Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.37- 3.38 Human Nervous System- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.37- 3.38 Human Nervous System- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.37- 3.38 Human Nervous System- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
3.37 understand that the central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord and is linked to sense organs by nerves
3.38 understand that stimulation of receptors in the sense organs sends electrical impulses along nerves into and out of the central nervous system, resulting in rapid responses
Central Nervous System (CNS)
🌱 What is the CNS?
The central nervous system (CNS) is the body’s main control system.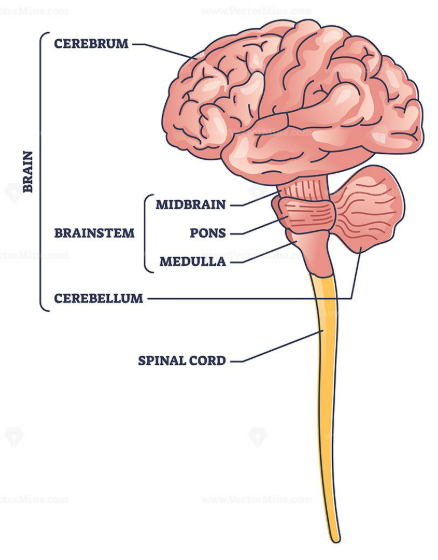 It consists of:
It consists of:
- Brain → control centre, processes information
- Spinal cord → carries signals to/from brain, controls reflexes
⚡ Link with Sense Organs
The CNS is connected to sense organs through nerves.
Process:
- Sense organs detect stimuli (light, sound, touch, chemicals, temperature)
- Sensory neurons carry signals → CNS
- Motor neurons → effectors (muscles/glands)
🧩 Functions of the Brain
- Cerebrum → memory, learning, voluntary movements, senses
- Cerebellum → balance and coordination
- Medulla → involuntary actions (breathing, heartbeat)
📊 Summary Table
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Brain | Processes and interprets information |
| Spinal cord | Pathway for nerve impulses, controls reflexes |
| Nerves | Connect CNS with sense organs and effectors |
| Sense organs | Detect changes (stimuli) |
📌 Quick Recap
CNS = Brain + Spinal cord.
Linked to sense organs via nerves.
Works with neurons to process stimuli and trigger responses.
How Receptors Trigger Rapid Responses
🌱 Introduction
Sense organs (eyes, ears, skin, nose, tongue) detect stimuli from the environment.
These stimuli trigger rapid responses via the nervous system.
🧩 Process of Nervous Response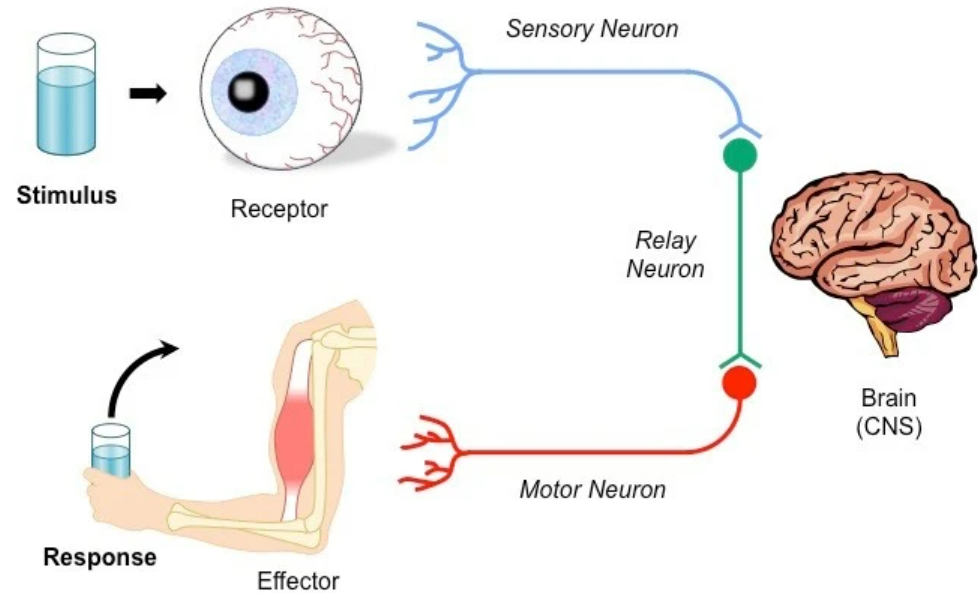
- Stimulus detected → receptors in sense organs detect a change (e.g., light, heat, pressure).
- Electrical impulse generated → sensory neurons carry the impulse to the CNS (brain or spinal cord).
- CNS processes information → decides the appropriate response.
- Impulse sent to effector → motor neurons carry signal to muscles or glands.
- Response occurs → muscle contracts or gland secretes.
🔹 Key Points
- Nervous responses are fast → impulses travel electronically along neurons.
- Reactions are specific → only the effector linked to the pathway responds.
- Allows organisms to react quickly to danger or environmental changes.
📊 Example Table
| Stimulus | Receptor | CNS | Effector | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hot object | Skin | Spinal cord | Arm muscles | Pull hand away |
| Bright light | Eye | Brain | Iris muscles | Pupil contracts |
| Loud noise | Ear | Brain | Muscles | Turn head toward sound |
📌 Quick Recap
Stimulus → receptor → sensory neuron → CNS → motor neuron → effector → response.
Ensures rapid, precise reactions.
Nervous system = main system for quick responses.
