CIE IGCSE Physics (0625) The Sun as a star Study Notes - New Syllabus
CIE IGCSE Physics (0625) The Sun as a star Study Notes
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
- Understanding the concepts of The Sun as a star
Key Concepts:
- Properties of the Sun
- How Stars Produce Energy
Properties of the Sun
Properties of the Sun
- The Sun is classified as a medium-sized star, known as a G-type main-sequence star (G2V).
- It is a yellow star located at the center of our Solar System, with a diameter of about 1.39 million km.

Composition of the Sun
- The Sun consists mostly of hydrogen (about 74%) and helium (about 24%).
- Other heavier elements such as oxygen, carbon, and iron make up about 2%.
Energy Emission
- The Sun generates energy through nuclear fusion in its core, where hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium, releasing energy.
- This energy is radiated outward and eventually emitted as electromagnetic radiation.
Sun’s Electromagnetic Radiation
- The Sun emits radiation across the entire electromagnetic spectrum.
- The majority of the energy is radiated in the:
- Infrared (IR) – felt as heat
- Visible light – the light we see
- Ultraviolet (UV) – mostly absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere but causes sunburn
- This mix of radiation makes life on Earth possible, drives weather and climate, and provides energy for photosynthesis.
Example:
Which of the following statements about the Sun is correct?
- The Sun is a large star composed mainly of oxygen and nitrogen.
- The Sun is a medium-sized star made mostly of hydrogen and helium.
- The Sun generates energy through nuclear fission of helium into hydrogen.
- The Sun only emits energy in the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Correct Answer: B
The Sun is a medium-sized star, primarily composed of hydrogen (about 74%) and helium (about 24%). It produces energy through nuclear fusion, not fission, and it emits radiation in the infrared, visible, and ultraviolet parts of the spectrum—not just visible light.
How Stars Produce Energy
How Stars Produce Energy
- Stars, including our Sun, produce energy through nuclear reactions in their cores.
- The primary process is nuclear fusion, where lighter elements combine to form heavier ones, releasing vast amounts of energy.
Fusion in Stable Stars
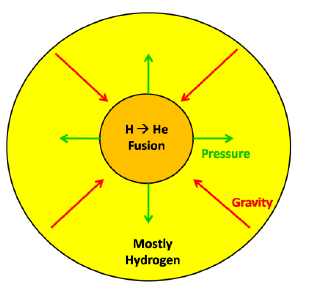
In stable, main-sequence stars like the Sun, the dominant reaction is:
- Hydrogen nuclei (protons) fuse to form helium nuclei.
- This process releases energy in the form of light and heat due to the mass difference being converted into energy (as per Einstein’s equation \( E = mc^2 \)).
Stability in a star is maintained by a balance between:
- Inward gravitational force (trying to collapse the star), and
- Outward radiation pressure from the energy produced in fusion.
Fusion Reactions in the Sun:

- The fusion of hydrogen occurs through a process called the proton-proton chain reaction.
- Overall, 4 hydrogen nuclei fuse to make 1 helium nucleus, plus energy and subatomic particles like positrons and neutrinos.
Example:
Explain how energy is produced in a stable star like the Sun. Include the type of nuclear reaction and the elements involved.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Energy in stable stars is produced through nuclear fusion. In stars like the Sun, hydrogen nuclei (protons) fuse to form helium nuclei in a reaction known as the proton-proton chain. This reaction releases a large amount of energy because some of the mass is converted into energy, as described by Einstein’s equation \( E = mc^2 \).
The outward pressure from this energy balances the inward pull of gravity, keeping the star stable.
