Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.21 structure of the leaf- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.21 structure of the leaf- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.21 structure of the leaf- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.21 describe the structure of the leaf and explain how it is adapted for photosynthesis
Structure of the Leaf & Adaptations for Photosynthesis
📝 Introduction
Leaves are the main photosynthetic organs in plants.
Their structure is specially adapted to:
- Absorb maximum light
- Allow efficient gas exchange
- Transport water + food
📐 Main Leaf Structures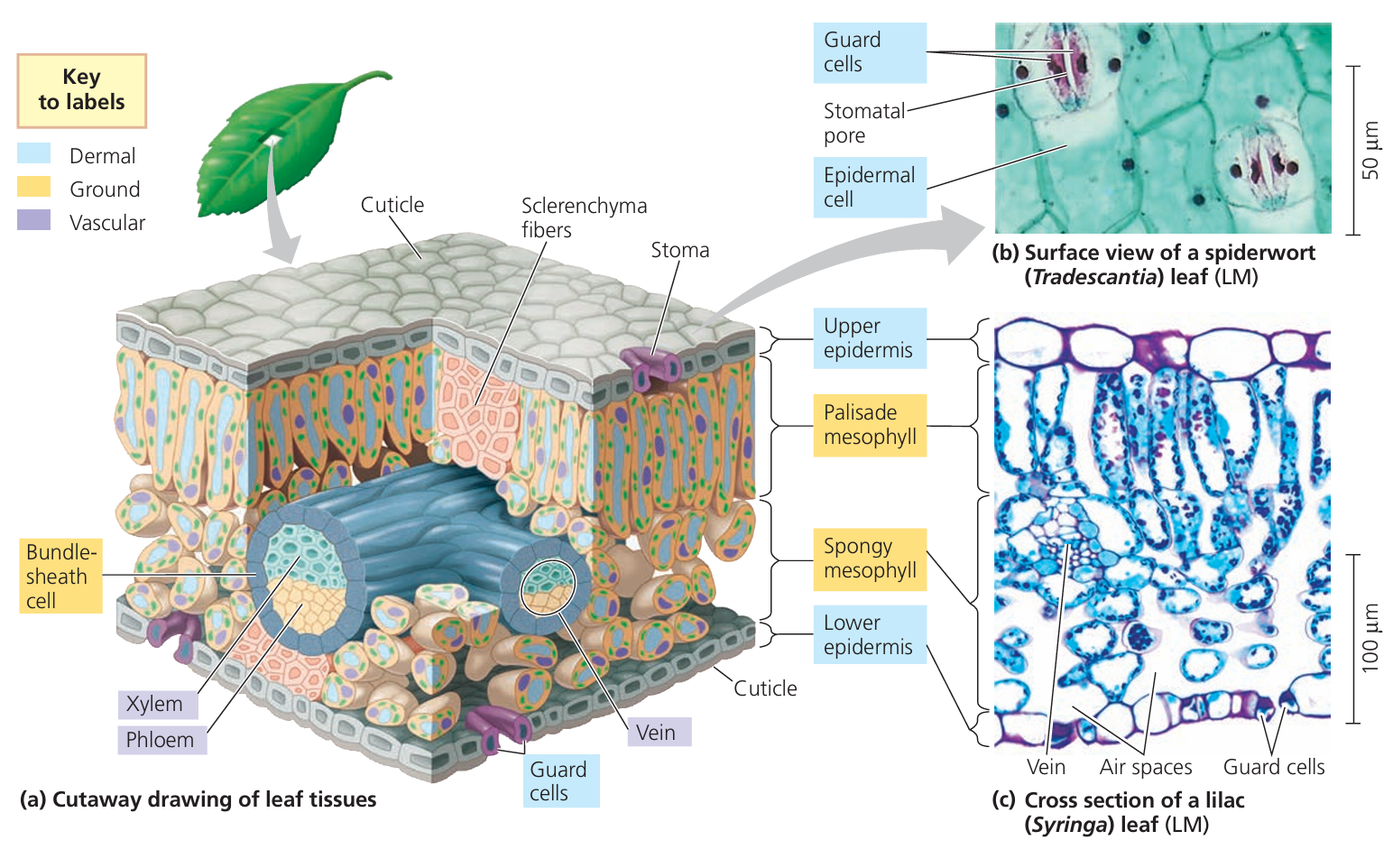
Waxy Cuticle
- Thin, transparent, waterproof layer on top.
- Reduces water loss but let’s light pass through.
Upper Epidermis
- Transparent cells with no chloroplasts.
- Function: lets light through to mesophyll.
Palisade Mesophyll
- Tightly packed, column-shaped cells.
- Contain many chloroplasts → main site of photosynthesis.
- Located at top → get maximum light.
Spongy Mesophyll
- Loosely packed cells with air spaces.
- Allows diffusion of CO₂ in and O₂ out.
- Some chloroplasts for extra photosynthesis.
Stomata (mostly lower epidermis)
- Tiny pores that open/close (controlled by guard cells).
- Allow gas exchange: CO₂ in, O₂ + water vapour out.
Guard Cells
- Special kidney-shaped cells around stomata.
- Control opening/closing to balance gas exchange and water loss.
Veins (Vascular Bundles: Xylem + Phloem)
- Xylem: carries water + minerals to leaf.
- Phloem: carries away glucose made in photosynthesis.
🌟 How Leaf is Adapted for Photosynthesis
| Feature | Adaptation |
|---|---|
| Broad + flat | Large surface area to absorb maximum light. |
| Thin | Short distance for diffusion of gases. |
| Palisade cells | Packed with chloroplasts → efficient light capture. |
| Chloroplasts | Contain chlorophyll to absorb light energy. |
| Spongy layer | Air spaces → faster diffusion of CO₂ & O₂. |
| Stomata with guard cells | Regulate gas exchange + water loss. |
| Veins (xylem + phloem) | Xylem = water supply; Phloem = transport sugars away. |
| Transparent cuticle + epidermis | Light passes easily to mesophyll cells. |
⚡ Quick Recap
Cuticle/Epidermis → light in, water out.
Palisade → chloroplast-rich, photosynthesis hub.
Spongy → air spaces for diffusion.
Stomata/Guard cells → gas exchange control.
Veins → water in, sugars out.
👉 Leaf = solar panel (light capture) + factory (photosynthesis) + transport system (veins).
