Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.10 role of enzymes- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.10 role of enzymes- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.10 role of enzymes- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.10 understand the role of enzymes as biological catalysts in metabolic reactions
Enzymes – Biological Catalysts
📝 Introduction
- In living organisms, chemical reactions = metabolic reactions (e.g., respiration, photosynthesis, digestion).
- These reactions are usually too slow at normal body temperatures.
- Cells use enzymes (special proteins) to speed them up safely.
Enzymes = biological catalysts.
🔑 Key Features of Enzymes
- Proteins (made of amino acids).
- Catalysts → speed up reactions without being used up.
- Specific → one enzyme works on one substrate (“lock and key” idea).
- Work best at an optimum temperature + pH.
🧪 Role in Metabolic Reactions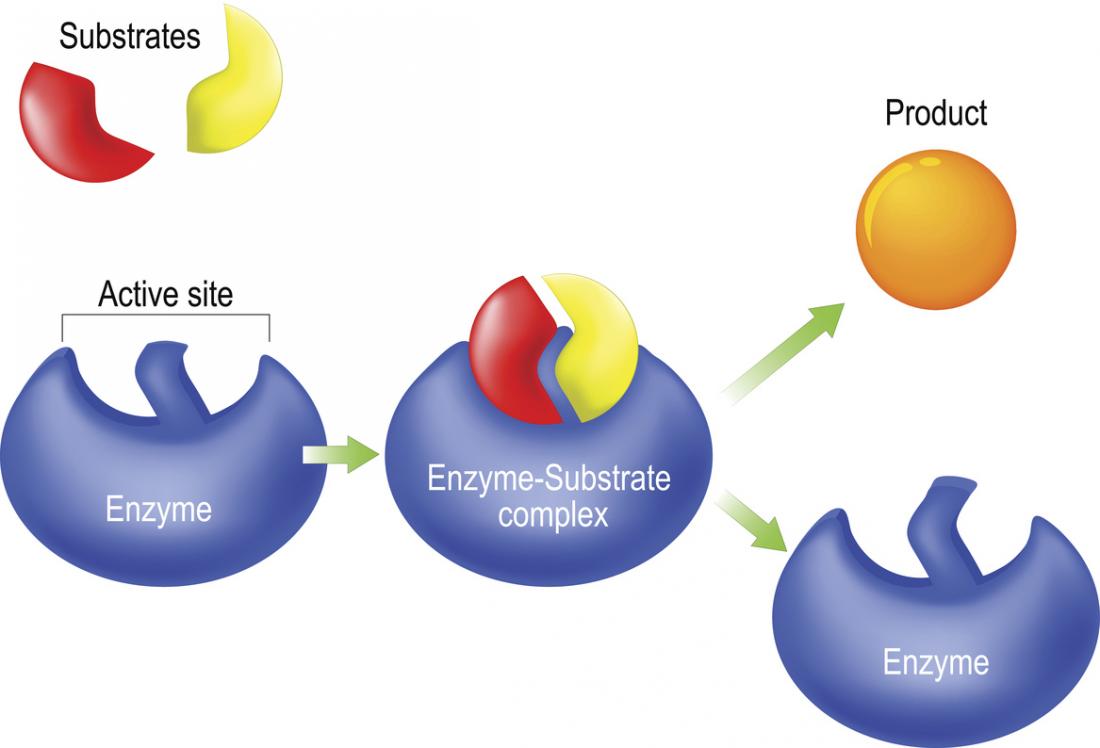
1. Digestion (breaking molecules)
- Amylase: starch → maltose
- Protease: protein → amino acids
- Lipase: fat → fatty acids + glycerol
These reactions would be too slow without enzymes.
2. Respiration & Energy Release
- Enzymes control each step of breaking down glucose in respiration.
- Release of ATP (energy) is fast enough to support life.
3. Photosynthesis
- Controlled by enzymes (e.g., rubisco) in chloroplasts.
- Helps plants convert CO₂ + H₂O → glucose + O₂.
4. DNA & Protein Synthesis
- Enzymes control copying DNA before cell division.
- Also join amino acids together to build proteins.
🔑 Why Enzymes Are Essential
Without enzymes, most metabolic reactions would be far too slow to support life.
Enzymes allow reactions to happen:
- Fast enough
- At normal body temperatures (not extreme heat like in labs)
They make metabolism efficient and controlled.
📊 Summary Table – Enzyme Role in Metabolism
| Process | Example Enzyme | Substrate → Product |
|---|---|---|
| Digestion of starch | Amylase | Starch → Maltose |
| Digestion of protein | Protease | Protein → Amino acids |
| Digestion of fat | Lipase | Fat → Fatty acids + Glycerol |
| Respiration | Many enzymes | Glucose → ATP + CO₂ + H₂O |
| Photosynthesis | Rubisco, others | CO₂ + H₂O → Glucose + O₂ |
| DNA replication | DNA polymerase | Builds new DNA strand |
⚡ Quick Recap
Enzymes = biological catalysts (proteins).
Speed up reactions without being used up.
Specific to substrates (“lock & key”).
Roles: digestion, respiration, photosynthesis, DNA/protein synthesis.
Without enzymes → reactions too slow → life impossible.
