Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.40 B diffusion in gas exchange- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.40 B diffusion in gas exchange- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.40 B diffusion in gas exchange- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.40B understand the role of diffusion in gas exchange
Role of Diffusion in Gas Exchange
📝 Introduction
Gas exchange = process by which oxygen enters the body and carbon dioxide is removed.
This happens by diffusion – movement of particles from high concentration → low concentration.
🔑 How Diffusion Works in Gas Exchange
- Oxygen (O₂):
- Higher conc. in air (alveoli or leaf air spaces)
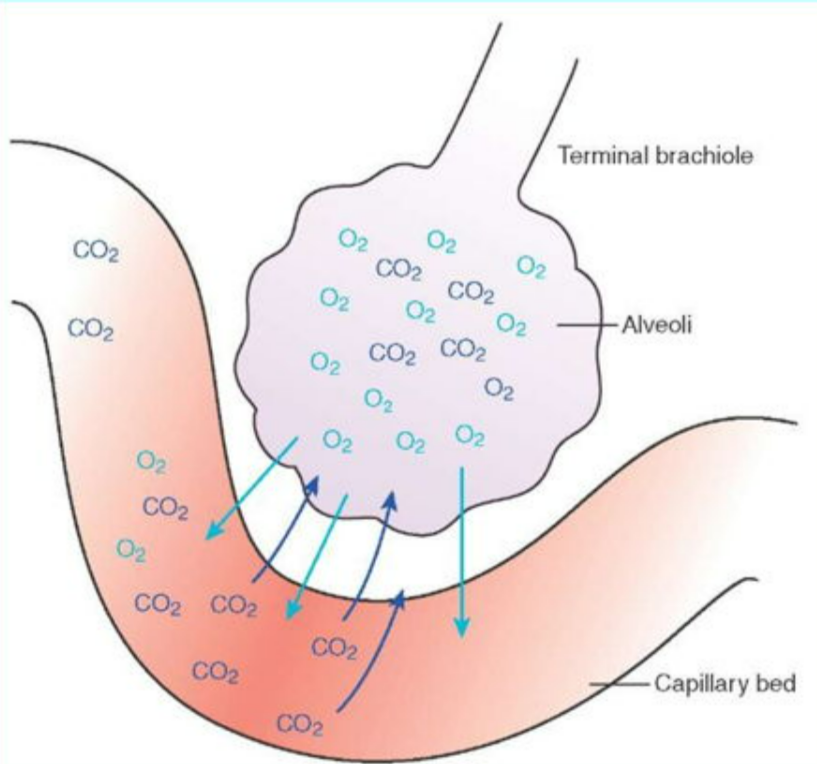
- Lower conc. in blood (capillaries) or cells
- Diffuses into blood/cells
- Higher conc. in air (alveoli or leaf air spaces)
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂):
- Higher conc. in blood/cells (waste product of respiration)
- Lower conc. in alveoli/leaf air spaces
- Diffuses out into lungs/atmosphere
🌟 Adaptations for Efficient Diffusion
In Humans (Lungs – Alveoli):
- Large surface area (millions of alveoli)
- Thin walls (one cell thick → short diffusion distance)
- Moist lining (gases dissolve → easier diffusion)
- Good blood supply (maintains steep conc. gradient)
- Constant ventilation (fresh O₂ in, CO₂ out)
In Plants (Leaves):
- Broad surface area → more diffusion
- Thin structure → short diffusion distance
- Air spaces inside leaf → faster movement of gases
- Stomata (pores) open/close to regulate gas exchange
⚡ Why Diffusion is Important
- Supplies oxygen for respiration
- Removes carbon dioxide (toxic if builds up)
- Maintains efficient energy release (ATP) in cells
- In plants → balance between photosynthesis & respiration
📌 Quick Recap
Gas exchange = by diffusion (high → low conc.)
O₂ in, CO₂ out
Humans: alveoli adaptations (large SA, thin walls, moist, blood supply, ventilation)
Plants: stomata + air spaces + thin leaves
Essential for respiration and energy supply
