Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.6B stem cells- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.6B stem cells- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-2.6B stem cells- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.6B understand the advantages and disadvantages of using stem cells in medicine
Stem Cells in Medicine
📝 Introduction
Stem cells = undifferentiated cells that can divide and develop into different specialised cells.
Found in:
• Embryos → can become any cell type (pluripotent).
• Adult tissues (bone marrow) → limited types (multipotent).
Used in medicine for treating diseases and injuries.
✅ Advantages of Using Stem Cells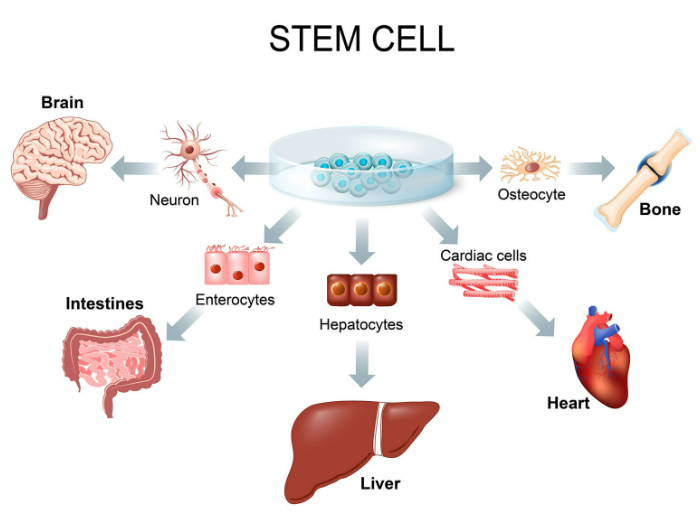
- Replace Damaged Cells or Tissues:
Example: Bone marrow stem cells → treat leukaemia. Skin stem cells → repair severe burns. - Potential to Treat Many Diseases:
Could treat conditions where cells are permanently damaged: Diabetes (pancreatic cells), Parkinson’s disease (nerve cells), Spinal cord injuries. - Research and Drug Testing: Stem cells can be used to test new drugs safely before using them in humans.
- Reduced Organ Transplant Problems: Patient’s own stem cells → less chance of organ rejection.
❌ Disadvantages / Risks
- Ethical Issues: Embryonic stem cells involve destruction of embryos → raises moral concerns.
- Risk of Tumours: Stem cells can divide uncontrollably → may form cancers if not carefully controlled.
- Immune Rejection: If donor stem cells are used → risk of immune system rejecting them.
- Cost and Complexity: Stem cell therapy is expensive and technically challenging.
📊 Summary Table – Stem Cells in Medicine
| Aspect | Advantage | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Cell replacement | Replace damaged cells/tissues | Bone marrow → leukaemia; Skin → burns |
| Disease treatment | Potential to treat diseases | Diabetes, Parkinson’s, spinal injuries |
| Drug research | Safe drug testing | Laboratory experiments |
| Reduced rejection | Patient’s own cells | Personalized therapy |
| Risks | Ethical concerns, tumours, rejection, cost | Embryo destruction, cancer risk, immune response |
⚡ Quick Recap
Stem cells = undifferentiated cells that can become specialised.
Advantages:
• Repair/replace damaged tissues
• Treat diseases (diabetes, Parkinson’s, spinal injury)
• Test drugs safely
• Reduce organ rejection
Disadvantages:
• Ethical concerns (embryos)
• Risk of tumours
• Immune rejection if donor cells used
• High cost & complex technology
