Edexcel iGCSE Biology-1.3 Common Features of Prokaryotic Organisms- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-1.3 Common Features of Prokaryotic Organisms- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-1.3 Common Features of Prokaryotic Organisms- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
1.3 describe the common features shown by prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria
- Bacteria: these are microscopic single-celled organisms; they have a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm and plasmids; they lack a nucleus but contain a circular chromosome of DNA; some bacteria can carry out photosynthesis but most feed off other living or dead organisms.
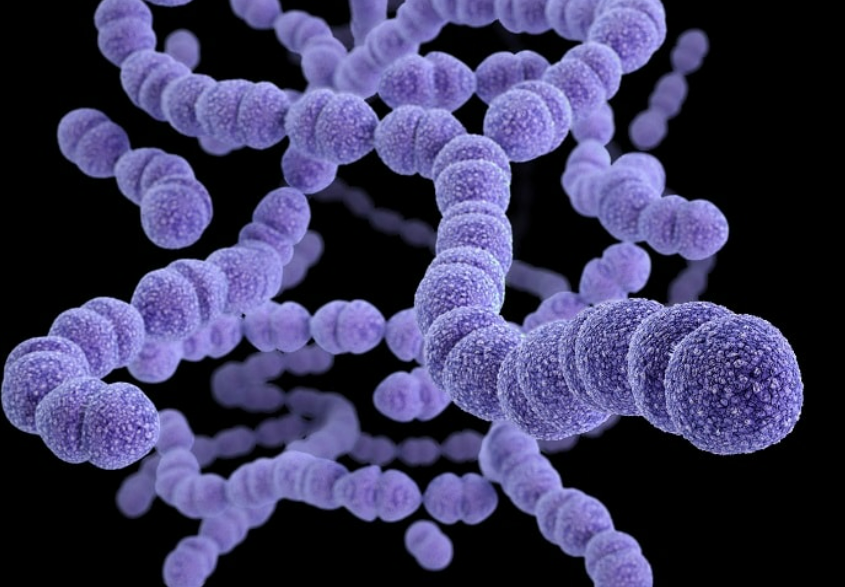
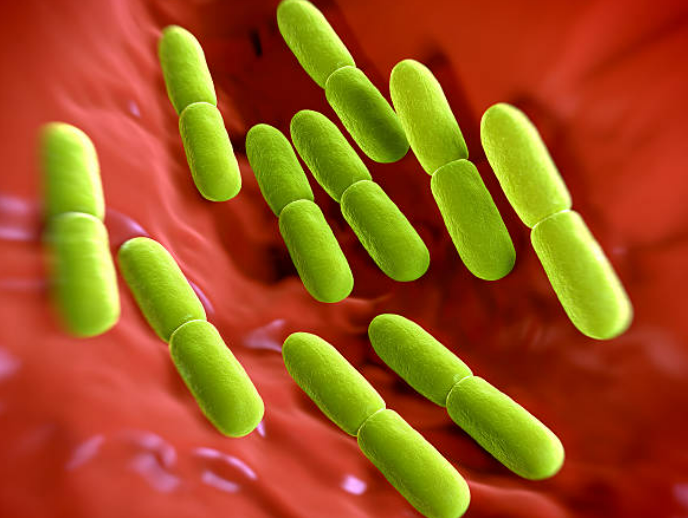
Examples include Lactobacillus bulgaricus, a rod-shaped bacterium used in the production of yoghurt from milk, and Pneumococcus, a spherical bacterium that acts as the pathogen causing pneumonia.
Prokaryotic Organisms – Bacteria
📝 Introduction
Bacteria are the main group of prokaryotes you need to study.
They are always single-celled, much simpler than eukaryotes (plants, animals, fungi, protoctists), and have no true nucleus.
🔑 Common Features of Bacteria
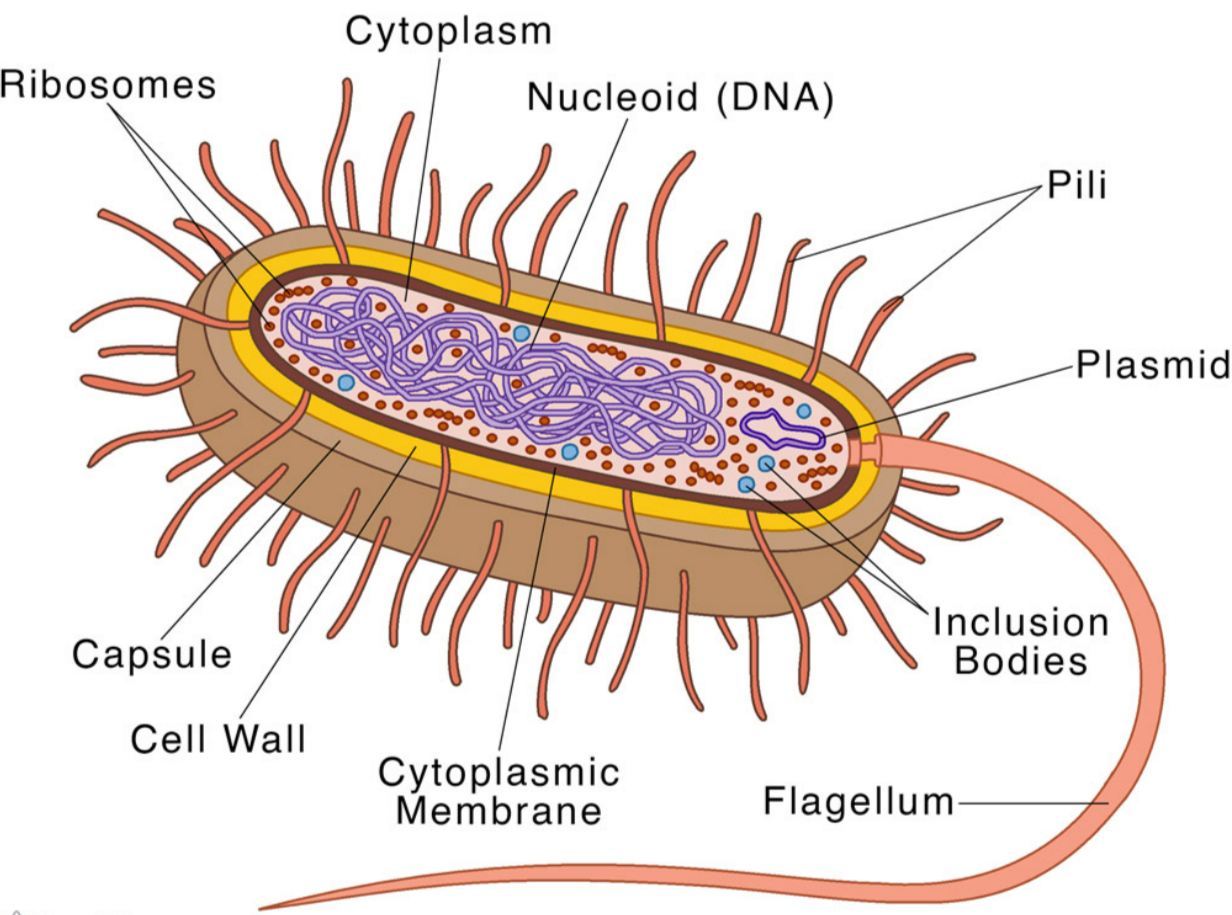
- Microscopic & Single-Celled → much smaller than eukaryotic cells.
Cell Structure
- Cell wall → provides shape + protection (not made of cellulose).
- Cell membrane → controls entry and exit of substances.
- Cytoplasm → contains enzymes; site of reactions.
- Plasmids → small circular DNA pieces, transferable between bacteria.
Genetic Material
- No nucleus → instead have a single circular DNA chromosome floating in cytoplasm.
Nutrition
- Some can photosynthesise.
- Most are heterotrophic → feed on living organisms (parasites) or dead matter (saprophytes).

🧪 Examples
- Lactobacillus bulgaricus → rod-shaped, used in making yoghurt (fermentation).
- Pneumococcus → spherical, pathogen causing pneumonia in humans.
📊 Summary Table – Bacteria Features
| Feature | Description | Notes/Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Cell type | Prokaryotic (single-celled) | Smaller than eukaryotes |
| Nucleus | No true nucleus | Circular DNA in cytoplasm |
| Other DNA | Plasmids | Carry extra genes |
| Cell wall | Present (not cellulose) | Provides support |
| Nutrition | Photosynthetic OR heterotrophic | Many feed on living/dead matter |
| Examples | Lactobacillus bulgaricus | Yoghurt production |
| Pneumococcus | Pneumonia pathogen |
⚡ Quick Recap
🦠 Bacteria = prokaryotes (no nucleus, circular DNA).
Have cell wall, membrane, cytoplasm, plasmids.
Mostly feed on other organisms (few photosynthesise).
Examples:
– Lactobacillus bulgaricus → yoghurt-making.
– Pneumococcus → pneumonia-causing pathogen.
👉 Key difference from eukaryotes → no true nucleus, plasmids, smaller + simpler structure.
🦠 Bacteria = prokaryotes (no nucleus, circular DNA).
Have cell wall, membrane, cytoplasm, plasmids.
Mostly feed on other organisms (few photosynthesise).
Examples:
– Lactobacillus bulgaricus → yoghurt-making.
– Pneumococcus → pneumonia-causing pathogen.
👉 Key difference from eukaryotes → no true nucleus, plasmids, smaller + simpler structure.