Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.35 Cell Energy- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.35 Cell Energy- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.35 Cell Energy- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.35 know that ATP provides energy for cells
ATP – Energy for Cells
📝 Introduction
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) = universal energy currency of all living cells.
Energy from food cannot be used directly by cells, it is stored in ATP molecules.
Cells break down ATP when energy is needed for reactions and activities.
⚙️ Structure of ATP
- Adenine (nitrogenous base)
- Ribose (sugar)
- Three phosphate groups
Energy is stored in bonds between phosphate groups → especially the last bond (high-energy bond).
🔑 How ATP Provides Energy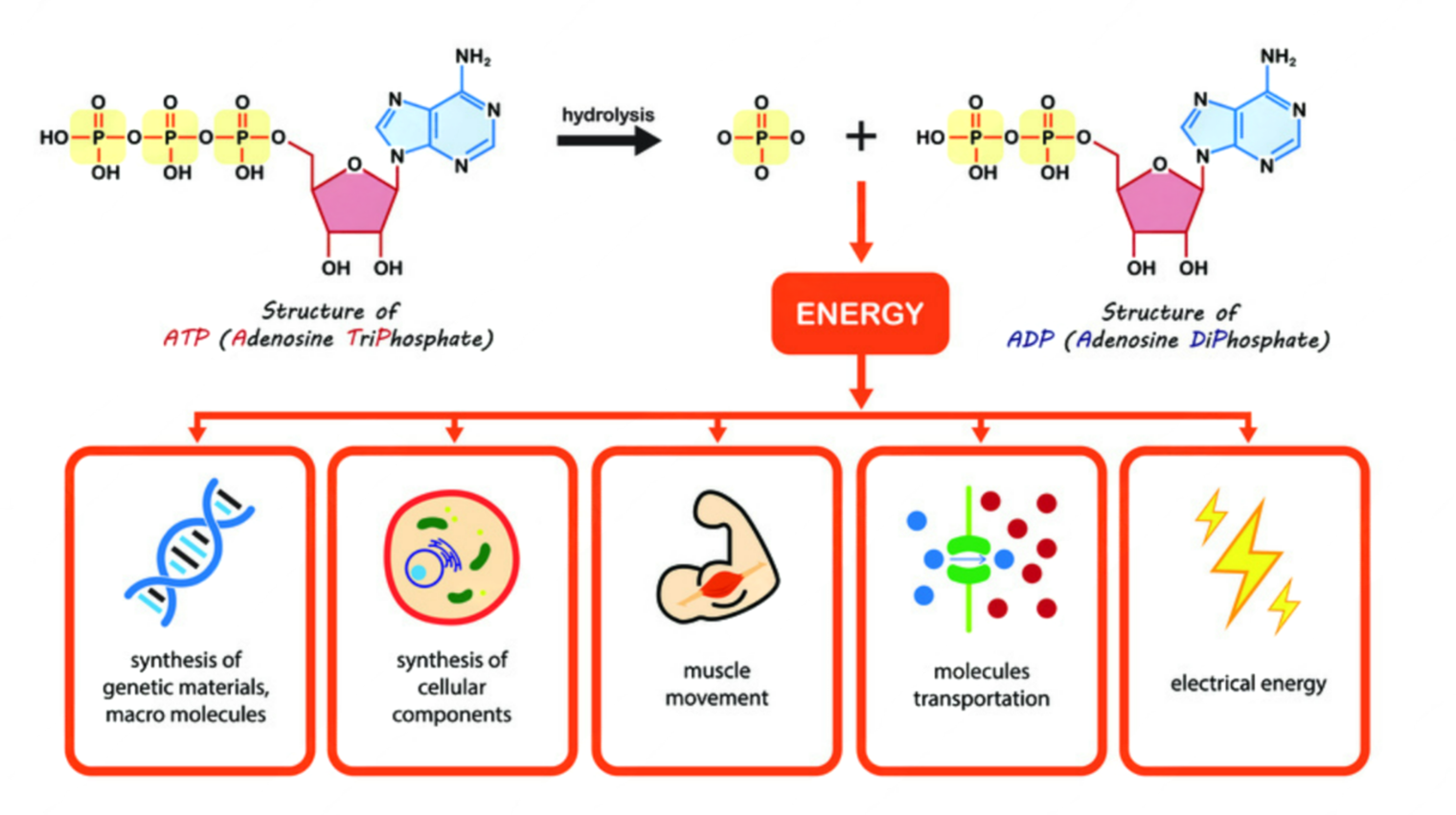
ATP → ADP + Pi + Energy
ATP loses one phosphate → becomes ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate).
Energy released is used by cells for:
- Muscle contraction
- Active transport (e.g., Na⁺/K⁺ pump)
- Synthesis of macromolecules (proteins, DNA)
- Cell division & growth
- Nerve impulses
ADP + Pi → ATP
ATP is regenerated from ADP using energy from respiration (mainly aerobic).
This makes ATP a recyclable energy currency.
📊 Summary Table
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Full form | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| Structure | Adenine + Ribose + 3 Phosphates |
| Energy storage | In high-energy phosphate bonds |
| Energy release | ATP → ADP + Pi + Energy |
| Energy used for | Muscle contraction, active transport, synthesis, growth, nerve impulses |
| Regeneration | ADP + Pi → ATP (using respiration) |
⚡ Quick Recap
ATP = energy currency of cell.
Energy comes from breaking last phosphate bond → ATP → ADP + Pi.
Recycled constantly using energy from respiration.
Powers all cell activities.
