Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.46 Structure of the Breathing System- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.46 Structure of the Breathing System- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.46 Structure of the Breathing System- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 2.45B practical: investigate the effect of light on net gas exchange from a leaf, using hydrogen- carbonate indicator
Structure of the Thorax
📝 Introduction
The thorax is the chest cavity where the lungs are located.
It is specially adapted for ventilation (breathing in and out) and gas exchange.
🌟 Main Structures
Ribs
- Curved bones forming the chest cage.
- Protect lungs & heart.
- Move up and out (inhalation) or down and in (exhalation) with help of muscles.
Intercostal Muscles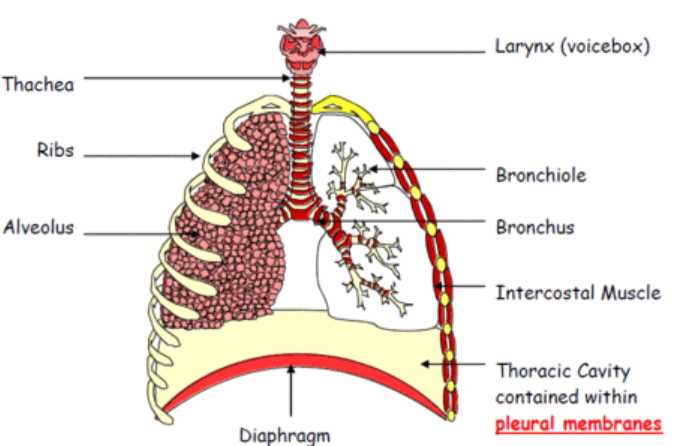
- Found between ribs.
- Two types:
- External intercostal muscles → contract during inhalation (lift ribs up & out).
- Internal intercostal muscles → contract during forced exhalation (pull ribs down & in).
Diaphragm
- Dome-shaped sheet of muscle under lungs.
- Contracts → flattens → increases chest volume (inhalation).
- Relaxes → domes up → decreases chest volume (exhalation).
Trachea
- Also called windpipe.
- Carries air to lungs.
- Supported by rings of cartilage (to keep it open).
- Lined with cilia & mucus → trap dust and microbes.
Bronchi
- Trachea splits into two bronchi (one for each lung).
- Carry air into left and right lungs.
Bronchioles
- Smaller branches of the bronchi inside lungs.
- Spread air evenly throughout lungs.
- End in alveoli.
Alveoli
- Tiny air sacs at the ends of bronchioles.
- Main site of gas exchange (O₂ into blood, CO₂ out).
- Adaptations:
- Very thin walls → short diffusion distance.
- Surrounded by capillaries → rich blood supply.
- Moist lining → gases dissolve easily.
- Huge number → large surface area.
Pleural Membranes
- Thin layers surrounding lungs.
- Pleural fluid between them acts as a lubricant → reduces friction during breathing.
- Also help lungs stick to chest wall, so they expand with the ribs.
📊 Summary Table
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Ribs | Protect organs, move during breathing |
| Intercostal muscles | Control rib movement for breathing |
| Diaphragm | Muscle controlling chest volume |
| Trachea | Air passage; kept open by cartilage |
| Bronchi | Two main air tubes to lungs |
| Bronchioles | Smaller air tubes spreading air |
| Alveoli | Site of gas exchange (O₂ in, CO₂ out) |
| Pleural membranes | Lubrication + lung expansion |
⚡ Quick Recap
✔ Thorax = chest cavity with lungs, ribs, muscles, diaphragm.
✔ Airway: Trachea → Bronchi → Bronchioles → Alveoli.
✔ Gas exchange: Happens in alveoli (thin, moist, large SA).
✔ Protection + movement: Ribs + intercostal muscles + diaphragm.
✔ Smooth movement: Pleural membranes with pleural fluid.
