CIE IGCSE Physics (0625) Power Study Notes - New Syllabus
CIE IGCSE Physics (0625) Power Study Notes
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
- Understanding the concepts of Power
Key Concepts:
- Power
Power
Power
- Power is the rate at which work is done or the rate at which energy is transferred or transformed.
SI Unit of Power: Watt (W)
- 1 watt = 1 joule/second → \( 1 \, \text{W} = 1 \, \text{J/s} \)
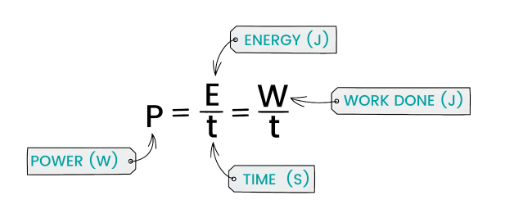
(a) Power as Work Done per Unit Time
Equation:
\( P = \dfrac{W}{t} \)
- \( P \) = Power (watts)
- \( W \) = Work done (joules)
- \( t \) = Time taken (seconds)
Explanation:
- This equation applies when a force causes an object to move and work is done over a time interval.
- The more work done in less time, the more powerful the process is.
Example:
A 60 kg student climbs a staircase of vertical height 3 m in 5 seconds. Calculate the power output.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Work done = gain in GPE
\( W = mgh = 60 \times 9.8 \times 3 = 1764 \, \text{J} \)
Step 2: Power = Work / Time
\( P = \dfrac{1764}{5} = \boxed{352.8 \, \text{W}} \)
(b) Power as Energy Transferred per Unit Time
Equation:
\( P = \dfrac{\Delta E}{t} \)
- \( P \) = Power (watts)
- \( \Delta E \) = Energy transferred (joules)
- \( t \) = Time taken (seconds)
Explanation:
- This form is commonly used when electrical or thermal energy is transferred over time.
- The faster the energy is transferred, the greater the power.
Example:
An electric kettle transfers 8400 J of thermal energy to water in 60 seconds. What is its power rating?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Use formula \( P = \dfrac{\Delta E}{t} \)
\( P = \dfrac{8400}{60} = \boxed{140 \, \text{W}} \)
The kettle operates at 140 watts.
Example:
A car engine does 40,000 J of work in moving the car 100 m in 8 seconds. Find the power output.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Given \( W = 40,000 \, \text{J}, t = 8 \, \text{s} \)
\( P = \dfrac{W}{t} = \dfrac{40000}{8} = \boxed{5000 \, \text{W}} \)
The car engine delivers 5000 watts (or 5 kW) of power.
