Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.48 Alveoli: Adaptations for Gas Exchange- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.48 Alveoli: Adaptations for Gas Exchange- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.48 Alveoli: Adaptations for Gas Exchange- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.48 explain how alveoli are adapted for gas exchange by diffusion between air in the lungs and blood in capillaries
Alveoli – Adaptations for Gas Exchange
📝 Introduction
Gas exchange happens in the alveoli, tiny air sacs in the lungs.
Oxygen (O₂) diffuses from alveoli → blood.
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) diffuses from blood → alveoli.
Exchange occurs by diffusion (movement from high to low concentration).
🌟 Key Adaptations of Alveoli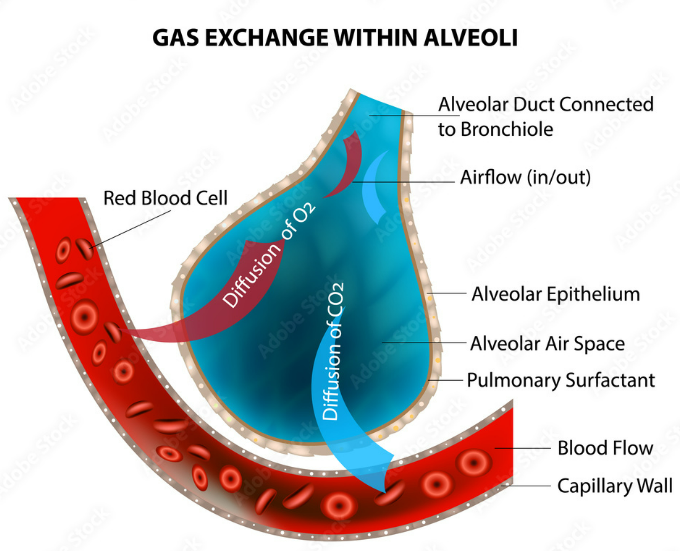
- Large Surface Area
Millions of alveoli in lungs (like bunches of grapes).
Huge surface area for maximum diffusion of gases. - Thin Walls
Alveolar walls are 1 cell thick.
Short diffusion distance → gases move quickly. - Rich Blood Supply
Surrounded by a dense network of capillaries.
Maintains steep concentration gradient for O₂ and CO₂. - Moist Lining
Dissolves gases (O₂ and CO₂) → makes diffusion easier. - Elastic Walls
Stretch and recoil during breathing.
Helps push air out and draw air in efficiently. - Good Ventilation
Constant airflow in alveoli → keeps O₂ levels high and CO₂ levels low.
Maintains strong diffusion gradient.
🔄 Diffusion Process
- Oxygen (O₂):
High concentration in alveoli → diffuses into low concentration blood (in capillaries). - Carbon Dioxide (CO₂):
High concentration in blood → diffuses into alveoli → exhaled.
📊 Summary Table
| Adaptation | How it helps gas exchange |
|---|---|
| Millions of alveoli | Large surface area |
| Thin walls (1 cell) | Short diffusion distance |
| Dense capillary network | Maintains concentration gradients |
| Moist lining | Gases dissolve easily |
| Elastic walls | Efficient ventilation |
| Constant airflow | Keeps gradients steep |
⚡ Quick Recap
Alveoli = tiny air sacs for O₂ in, CO₂ out.
SA ↑ + thin walls + capillaries + moist lining + ventilation = perfect for diffusion.
Diffusion always goes high → low concentration.
