Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.47 Role of the Intercostal Muscles & Diaphragm- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.47 Role of the Intercostal Muscles & Diaphragm- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.47 Role of the Intercostal Muscles & Diaphragm- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.47 understand the role of the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm in ventilation
Role of Intercostal Muscles & Diaphragm in Ventilation
📌 Introduction
Ventilation = process of moving air in and out of lungs.
It depends on changes in chest volume and air pressure, controlled by intercostal muscles and the diaphragm.
🌬️ Inhalation (Breathing In)
- External intercostal muscles contract → ribs move up & out.
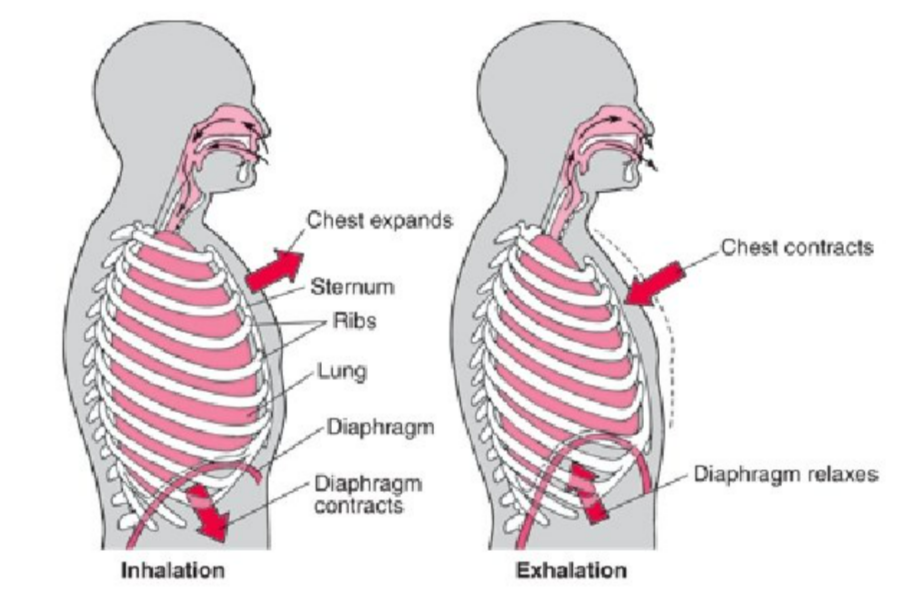
- Diaphragm contracts → flattens downwards.
- Chest cavity volume increases.
- Pressure inside lungs drops below air pressure outside.
- Air moves into lungs (from high to low pressure).
🌬️ Exhalation (Breathing Out)
- External intercostal muscles relax → ribs move down & in.
- Diaphragm relaxes → domes upwards.
- Chest cavity volume decreases.
- Pressure inside lungs increases above outside air pressure.
- Air moves out of lungs.
💪 Forced Exhalation (e.g., coughing, exercise)
- Internal intercostal muscles contract → pull ribs sharply down & in.
- This helps push air out faster.
📊 Summary Table
| Stage | Intercostal Muscles | Diaphragm | Chest Volume | Air Pressure | Air Movement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhalation | External contract | Contracts, flattens | ↑ Increases | ↓ Lower than outside | Air in |
| Exhalation | External relax (internal may contract in force) | Relaxes, domes up | ↓ Decreases | ↑ Higher than outside | Air out |
⚡ Quick Recap
Inhalation → External intercostals contract, diaphragm flattens, chest volume ↑, pressure ↓, air in.
Exhalation → Muscles relax, diaphragm domes up, chest volume ↓, pressure ↑, air out.
Forced exhalation → Internal intercostals help.
