Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.15 Structure & Function of the Heart- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.15 Structure & Function of the Heart- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.15 Structure & Function of the Heart- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
3.15 describe the structure of the heart and how it functions
Structure & Function of the Heart
📝 Introduction
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood around the body.
Works as a double circulatory system → blood passes through the heart twice in one complete circuit.
Right side → pumps blood to the lungs (pulmonary circulation).
Left side → pumps blood to the rest of the body (systemic circulation).
🧩 Structure of the Heart
- Chambers (4 total):
- Right atrium → receives deoxygenated blood from body (via vena cava).
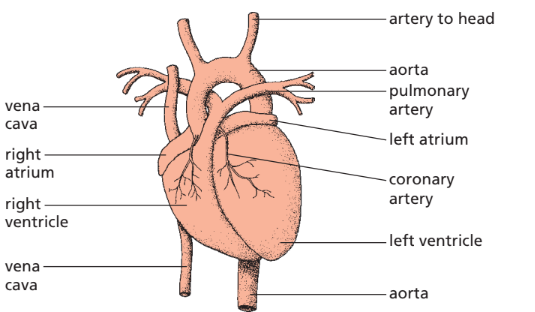 Right ventricle → pumps it to lungs (via pulmonary artery).
Right ventricle → pumps it to lungs (via pulmonary artery).- Left atrium → receives oxygenated blood from lungs (via pulmonary vein).
- Left ventricle → pumps oxygenated blood to the whole body (via aorta).
- Valves:
- Atrioventricular valves (AV) → between atria & ventricles; prevent backflow when ventricles contract.
- Semilunar valves → at exits of pulmonary artery & aorta; stop backflow into ventricles.
- Walls: Left ventricle wall is thicker → pumps blood at higher pressure to whole body.
Right ventricle wall thinner → pumps only to lungs (shorter distance). - Septum: Wall of muscle dividing left & right sides → keeps oxygenated & deoxygenated blood separate.
- Coronary arteries: Supply oxygen & nutrients to heart muscle itself.
⚙️ How the Heart Functions (Cardiac Cycle)
- Atrial Systole (atria contract): Blood forced into ventricles through AV valves.
- Ventricular Systole (ventricles contract): Blood forced into arteries (aorta & pulmonary artery).
AV valves close → “lub” sound. - Diastole (relaxation): Heart chambers relax, blood fills atria again.
Semilunar valves close → “dub” sound.
This cycle repeats about 70–80 times per minute in adults (resting heartbeat).
📊 Summary Table
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Right atrium | Collects deoxygenated blood from body |
| Right ventricle | Pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs |
| Left atrium | Collects oxygenated blood from lungs |
| Left ventricle | Pumps oxygenated blood to body |
| Valves | Prevent backflow of blood |
| Septum | Separates oxygenated & deoxygenated blood |
| Coronary arteries | Nourish heart muscle |
⚡ Quick Recap
Heart = double pump → right side (lungs), left side (body).
Left ventricle thicker → needs more force.
Valves stop backflow → ensure one-way flow.
Cardiac cycle = atrial systole → ventricular systole → diastole.
Coronary arteries keep heart alive.
