Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.43 The Role of Skin in Temperature Regulation- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.43 The Role of Skin in Temperature Regulation- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.43 The Role of Skin in Temperature Regulation- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
3.43 describe the role of the skin in temperature regulation, with reference to sweating, vasoconstriction and vasodilation
Role of the Skin in Temperature Regulation
🌱 Introduction
The skin helps maintain a stable body temperature (homeostasis).
It regulates heat through sweating, vasoconstriction, and vasodilation.
Works with the nervous system to respond to temperature changes.
🔥 1. Sweating (Cooling Mechanism)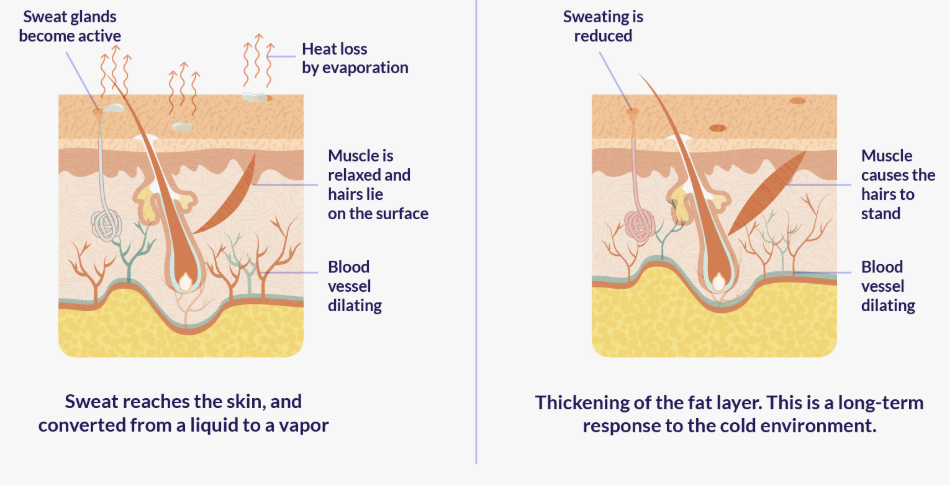
- When body temperature rises, sweat glands produce sweat.
- Sweat is mostly water with salts.
- Evaporation of sweat from the skin surface removes heat → cools the body.
- Example: Exercise → increased sweating prevents overheating.
❄️ 2. Vasoconstriction (Reducing Heat Loss)
- When body temperature drops, blood vessels near the skin narrow (constrict).
- Less blood flows near skin surface → reduces heat loss.
- Skin may look paler due to reduced blood flow.
- Example: Cold weather → vasoconstriction conserves body heat.
🌞 3. Vasodilation (Increasing Heat Loss)
- When body temperature rises, blood vessels near the skin widen (dilate).
- More blood flows near skin surface → more heat radiates from body.
- Skin may look redder due to increased blood flow.
- Example: Hot weather → vasodilation helps cool the body.
📊 Summary Table
| Mechanism | Condition | How it works | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sweating | Body too hot | Sweat evaporates from skin | Cools body |
| Vasoconstriction | Body too cold | Blood vessels narrow | Conserves heat |
| Vasodilation | Body too hot | Blood vessels widen | Radiates heat |
📌 Quick Recap
Skin regulates temperature via:
– Sweating → cooling by evaporation.
– Vasoconstriction → reduces heat loss in cold.
– Vasodilation → increases heat loss in heat.
Works with nervous system to maintain homeostasis.
