Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.1 Sexual & Asexual Reproduction: Differences- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.1 Sexual & Asexual Reproduction: Differences- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.1 Sexual & Asexual Reproduction: Differences- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
4.1 understand the differences between sexual and asexual reproduction
Sexual vs Asexual Reproduction
🌱 Introduction
Reproduction is the biological process by which new organisms are produced.
There are two main types: sexual and asexual reproduction.
🧬 Asexual Reproduction 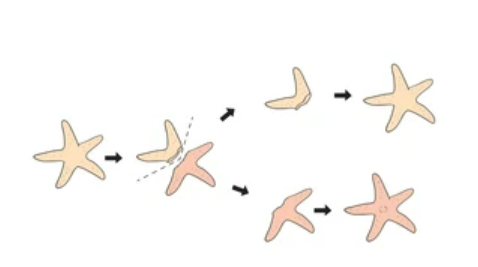
- Definition: Involves only one parent. No fusion of gametes.
- Process: Offspring are produced by mitosis.
- Key Features:
- Offspring are genetically identical to parent → called clones
- No variation (except for mutations)
- Fast and energy-efficient
- Examples: Bacteria (binary fission), plants (strawberry runners, potato tubers), fungi (spores)
🌹 Sexual Reproduction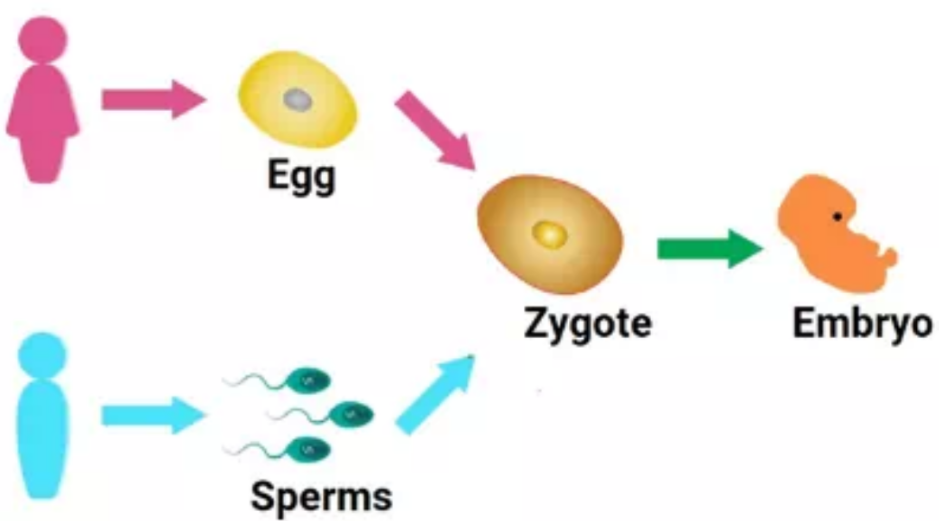
- Definition: Involves two parents. Fusion of male and female gametes.
- Process: Gametes (produced by meiosis) fuse → zygote → offspring.
- Key Features:
- Offspring are genetically varied (due to mixing of DNA)
- Increases variation in population
- Slower and requires more energy
- Examples: Humans and animals (sperm + egg), flowering plants (pollen + ovule)
📊 Comparison Table
| Feature | Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
|---|---|---|
| Parents | One parent | Two parents |
| Gametes | Not involved | Involves gametes (fusion) |
| Cell division | Mitosis | Meiosis + fertilisation |
| Offspring | Clones (genetically identical) | Genetically varied |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Variation | None (except mutations) | Present |
| Examples | Bacteria, fungi, potatoes | Humans, animals, flowering plants |
📌 Quick Recap
– Asexual reproduction → fast, one parent, clones, no variation.
– Sexual reproduction → two parents, gametes, variation, slower.
