Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.16 factors affect the rate of movement- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.16 factors affect the rate of movement- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.16 factors affect the rate of movement- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.16 understand how factors affect the rate of movement of substances into and out of cells, including the effects of surface area to volume ratio, distance, temperature and concentration gradient
Factors Affecting Movement of Substances
📝 Introduction
Substances move in/out of cells by diffusion, osmosis, or active transport.
The rate (how fast it happens) depends on several factors:
🔑 Factors
1. Surface Area to Volume Ratio (SA:V)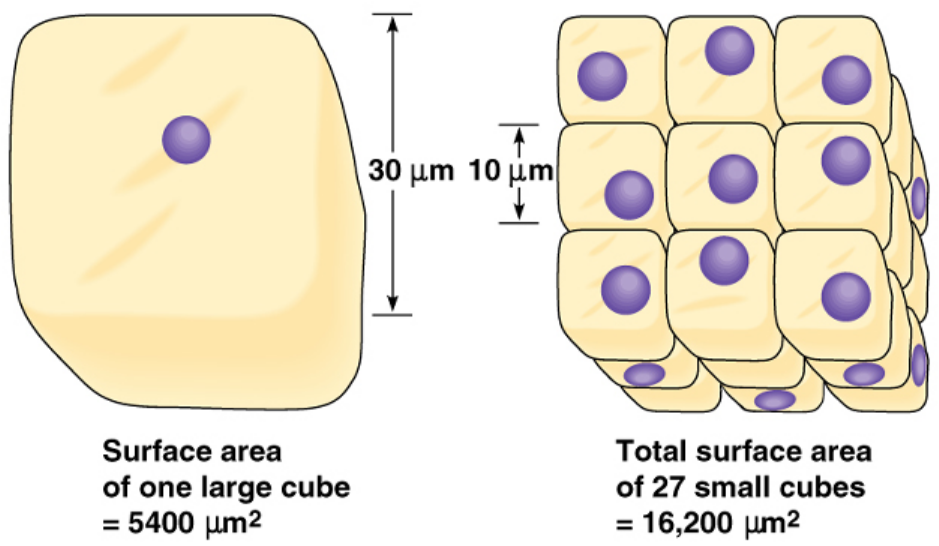
- Larger surface area → more space for particles to pass through.
- Smaller organisms (e.g. single-celled) have a large SA:V ratio, so exchange is fast.
- Larger organisms have a smaller SA:V ratio, so they need specialised exchange surfaces (lungs, gills, villi).
Example: Amoeba relies on diffusion, but humans need lungs.
2. Distance
- The shorter the distance, the faster the movement.
- Thin membranes = faster diffusion.
Example: Alveoli in lungs have one-cell-thick walls for fast gas exchange.
3. Temperature
- Higher temperature = particles move faster = more collisions = quicker diffusion.
- Low temperature = slower movement.
Example: Oxygen diffuses faster into warm blood than in colder conditions.
4. Concentration Gradient
- Bigger difference in concentration = faster movement.
- Steeper gradient → more collisions across the membrane.
- Once concentrations equalize, movement stops.
Example: In lungs, high O₂ in alveoli + low O₂ in blood → steep gradient → fast diffusion.
📊 Summary Table
| Factor | Effect on rate | Example |
|---|---|---|
| SA:V ratio | Higher SA:V = faster exchange | Amoeba vs Human |
| Distance | Shorter = faster | Thin alveoli walls |
| Temperature | Higher = faster | Warm blood speeds gas exchange |
| Conc. gradient | Steeper = faster | O₂ from alveoli → blood |
⚡ Quick Recap
SA:V ↑ → faster (small organisms fast exchange).
Distance ↓ → faster (thin walls).
Temp ↑ → faster (more kinetic energy).
Gradient ↑ → faster (steeper concentration difference).
👉 Mnemonic: “Some Dogs Take Cookies” (Surface area, Distance, Temperature, Concentration gradient).
