CIE AS/A Level Physics 18.2 Uniform electric fields Study Notes- 2025-2027 Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Physics 18.2 Uniform electric fields Study Notes – New Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Physics 18.2 Uniform electric fields Study Notes at IITian Academy focus on specific topic and type of questions asked in actual exam. Study Notes focus on AS/A Level Physics latest syllabus with Candidates should be able to:
- ecall and use E = ∆V / ∆d to calculate the field strength of the uniform field between charged parallel plate
- describe the effect of a uniform electric field on the motion of charged particles
Electric Field Between Parallel Plates
For two oppositely charged parallel plates, the electric field between them (away from the edges) is uniform. The field strength is related to the potential difference across the plates and their separation.
Formula for Uniform Electric Field Strength: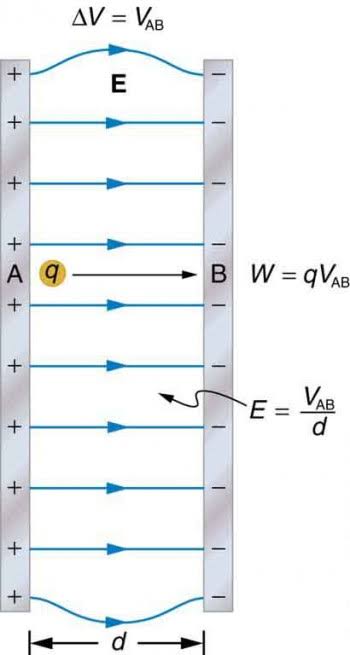
\( \mathrm{E = \dfrac{\Delta V}{\Delta d}} \)
- \( \mathrm{E} \) = electric field strength (N C⁻¹ or V m⁻¹)
- \( \mathrm{\Delta V} \) = potential difference between plates (V)
- \( \mathrm{\Delta d} \) = separation between plates (m)
Meaning:
The electric field tells you how much the potential changes per metre between the plates.
Characteristics of Uniform Fields:
- Field lines are straight, parallel, and evenly spaced.
- Field strength is the same at every point between the plates (except edges).
- A positive charge moves towards lower potential.
Example
The potential difference across two parallel plates is 300 V. The plates are separated by 0.020 m. Calculate the electric field strength between the plates.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use:
\( \mathrm{E = \dfrac{\Delta V}{\Delta d}} \)
\( \mathrm{E = \dfrac{300}{0.020} = 1.5\times 10^{4}\ V\,m^{-1}} \)
Electric field strength = \( \mathrm{1.5\times 10^{4}\ V\,m^{-1}} \)
Example
A uniform electric field of strength \( \mathrm{4.0\times 10^{3}\ V\,m^{-1}} \) is required between two parallel plates. If the plates are separated by 5.0 mm, calculate the potential difference needed.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Convert distance:
\( \mathrm{\Delta d = 5.0\ mm = 5.0\times 10^{-3}\ m} \)
Use:
\( \mathrm{\Delta V = E\Delta d} \)
\( \mathrm{\Delta V = (4.0\times 10^{3})(5.0\times 10^{-3})} \)
\( \mathrm{\Delta V = 20\ V} \)
Required potential difference = 20 V
Example
An electron is accelerated from the negative plate to the positive plate in a uniform electric field. The field strength is \( \mathrm{2.5\times 10^{4}\ V\,m^{-1}} \) and the plates are 0.015 m apart. Calculate the potential difference across the plates and the gain in electric potential energy of the electron.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
1. Potential difference:
\( \mathrm{\Delta V = E\Delta d = (2.5\times 10^{4})(0.015)} \)
\( \mathrm{\Delta V = 375\ V} \)
2. Gain in electric potential energy:
Electron charge:
\( \mathrm{q = 1.6\times 10^{-19}\ C} \)
Use \( \mathrm{\Delta U = q\Delta V} \):
\( \mathrm{\Delta U = (1.6\times 10^{-19})(375)} \)
\( \mathrm{\Delta U = 6.0\times 10^{-17}\ J} \)
Potential difference = 375 V
Energy gain = \( \mathrm{6.0\times 10^{-17}\ J} \)
Effect of a Uniform Electric Field on Charged Particles
When a charged particle enters a uniform electric field, it experiences a constant force. This causes the particle to undergo uniform acceleration, similar to how objects accelerate in a uniform gravitational field.
Force on a Charged Particle:
\( \mathrm{F = qE} \)
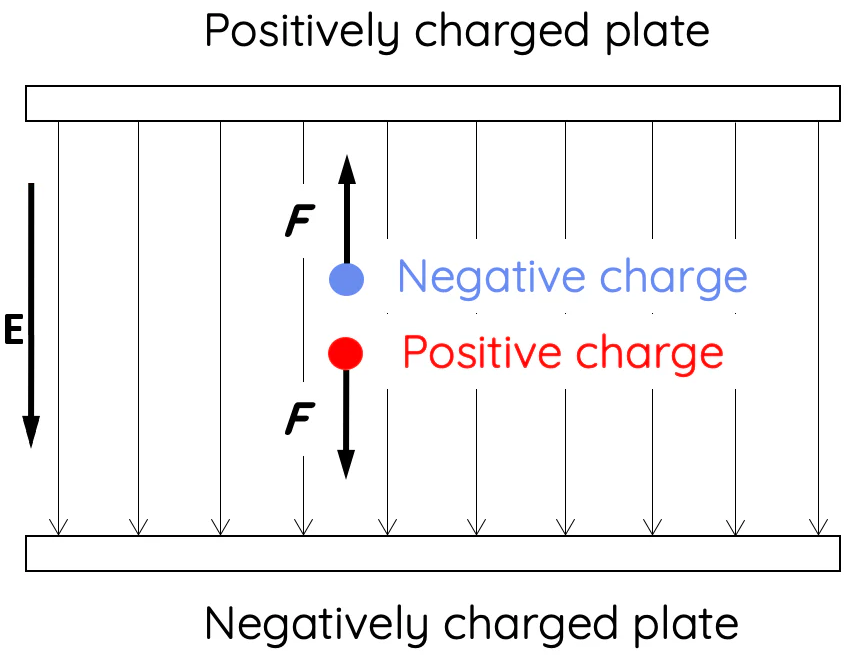
- If \( \mathrm{q > 0} \): force is in the direction of the electric field.
- If \( \mathrm{q < 0} \): force is opposite to the electric field.
Acceleration:
\( \mathrm{a = \dfrac{F}{m} = \dfrac{qE}{m}} \)
Resulting Motion:
- If the particle enters the field at rest: it accelerates in a straight line.
- If it enters with horizontal velocity:
- Horizontal motion remains constant (no horizontal force)
- Vertical motion becomes accelerated → a parabolic path (like projectile motion).
![]()
Example
A proton enters a uniform electric field directed upward. In which direction does the proton accelerate?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The proton has a positive charge. Therefore, the electric force \( \mathrm{F = qE} \) acts in the same direction as the field.
The proton accelerates upward.
Example
An electron enters a horizontal uniform electric field with an initial horizontal velocity. Describe the path it follows.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The electron is negatively charged, so it experiences a force opposite to the electric field direction.
Motion components:
- Horizontal velocity remains constant.
- Vertical acceleration occurs upward or downward depending on field direction.
The electron follows a parabolic path.
Example
An alpha particle (\( \mathrm{q = +3.2\times 10^{-19}\ C} \), \( \mathrm{m = 6.6\times 10^{-27}\ kg} \)) enters a uniform electric field of strength \( \mathrm{5.0\times 10^{3}\ V\,m^{-1}} \). Calculate its acceleration and describe its motion if it enters the field horizontally.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Acceleration:
\( \mathrm{a = \dfrac{qE}{m}} \)
\( \mathrm{a = \dfrac{(3.2\times 10^{-19})(5.0\times 10^{3})}{6.6\times 10^{-27}}} \)
\( \mathrm{a = \dfrac{1.6\times 10^{-15}}{6.6\times 10^{-27}} \approx 2.42\times 10^{11}\ m\,s^{-2}} \)
Description of motion:
- Constant horizontal velocity.
- Very large vertical acceleration in direction of electric field.
- Resulting path: a steep parabolic curve.
