slide. The kinetic energy of the child
at Y is 300J. The decrease in gravitational potential energy of the child as it moves from X to Y is 3200J.
(a) Determine the ratio ![]()
ratio = ………………………………………………… [1]
(b) Use the answer in (a) to calculate the ratio ![]()
ratio = ………………………………………………… [2]
(c) Calculate the length of the slide from X to Y.
length = ………………………………………………m [2]
(d) At end Y of the slide, the child is brought to rest by a board, as shown in Fig. 4.2.
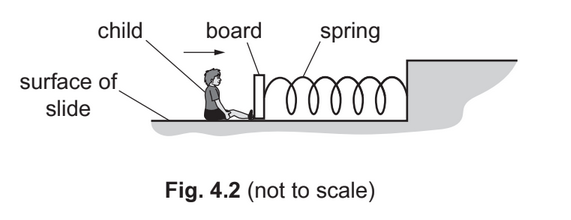
A spring connects the board to a fixed point. The spring obeys Hooke’s law and has a spring constant of 63Nm–1. The child hits the board so that it moves to the right and compresses the
spring. The speed of the child becomes zero when the elastic potential energy of the spring has increased to its maximum value of 140J.
(i) Calculate the maximum compression of the spring.
maximum compression = ………………………………………………m [2]
(ii) Calculate the percentage efficiency of the transfer of the kinetic energy of the child to the elastic potential energy of the spring.
percentage efficiency = …………………………………………….. % [1]
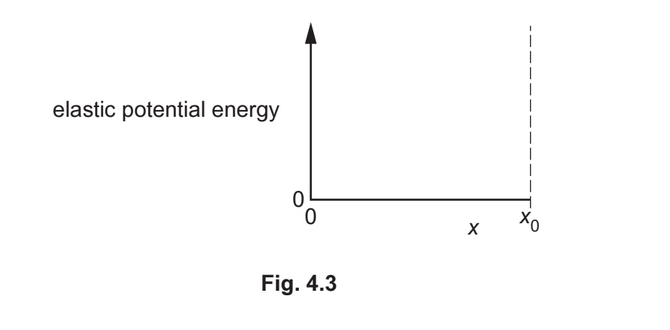
(iii) The maximum compression of the spring is \(x_0\). On Fig. 4.3, sketch a graph to show the variation of the elastic potential energy of the spring with its compression x from x = 0 to
\(x = x_0\). Numerical values are not required.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)ratio = 300 / 3200
= 0.094
(b)\(E= 1/2mv^ 2\) or E∝ \(v^ 2\)
ratio \(= (0.094)^{0.5}\)
= 0.31
(c) work (done against frictional force) = 3200– 300 (=2900)
length = 2900 / 76 = 38 m

(d)(ii) percentage efficiency = (140 / 300) × 100
= 47%
(d)(iii) curved line from the origin
gradient of line increases
Question
(a) State what is meant by work done. [1]
(b) A beach ball is released from a balcony at the top of a tall building. The ball falls vertically
from rest and reaches a constant (terminal) velocity. The gravitational potential energy of the
ball decreases by 60J as it falls from the balcony to the ground. The ball hits the ground with
speed 16ms−1 and kinetic energy 23J.
(i) Show that the mass of the ball is 0.18kg. [2]
(ii) Calculate the height of the balcony above the ground.
height = …………………………………………….. m [2]
(iii) Determine the average resistive force acting on the ball as it falls from the balcony to the
ground.
average resistive force = …………………………………………….. N [2]
(c) State and explain the variation, if any, in the magnitude of the acceleration of the ball in
(b) during the time interval when the ball is moving downwards before it reaches constant
(terminal) velocity. [3]
[Total: 10]
Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) force × displacement in the direction of the force
(b) (i) E = ½mv2
(m =) 23 × 2 / 162 = 0.18 (kg)
(b) (ii) (Δ)E = mg(Δ)h
60 = 0.18 × 9.81 × h
h = 34 m
(b )(iii) (work done =) 60 – 23
= 37 (J)
average resistive force = 37 / 34
= 1.1 N
(c) air resistance (acting on ball) increases
resultant force (on ball) decreases
or weight constant and air resistance increases
acceleration decreases
