Question
A piece of wire has a length of 0.80 m and a diameter of \(5.0\times 10^{-4}m\). The I–V characteristic of the wire is shown.
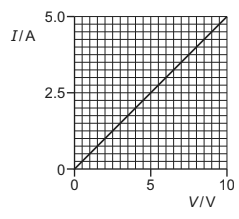
What is the resistivity of the metal from which the wire is made?
A \(1.2\times 10^{-7}\Omega m\)
B \(1.6\times 10^{-7}\Omega m\)
C \(4.9\times 10^{-7}\Omega m\)
D \(2.0\times 10^{-6}\Omega m\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Two copper wires S and T, of equal length, are connected in parallel. Wire S has a diameter of 3.0 mm. Wire T has a diameter of 1.5 mm. A potential difference is applied across the ends of this parallel arrangement. What is the value of the ratio \(\frac{current \ in\ S}{current \ in \ T}\)
A \(\frac{1}{4}\) B \(\frac{1}{2}\) C \(2\) D \(4\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
The diagram shows a network of resistors. Each resistor has resistance R.
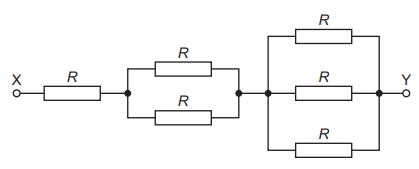
What is the total resistance of the network between points X and Y? 
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Three resistors are connected in series with a battery, as shown. The battery has negligible
internal resistance.
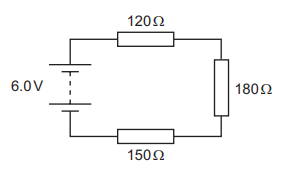
What is the potential difference across the 180 Ω resistor?
A 1.6V B 2.4V C 3.6V D 4.0V
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
A cylindrical metal wire X has resistance R. The same volume of the same metal is made into a
cylindrical wire Y of double the length.
What is the resistance of wire Y?
A R B 2R C 4R D 8R
