Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.22B Kidney: Excretion & Osmoregulation- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.22B Kidney: Excretion & Osmoregulation- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.22B Kidney: Excretion & Osmoregulation- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
3.22B understand how the kidney carries out its roles of excretion and osmoregulation
Kidney – Excretion & Osmoregulation
🌱 Introduction
Kidney = Excretory + Osmoregulatory organ.
Main functions:
Excretion → removal of urea, excess salts, excess water.
Osmoregulation → controlling water balance in blood to keep conditions constant.
1️⃣ Excretion by the Kidney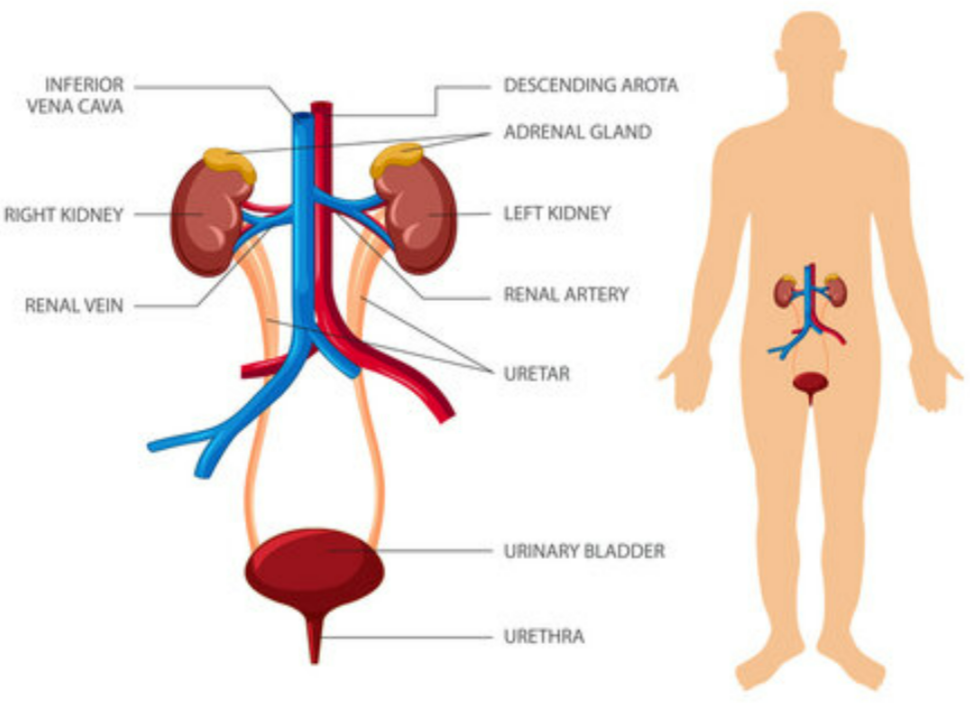
- Step 1: Blood enters kidney via renal artery (rich in urea, salts, water).
- Step 2: Filtration in nephrons:
Small molecules (urea, salts, glucose, water) are filtered out of blood in the glomerulus → Bowman’s capsule.
Large molecules (proteins, blood cells) stay in blood. - Step 3: Selective reabsorption in tubules:
Useful substances reabsorbed:
– All glucose (for respiration)
– Some salts (as needed)
– Most water (depends on body needs) - Step 4: Formation of urine:
Leftover = urea + excess salts + excess water → urine.
Urine passes: collecting duct → ureter → bladder → urethra.
2️⃣ Osmoregulation by the Kidney
- Osmoregulation: controlling water content of blood.

- Carried out in collecting ducts of nephrons under control of ADH (antidiuretic hormone).
- When blood water is low (dehydrated):
– Pituitary releases more ADH.
– Collecting ducts become more permeable → more water reabsorbed into blood.
– Urine = small volume, very concentrated. - When blood water is high (too much water):
– Pituitary releases less ADH.
– Collecting ducts become less permeable → less water reabsorbed.
– Urine = large volume, very dilute.
📊 Summary Table
| Role | Process | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| Excretion | Filtration + selective reabsorption + urine formation | Removes urea, excess salts & water |
| Osmoregulation | ADH regulates collecting duct permeability | Balances blood water → concentrated or dilute urine |
⚡ Quick Recap
Excretion → kidneys remove urea, salts, water → forms urine.
Osmoregulation → kidneys control water balance using ADH.
Low water → more ADH, concentrated urine.
High water → less ADH, dilute urine.
Mnemonic: “Kidneys Keep it Clean & Controlled”
Clean = Excretion (removing wastes).
Controlled = Osmoregulation (water balance).

