Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.15 Diffusion, Osmosis & Active Transport- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.15 Diffusion, Osmosis & Active Transport- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.15 Diffusion, Osmosis & Active Transport- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.15 understand the processes of diffusion, osmosis and active transport by which substances move into and out of cells
Movement of Substances – Diffusion, Osmosis & Active Transport
📝 Introduction
Cells constantly exchange substances (like gases, water, nutrients, waste) with their surroundings.
This happens by three main processes:
- Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Active Transport
🌬️ Diffusion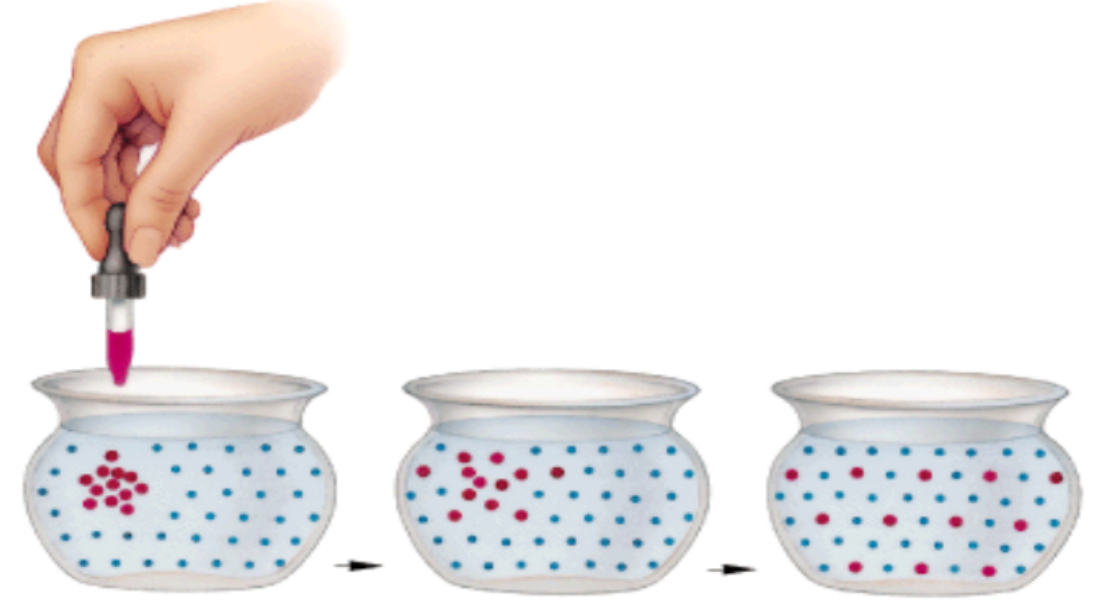
- Definition: The net movement of particles from an area of high concentration → low concentration, down a concentration gradient.
- Passive process → no energy needed.
- Occurs in gases and liquids.
Examples:
- Oxygen diffuses from alveoli → blood.
- Carbon dioxide diffuses out of cells during respiration.
💧 Osmosis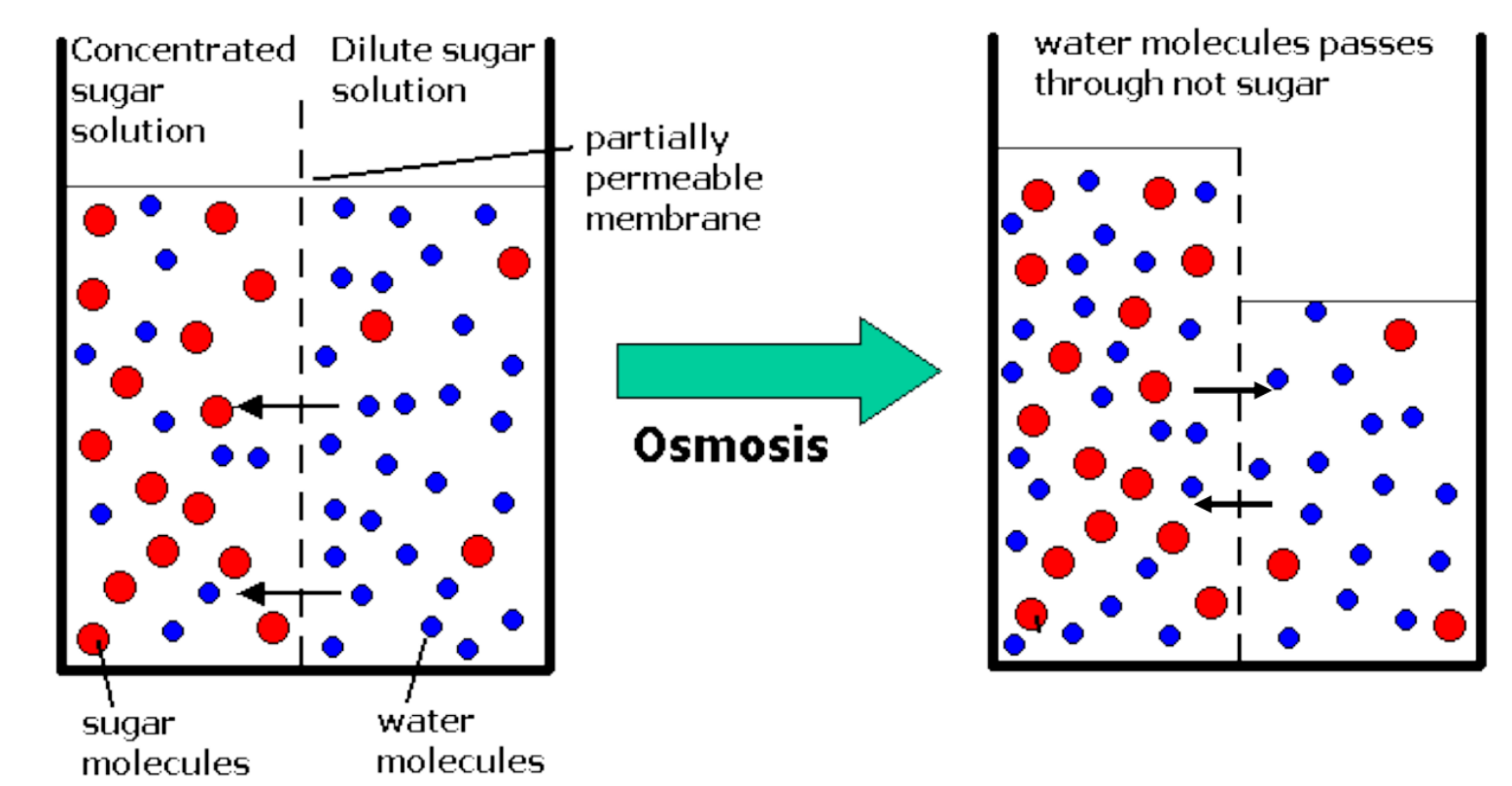
- Definition: The net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher water concentration (dilute solution) → lower water concentration (concentrated solution).
- Passive process → no energy needed.
Examples:
- Water moving into root hair cells from soil.
- Water movement in kidney tubules.
⚡ Active Transport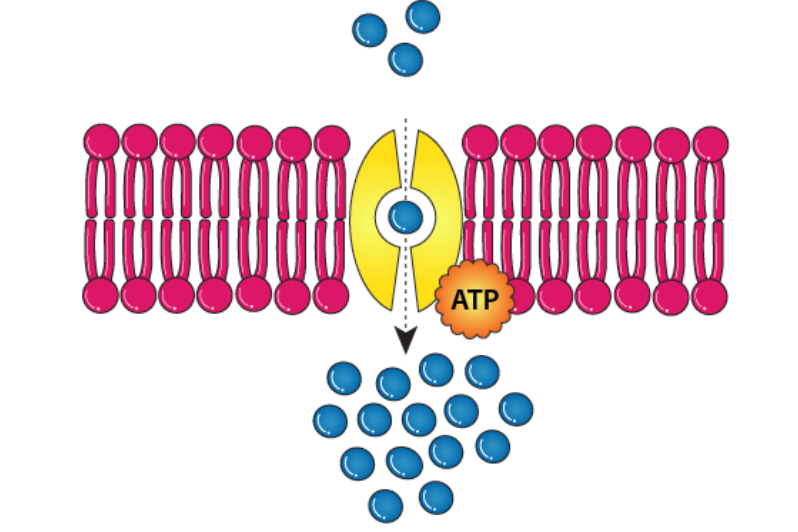
- Definition: The movement of substances against the concentration gradient (from low → high concentration) using energy (ATP).
- Requires membrane proteins (pumps).
Examples:
- Root hair cells absorbing mineral ions (like nitrates) from soil.
- Small intestine cells absorbing glucose from digested food even when concentration inside is already high.
📊 Comparison Table
| Feature | Diffusion | Osmosis | Active Transport |
|---|---|---|---|
| What moves? | Particles (gases/solutes) | Water molecules only | Particles (ions, molecules) |
| Direction | High → Low | High water conc → Low water conc | Low → High (against gradient) |
| Energy needed? | No | No | Yes (ATP) |
| Membrane needed? | Not always | Yes (partially permeable) | Yes |
| Example | O₂ into blood | Water into root hair cell | Nitrates into root hair cell |
🎯 Tips
- Osmosis = only water + partially permeable membrane.
- Active transport = always needs energy (ATP) + goes against gradient.
⚡ Quick Recap
Diffusion → high to low, passive.
Osmosis → water only, high to low across partially permeable membrane, passive.
Active Transport → low to high, needs energy.
👉 Mnemonic: DOA (Diffusion = Passive, Osmosis = Water Passive, Active transport = Needs ATP).
