Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.34 process of respiration- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.34 process of respiration- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.34 process of respiration- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.34 understand how the process of respiration produces ATP in living organisms
Respiration – Producing Energy (ATP) in Living Organisms
📝 Introduction
All living organisms need energy to:
- Grow
- Move
- Maintain body functions
- Carry out chemical reactions
Energy is obtained from food molecules (mainly glucose) through respiration.
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) = energy currency of the cell.
🔑 What is Respiration?
Definition: Respiration is the chemical process that breaks down glucose (or other nutrients) to release energy in the form of ATP.
Two main types:
– Aerobic respiration (with oxygen)
– Anaerobic respiration (without oxygen)
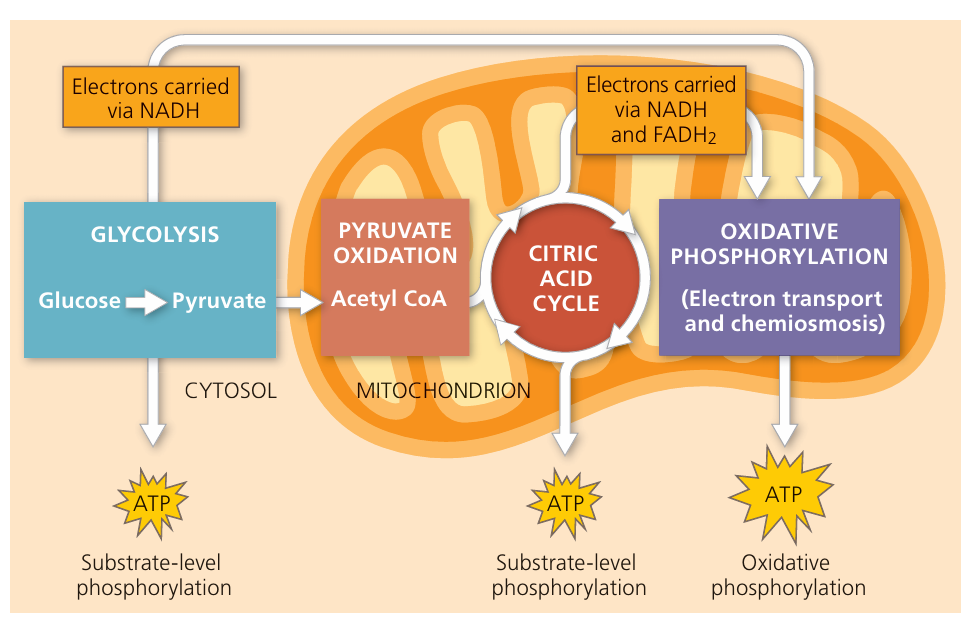
⚙️ Aerobic Respiration
Equation:
Word equation: Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
Chemical equation: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy (ATP)
Where it happens: Mainly in mitochondria of cells.
ATP yield: ~36–38 ATP molecules per glucose molecule.
- Requires oxygen.

- Produces CO₂ and H₂O as waste products.
- Very efficient → produces lots of energy.
⚙️ Anaerobic Respiration
Word equation (humans): Glucose → Lactic acid + Energy
Word equation (plants & yeast): Glucose → Ethanol + Carbon dioxide + Energy
Where it happens: Cytoplasm of cells.
ATP yield: Only ~2 ATP per glucose molecule → much less than aerobic.
- Occurs when oxygen is insufficient (e.g., intense exercise).
- Produces lactic acid in humans → causes muscle fatigue.
- Produces ethanol + CO₂ in yeast → used in fermentation.
📊 Summary Table
| Type | Oxygen Needed? | Products | ATP Yield | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerobic | Yes | CO₂ + H₂O | 36–38 | Mitochondria |
| Anaerobic (humans) | No | Lactic acid | 2 | Cytoplasm |
| Anaerobic (plants/yeast) | No | Ethanol + CO₂ | 2 | Cytoplasm |
⚡ Quick Recap
Respiration → ATP → energy for all life processes.
Aerobic = glucose + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O + lots of ATP.
Anaerobic = glucose → lactic acid (humans) or ethanol + CO₂ (plants/yeast) → little ATP.
Location: Mitochondria (aerobic), Cytoplasm (anaerobic).

