Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.2 cell structures- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.2 cell structures- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.2 cell structures- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.2 describe cell structures, including the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, chloroplasts, ribosomes and vacuole
Cell Structures
📝 Introduction
Cells are the basic units of life.
Different parts inside a cell are called cell structures (organelles), and each one has a specific function.
🧠 Nucleus
- Control centre of the cell.
- Contains DNA → genetic material that controls cell activities (e.g., protein production).
- Surrounded by a nuclear membrane that protects it.
- Present in animal, plant, and protoctist cells (not in bacteria/viruses).
💧 Cytoplasm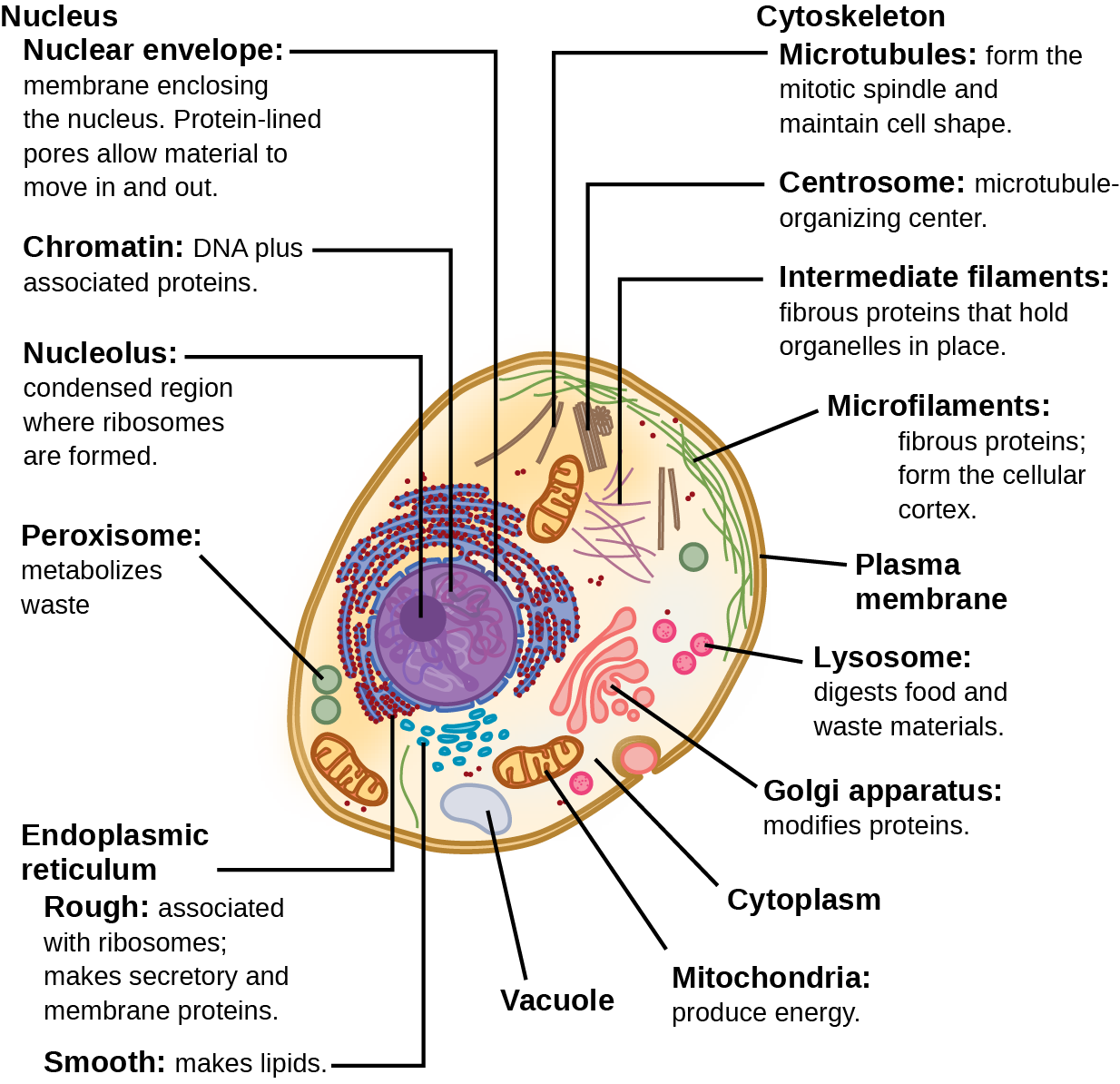
- Jelly-like fluid inside the cell.
- Many chemical reactions (like respiration, protein synthesis) happen here.
- Contains organelles floating in it.
🛡️ Cell Membrane
- Thin layer surrounding the cell.
- Partially permeable → controls what enters and leaves the cell (nutrients, gases, waste).
- Found in all cells (plants, animals, fungi, protoctists, bacteria).
🧱 Cell Wall
- Provides support and shape to the cell.
- In plants → made of cellulose.
- In fungi → made of chitin.
- Bacterial cell walls → not cellulose, different material.
- Animal cells don’t have cell walls.
🔋 Mitochondria
- Known as the “powerhouse of the cell”.
- Site of aerobic respiration → releases energy from glucose.
- More mitochondria = higher energy demand (e.g., muscle cells, sperm cells).
🌱 Chloroplasts (Plants only)
- Contain chlorophyll → green pigment that absorbs light.
- Site of photosynthesis → makes glucose.
- Found in green parts of plants (leaves, sometimes stems).
⚙️ Ribosomes
- Tiny organelles (too small to see with light microscopes).
- Site of protein synthesis (making proteins from amino acids).
- Found in cytoplasm or attached to rough ER (in eukaryotes).
💦 Vacuole (Plants mainly)
- Large central vacuole in plants, filled with cell sap (water, sugars, salts).
- Helps maintain turgor pressure → keeps the plant upright.
- In animal cells → vacuoles are small and temporary.
📊 Summary Table – Cell Structures
| Structure | Function | Found in |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Controls activities, stores DNA | Plants & animals |
| Cytoplasm | Site of chemical reactions | All cells |
| Cell membrane | Controls entry/exit of substances | All cells |
| Cell wall | Support & shape (cellulose/chitin) | Plants, fungi, bacteria |
| Mitochondria | Aerobic respiration, energy release | Plants & animals |
| Chloroplasts | Photosynthesis, contain chlorophyll | Plants only |
| Ribosomes | Protein synthesis | All cells |
| Vacuole | Storage & turgor (large in plants) | Plants (large), animals (small) |
⚡ Quick Recap
Nucleus → controls cell, holds DNA.
Cytoplasm → chemical reactions.
Cell membrane → controls movement in/out.
Cell wall → structure & support (plants, fungi, bacteria).
Mitochondria → respiration = energy.
Chloroplasts → photosynthesis (plants).
Ribosomes → make proteins.
Vacuole → storage, keeps plant upright.
