Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.27 structure and function of the human alimentary canal- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.27 structure and function of the human alimentary canal- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.27 structure and function of the human alimentary canal- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.27 describe the structure and function of the human alimentary canal, including the mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum and ileum), large intestine (colon and rectum) and pancreas
Human Alimentary Canal – Structure & Function
📝 Introduction
The alimentary canal is the long tube running from mouth → anus.
Its job is to digest food into smaller, soluble molecules and absorb them for use in the body.
🧩 Main Parts
1. Mouth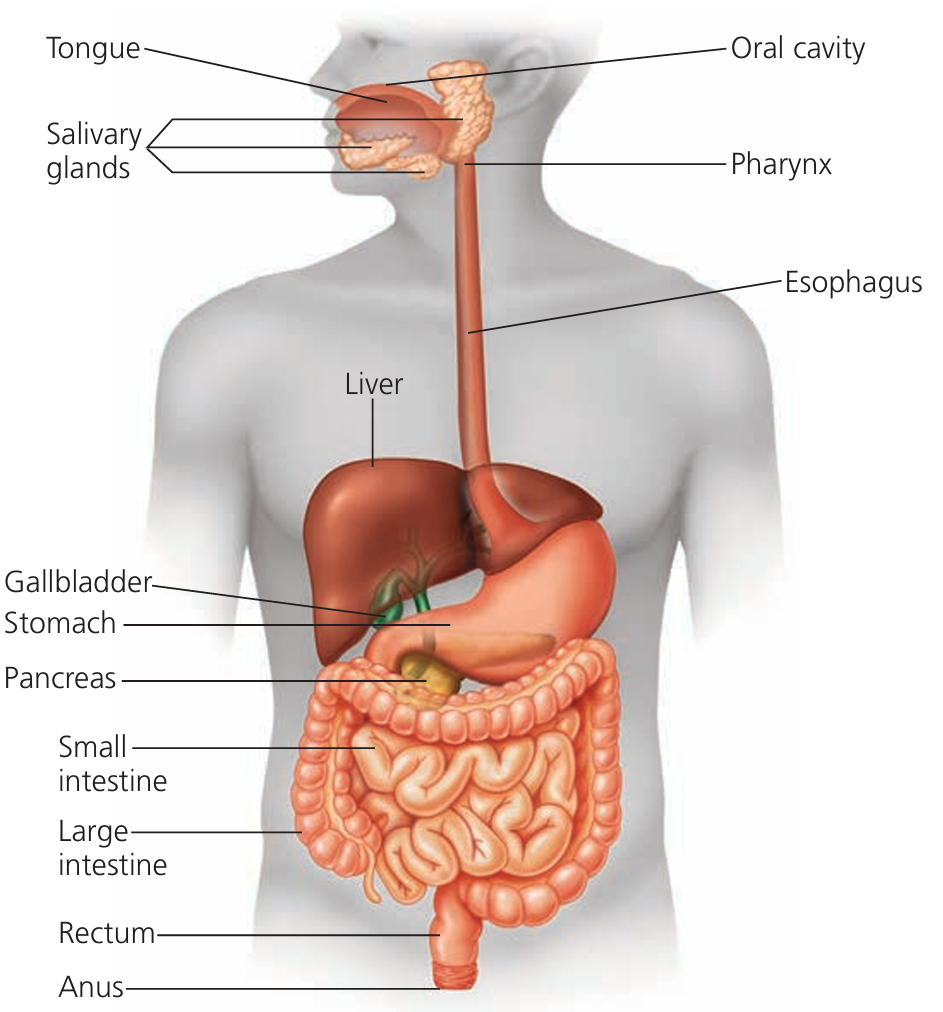
- Structure: Teeth, tongue, salivary glands.
- Functions:
- Mechanical digestion → teeth break food into smaller pieces → ↑ surface area.
- Chemical digestion → saliva has amylase → starch → maltose.
- Tongue mixes food with saliva → forms bolus for swallowing.
2. Oesophagus
- Structure: Muscular tube connecting mouth → stomach.
- Functions: Moves bolus by peristalsis (waves of muscle contraction). No digestion here.
3. Stomach
- Structure: Muscular sac with glands secreting gastric juice.
- Functions:
- Mechanical digestion → muscles churn food into chyme.
- Chemical digestion:
- Pepsin (protease) → proteins → peptides.
- HCl → kills bacteria + provides acidic pH for pepsin.
4. Small Intestine
- a) Duodenum (first part):
- Pancreas enzymes:
- Amylase → starch → maltose
- Protease → proteins → amino acids
- Lipase → lipids → fatty acids + glycerol
- Liver (bile): Neutralises acid + emulsifies fats (↑ surface area for lipase).
- Digestion of all food groups completed here.
- Pancreas enzymes:
- b) Ileum (second part):
- Specially adapted for absorption:
- Long length + villi + microvilli → very large surface area.
- Thin walls → short diffusion distance.
- Rich blood supply → maintains concentration gradient.
- Absorbs glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol, vitamins, minerals.
5. Large Intestine
- a) Colon: Absorbs water + some minerals → forms semi-solid faeces.
- b) Rectum: Stores faeces before egestion.
6. Pancreas (Accessory organ)
- Produces pancreatic juice with amylase, protease, lipase.
- Secreted into duodenum.
📊 Summary Table
| Part | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Mouth | Teeth, tongue, saliva | Mechanical + amylase digestion of starch |
| Oesophagus | Muscular tube | Moves bolus by peristalsis |
| Stomach | Muscular sac, HCl, pepsin | Churns food, digests proteins, kills bacteria |
| Duodenum | Connected to bile + pancreatic ducts | Neutralises acid, completes digestion |
| Ileum | Long, villi/microvilli | Absorbs small molecules into blood |
| Colon | Wide tube | Absorbs water, forms faeces |
| Rectum | End chamber | Stores faeces |
| Pancreas | Gland under stomach | Produces digestive enzymes |
⚡ Quick Recap
Mouth = chew + amylase.
Oesophagus = peristalsis.
Stomach = churn + pepsin + HCl.
Duodenum = enzymes + bile → finish digestion.
Ileum = villi → absorption.
Colon = water absorption.
Rectum = stores faeces.
Pancreas = enzyme factory.
