Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.14 B Platelets & Blood Clotting- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.14 B Platelets & Blood Clotting- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.14 B Platelets & Blood Clotting- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
3.14B understand how platelets are involved in blood clotting, which prevents blood loss and the entry of micro-organisms
Role of Platelets in Blood Clotting
📝 Introduction
Platelets (thrombocytes) are small cell fragments in the blood.
Their main role: prevent blood loss and stop pathogens from entering through wounds.
Blood clotting is also called coagulation.
🔑 How Platelets Work in Clotting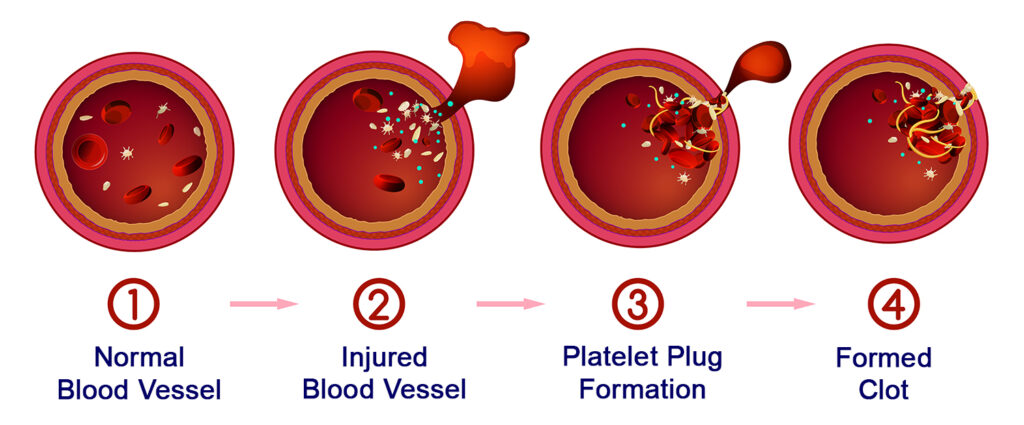
- Detection of Injury
When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets stick to the broken area.
They release chemicals to signal more platelets. - Formation of Platelet Plug
Platelets clump together at the wound → forms a temporary platelet plug. - Fibrin Mesh Formation
Chemicals from platelets trigger fibrinogen → fibrin conversion.
Fibrin threads form a mesh over the wound.
RBCs get trapped → stable clot formed. - Protection Against Micro-organisms
Clot seals the wound → prevents entry of bacteria and viruses.
🔑 Key Points
- Platelets are cell fragments, not full cells.
- Blood clotting is a vital defence mechanism.
- The clot is temporary → tissue heals underneath, then clot dissolves.
- Vitamin K and calcium ions are essential for clotting.
📊 Summary Table
| Step | What Happens | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Platelet adhesion | Platelets stick to damaged vessel | Detect injury |
| Platelet aggregation | Platelets clump together | Form temporary plug |
| Fibrin formation | Fibrin mesh traps RBCs | Stable clot |
| Protection | Wound sealed | Prevent blood loss & infection |
⚡ Quick Recap
Platelets → clot formation → prevents blood loss & infection.
Steps: stick → clump → fibrin mesh → stable clot.
Vitamin K & calcium → essential for clotting.
