Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.4 structure of plant and animal cells- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.4 structure of plant and animal cells- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.4 structure of plant and animal cells- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.4 know the similarities and differences in the structure of plant and animal cells
Similarities and Differences: Plant & Animal Cells
📝 Introduction
Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic → they have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
They share many structures, but some features are unique to each type.
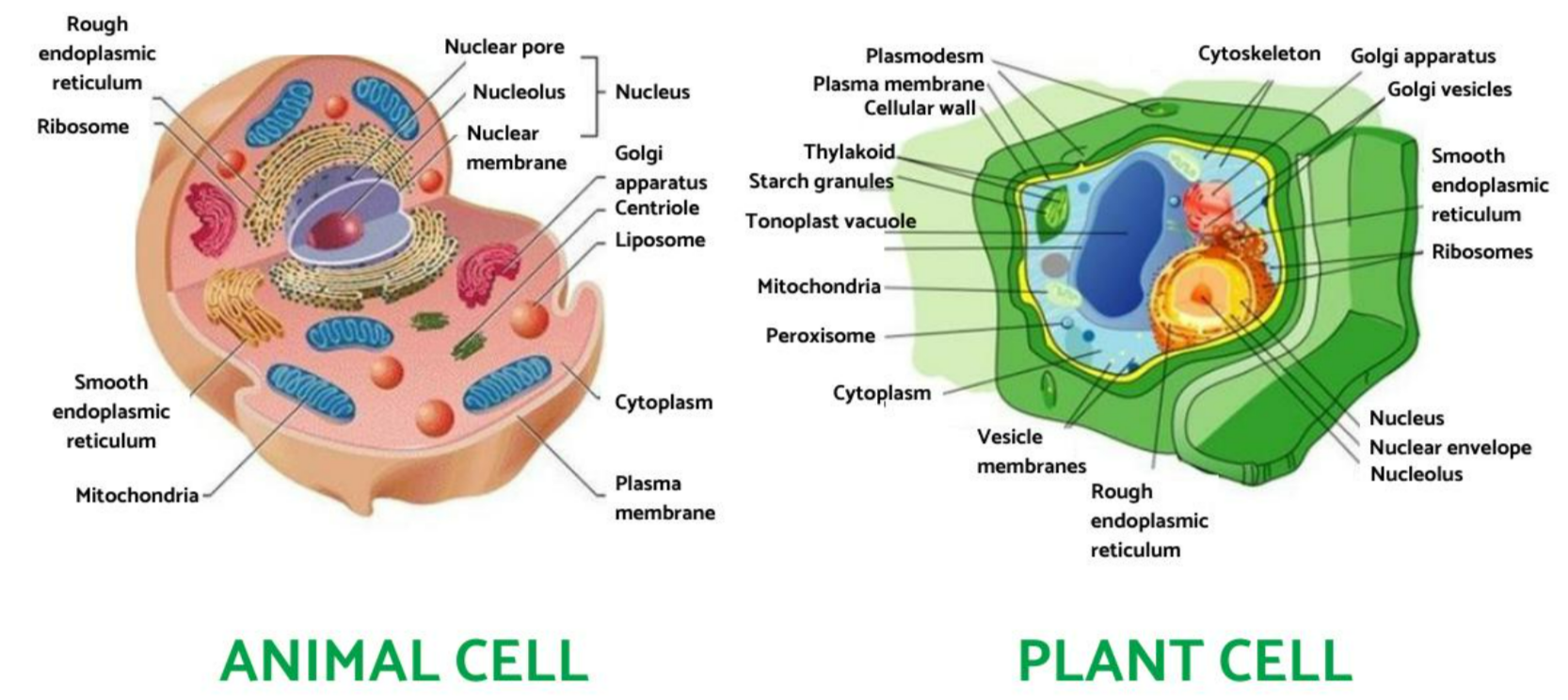
🔹 Similarities
| Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Nucleus | Controls cell activities, contains DNA |
| Cytoplasm | Site of chemical reactions, holds organelles |
| Ribosomes | Protein synthesis |
| Cell Membrane | Controls entry/exit of substances |
| Mitochondria | Aerobic respiration, energy release |
| Vacuole | Storage of materials (small temporary vacuoles in animals) |
✅ Both plant and animal cells share these essential organelles and basic functions.
🌱 Differences
| Feature | Plant Cell | Animal Cell | Function / Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Present (cellulose) | Absent | Provides support & shape |
| Chloroplasts | Present | Absent | Photosynthesis → makes glucose |
| Vacuole | Large central vacuole, permanent | Small, temporary | Maintains turgor pressure in plants |
| Shape | Usually rectangular/fixed | Usually round/irregular | Due to rigid cell wall in plants |
| Energy storage | Starch | Glycogen | Different carbohydrate storage forms |
📝 Key Points
- Plant cells can make their own food → chloroplasts.
- Animal cells can move and respond faster → no rigid wall, flexible shape.
- Plant cells have structural support → large vacuole + cell wall.
- Both have nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes, mitochondria → perform basic life processes.
⚡ Quick Recap
Similarities: Nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes, mitochondria, cell membrane, vacuoles.
Plant-only: Cell wall, chloroplasts, large central vacuole, starch storage.
Animal-only: No cell wall, no chloroplasts, small vacuoles, glycogen storage, flexible shape.
