Question
The warning signal on an ambulance has a frequency of 600 Hz. The speed of sound is \(330 m s^{–1}\). The ambulance is travelling with a constant velocity of \(25 m s^{–1}\) towards an observer. The ambulance passes, and then moves away from the observer with no change in velocity.
Which overall change in observed frequency takes place between the times at which the ambulance is a long way behind the observer and when it is a long way in front of the observer?
A \(49\) Hz B \(84\) Hz C \(91\) Hz D \(98\) Hz
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
A glass tube is closed at one end and has a loudspeaker at the other end.

A stationary wave is formed with a node at the closed end of the tube when the sound has
frequency f0. There are no other nodes.
The frequency of the sound is then slowly increased.
What is the frequency of the sound that produces the next stationary wave?
A 1.25f0 B 1.50f0 C 2.00f0 D 3.00f0
Answer/Explanation
Ans
Question
With which waves can the Doppler effect be observed?
A all waves including sound and light
B light waves only
C sound and light waves only
D sound waves only
Answer/Explanation
Ans :
Question
A stationary wave is formed from two identical sound waves.
A microphone is placed at a position of maximum loudness. It is then moved along the stationary
wave from this first position of maximum loudness to the fourth position of maximum loudness.
The microphone moves a distance of 12 cm.
The speed of sound is 330 m s -1.
What is the frequency of the sound waves?
A 4100 Hz B 5500 Hz C 8300 Hz D 11 000Hz
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
A loudspeaker emitting a sound wave of a single frequency is placed a distance L from a
reflecting surface, as shown.
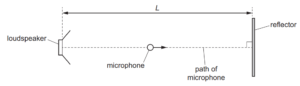
A stationary wave is formed with an antinode at the loudspeaker. A microphone is moved from
the loudspeaker to the reflector.
Before the microphone reaches the reflector, it detects four points where the sound intensity is a
minimum.
What is the wavelength of the sound wave?
Answer/Explanation
Ans
