Edexcel iGCSE Biology-1.4 Pathogens- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-1.4 Pathogens- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-1.4 Pathogens- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
1.4 understand the term pathogen and know that pathogens may include fungi, bacteria, protoctists or viruses
- Viruses: these are not living organisms. They are small particles, smaller than bacteria; they are parasitic and can reproduce only inside living cells; they infect every type of living organism. They have a wide variety of shapes and sizes; they have no cellular structure but have a protein coat and contain one type of nucleic acid, either DNA or RNA. Examples include the tobacco mosaic virus that causes discolouring of the leaves of tobacco plants by preventing the formation of chloroplasts, the influenza virus that causes ‘flu’ and the HIV virus that causes AIDS.
Pathogens & Viruses
📝 What is a Pathogen?
Pathogen = any microorganism that causes disease.
They can belong to different groups:
- Fungi → Athlete’s foot fungus
- Bacteria → Pneumococcus (causes pneumonia)
- Protoctists → Plasmodium (causes malaria)
- Viruses → HIV (causes AIDS)
👉 Remember: Not all microbes are harmful, but pathogens are the ones that cause illness.
🧬 Viruses – Unique Features
- Not living organisms (outside a host cell).
Smaller than bacteria → seen only with an electron microscope.
- Parasitic → must reproduce inside a living cell (hijack host machinery).
- Infect all types of organisms → animals, plants, bacteria, fungi.

- Show a wide variety of shapes and sizes.
- No cellular structure (unlike other organisms).
Structure
- Protein coat (capsid) → protective shell.
- Genetic material → either DNA or RNA (never both).
🧪 Examples of Viruses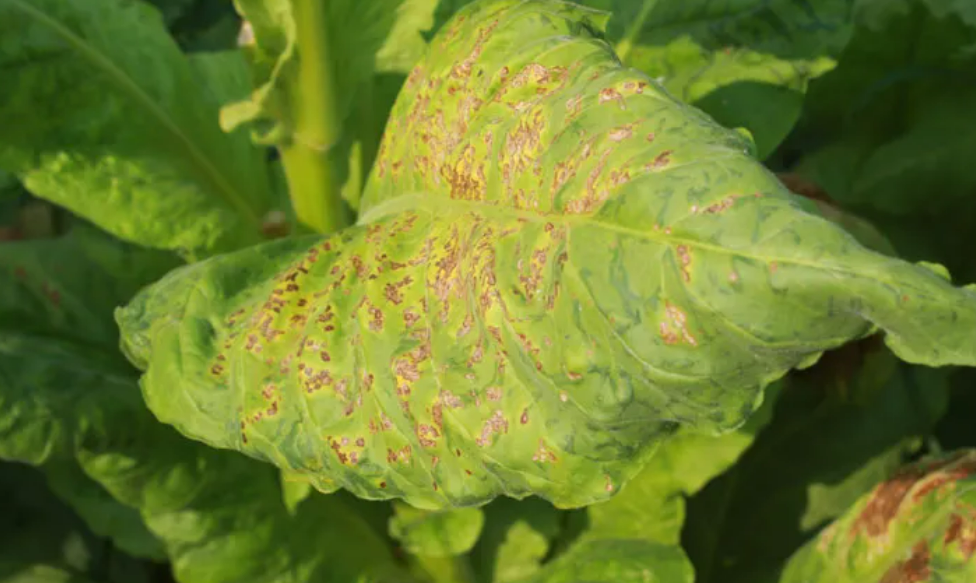
- Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) → infects tobacco plants, prevents chloroplast formation, causes mosaic-patterned leaves.
- Influenza Virus → causes flu in humans (fever, cough, sore throat, tiredness).
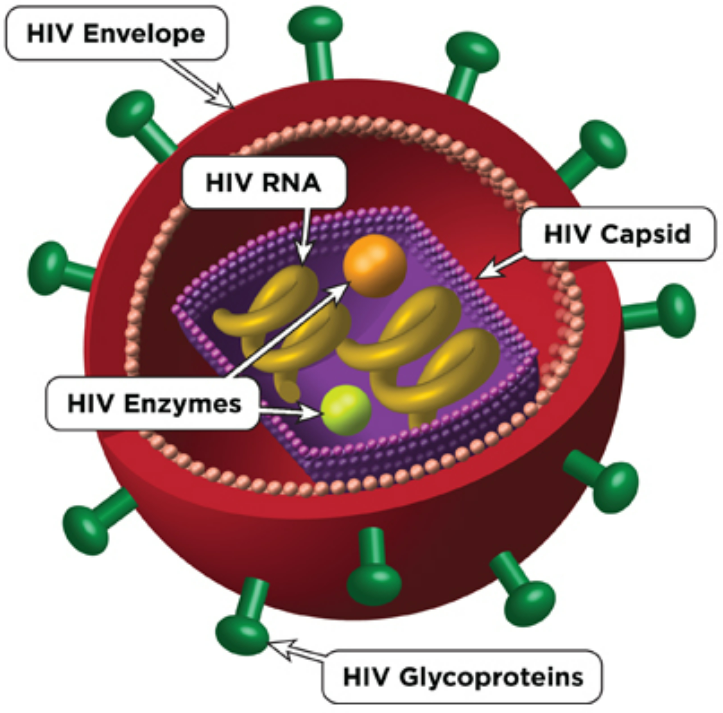
- HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) → causes AIDS, attacks immune system, weakens defence against infections.
📊 Summary Table – Pathogens & Viruses
| Pathogen Type | Example | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Fungi | Athlete’s foot | Eukaryotic, multicellular, saprotrophic |
| Bacteria | Pneumococcus | Prokaryotic, single-celled, no nucleus |
| Protoctists | Plasmodium | Eukaryotic, single-celled, malaria pathogen |
| Viruses | TMV, Influenza, HIV | Non-living, no cells, DNA or RNA + protein coat |
⚡ Quick Recap
Pathogen = disease-causing microorganism.
Can be fungi, bacteria, protoctists, or viruses.
Viruses: not living, tiny, parasitic, no cells, reproduce only inside hosts.
Structure = protein coat + DNA or RNA.
Examples:
– TMV → discolours tobacco leaves.
– Influenza virus → flu.
– HIV → AIDS (immune system failure).
👉 Key idea: Viruses blur the line between living and non-living.
Pathogen = disease-causing microorganism.
Can be fungi, bacteria, protoctists, or viruses.
Viruses: not living, tiny, parasitic, no cells, reproduce only inside hosts.
Structure = protein coat + DNA or RNA.
Examples:
– TMV → discolours tobacco leaves.
– Influenza virus → flu.
– HIV → AIDS (immune system failure).
👉 Key idea: Viruses blur the line between living and non-living.