Question
Water waves of wavelength \(\lambda\) are formed in a ripple tank. The waves are diffracted as they pass through a narrow gap of width d (d is greater than \(\lambda \)).
Which gap width and which wavelength will cause the largest decrease in the amount of diffraction?
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
A water wave in a ripple tank is diffracted as it passes through a gap in a barrier. Which two factors affect the angle of diffraction of the wave?
A the amplitude and frequency of the incident wave
B the amplitude of the incident wave and the width of the gap
C the wavelength and amplitude of the incident wave
D the wavelength of the incident wave and the width of the gap
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Which wave behaviour is shown in the diagram?
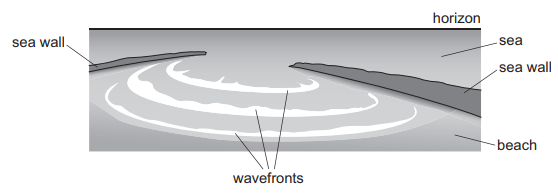
A diffraction
B Doppler shift
C interference
D superposition
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Which waves would best demonstrate diffraction through a doorway?
A sound waves
B ultraviolet waves
C visible light waves
D X-rays
Answer/Explanation
