Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.12 White Blood Cells & Immunity- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.12 White Blood Cells & Immunity- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.12 White Blood Cells & Immunity- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
3.12 understand how the immune system responds to disease using white blood cells, illustrated by phagocytes ingesting pathogens and lymphocytes releasing antibodies specific to the pathogen
The Immune System and White Blood Cells
📝 Introduction
The immune system protects the body against pathogens (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protoctists).
White blood cells (WBCs) are the main defenders.
Two key types of WBCs are involved in defending against disease: phagocytes and lymphocytes.
🫁 Phagocytes – “The Engulfers”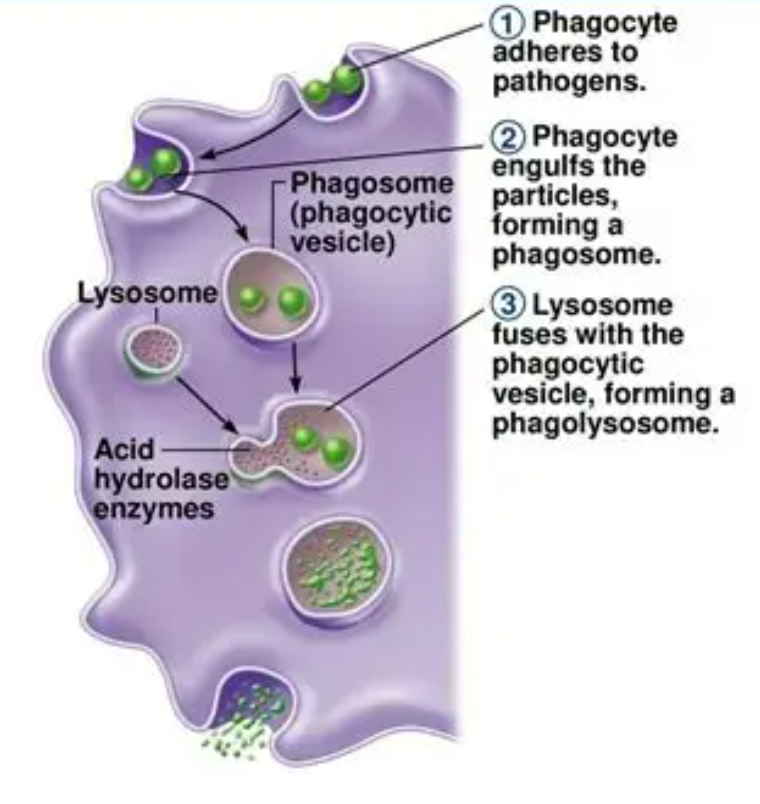
- Function: Engulf and destroy pathogens.
- Process (Phagocytosis):
- Phagocyte detects pathogen.
- Surrounds and engulfs it into a vesicle.
- Digestive enzymes inside phagocyte break down the pathogen.
- Role: First line of non-specific defence.
- Key point: Works against any pathogen (not specific).
🧬 Lymphocytes – “The Specialists”
- Function: Produce antibodies specific to the pathogen.

- Process:
- Lymphocyte recognizes a specific antigen on the pathogen.
- Produces antibodies → attach to pathogen → neutralise or mark it for destruction.
- Some lymphocytes become memory cells → faster response if the pathogen appears again.
- Role: Specific immunity.
- Key point: Each antibody is specific to one pathogen.
🔑 Summary Table
| White Blood Cell | Method | Specificity | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phagocyte | Engulf & digest | Non-specific | First line of defence |
| Lymphocyte | Produce antibodies | Specific | Long-term immunity, memory cells |
⚡ Quick Recap
Phagocytes → engulf pathogens (non-specific).
Lymphocytes → produce pathogen-specific antibodies → memory cells for future protection.
Immune response = detection → destruction → memory.
Protects against disease and prevents re-infection.

