Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.5B Absorption of Water by Root Hair Cells- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.5B Absorption of Water by Root Hair Cells- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-3.5B Absorption of Water by Root Hair Cells- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
3.5B understand how water is absorbed by root hair cells
Water Absorption by Root Hair Cells
📝 Introduction
Plants need water for photosynthesis, transport, cooling, and maintaining turgidity.
Water enters plants through root hair cells, which are specialised for absorption.
🔑 Structure of Root Hair Cells
- Long, thin extensions from root epidermal cells → provide a large surface area for absorption.
- Very thin cell wall → short distance for diffusion/osmosis.
- Direct contact with moist soil particles.
💧 Process of Water Absorption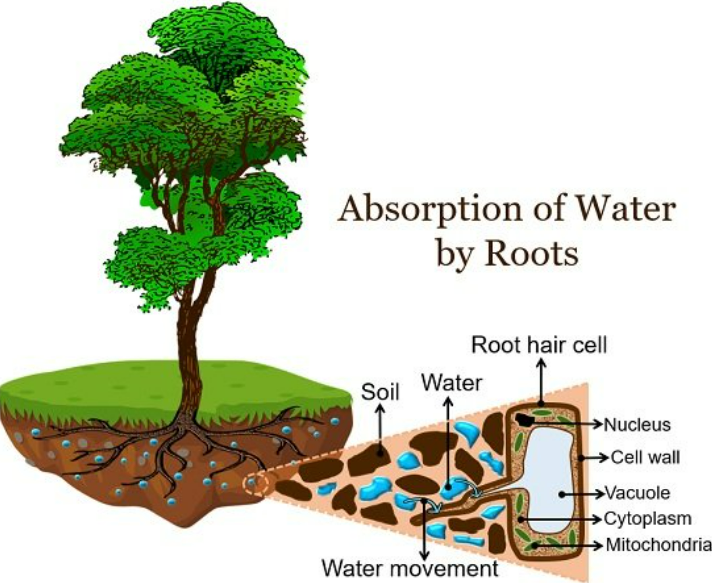
- Higher Water Concentration in Soil
Soil water (with dissolved minerals) usually has a higher water potential than the cytoplasm of root hair cells. - Osmosis into Root Hair Cells
Water moves by osmosis (from high water potential → low water potential) through the partially permeable membrane of root hair cells. - Movement to Xylem
After entering root hair cells, water moves:
• Cell to cell through the cytoplasm (symplast pathway).
• Or through the cell walls (apoplast pathway).
Finally, water reaches the xylem vessels in the root. - Transport Upwards
Xylem carries the absorbed water upwards to the stem and leaves.
📊 Key Points
| Feature of Root Hair Cell | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Long, thin projection | Large surface area for absorption |
| Thin cell wall | Short diffusion distance |
| Close contact with soil | Easy access to water |
| Contains concentrated cell sap | Low water potential → helps draw in water by osmosis |
⚡ Quick Recap
Root hair cells absorb water by osmosis.
Adaptations → long projection, thin walls, large SA.
Water potential gradient: soil → root hair cell → cortex → xylem → leaves.
Essential for photosynthesis, cooling, transport, and turgidity.
