Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.24 Nephron Structure- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.24 Nephron Structure- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.24 Nephron Structure- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
3.24B describe the structure of a nephron, including the Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus, convoluted tubules, loop of Henle and collecting duct
Structure of a Nephron
🌱 Introduction
Nephron = functional unit of the kidney.
Each kidney has about 1–1.5 million nephrons.
Function: filters blood, removes waste (urea), reabsorbs useful substances, and regulates water balance.
🔹 Main Parts of a Nephron
1. Bowman’s Capsule + Glomerulus
- Glomerulus: a ball/knot of capillaries where blood is filtered.
- Bowman’s capsule: cup-shaped structure surrounding the glomerulus.
- Together: site of ultrafiltration → small molecules (water, glucose, urea, salts) pass into capsule, but proteins & blood cells stay in blood.
2. Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)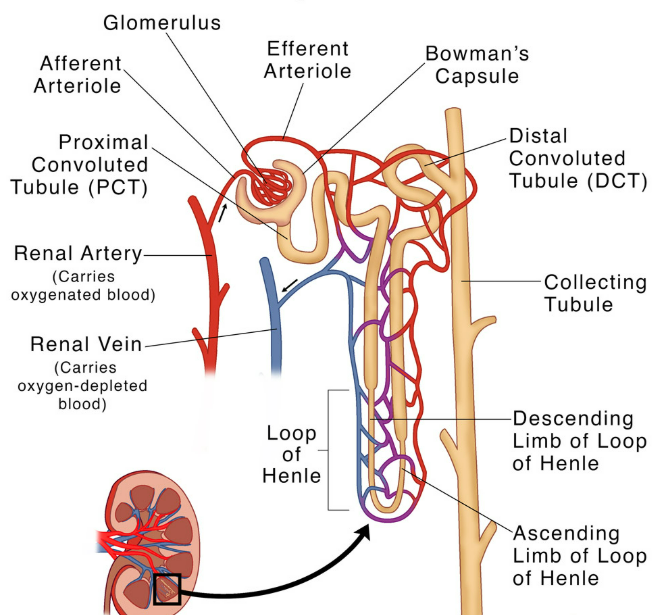
- Coiled tube after Bowman’s capsule.
- Function: selective reabsorption → glucose, amino acids, most water & salts taken back to blood.
- Cells with microvilli → large surface area for absorption.
3. Loop of Henle
- U-shaped structure (descending + ascending limb).
- Function: concentrates urine by reabsorbing water and salts → important for water balance.
4. Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
- Second coiled section.
- Function: adjusts salt levels (ion exchange), controlled by hormones (e.g., aldosterone).
5. Collecting Duct
- Long tube where many nephrons drain.
- Function: collects urine, reabsorbs water (controlled by ADH).
- Urine flows → renal pelvis → ureter → bladder.
📊 Summary Table
| Part of Nephron | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Bowman’s capsule + Glomerulus | Cup + capillary knot | Ultrafiltration → small molecules filtered |
| PCT | First coiled tubule, microvilli cells | Reabsorbs glucose, amino acids, water, salts |
| Loop of Henle | U-shaped tube | Maintains water & salt balance, concentrates urine |
| DCT | Second coiled tubule | Adjusts salt levels (hormone control) |
| Collecting duct | Long final tube | Water reabsorption (ADH), passes urine to pelvis |
⚡ Quick Recap
Bowman’s capsule + Glomerulus → filter blood.
PCT → take back glucose, amino acids, water.
Loop of Henle → concentrates urine.
DCT → fine-tunes salt levels.
Collecting duct → final water control, urine sent out.
👉 Flow: Glomerulus → Bowman’s capsule → PCT → Loop of Henle → DCT → Collecting duct.
