Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.14 & 4.15 The Genome & Genes- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.14 & 4.15 The Genome & Genes- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.14 & 4.15 The Genome & Genes- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
4.14 understand that the genome is the entire DNA of an organism and that a gene is a section of a molecule of DNA that codes for a specific protein
4.15 understand that the nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes on which genes are located
Genome & Genes
🌱 Introduction
DNA is the genetic material found in almost every cell.
It controls inheritance, protein production, and overall functioning of an organism.
Within DNA, we talk about two important terms: genome and gene.
📖 Genome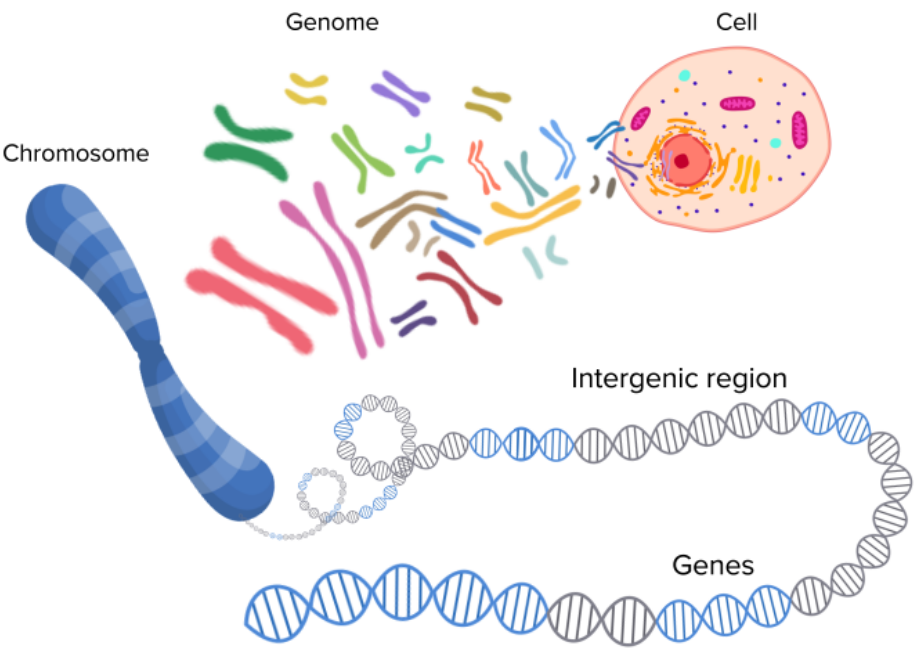
- Definition: The entire DNA of an organism.
- Includes:
- Coding regions → genes that code for proteins
- Non-coding regions → regulate gene activity
- Every cell (except gametes and red blood cells) contains the complete genome.
- Example: Human genome → ~3 billion base pairs of DNA, arranged in 23 pairs of chromosomes.
📖 Gene
- Definition: A section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for one specific protein (or polypeptide).
- Structure: Sequence of bases (A, T, C, G).
Order of bases → sequence of amino acids in a protein. - Function: Genes act as “instructions” for protein synthesis.
- Example: Insulin gene → insulin protein (regulates blood sugar).
⚙️ Relationship (Genome → Chromosome → Gene → Protein)
- Genome: Whole DNA of an organism
- Chromosomes: Packaged DNA structures
- Gene: Specific DNA section coding for a protein
- Protein: Determines traits and functions
📊 Summary Table
| Term | Definition | Key Features | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genome | Entire DNA of an organism | Contains all coding + non-coding DNA | Human genome = 23 pairs (~3 billion base pairs) |
| Chromosome | Long, coiled DNA molecule carrying many genes | Humans have 46 (23 pairs) | Chromosome 7 carries CF gene |
| Gene | Section of DNA coding for a protein | Base sequence → amino acid sequence → protein | Insulin gene → insulin protein |
📌 Quick Recap
– Genome = Whole DNA of an organism.
– Chromosomes = Packaged DNA within the genome.
– Gene = Specific section of DNA coding for a protein.
– Proteins from genes → control traits, enzymes, hormones, and cell functions.
– Mnemonic: “Genome = Grand total, Gene = Gives protein”
Chromosomes & Genes in the Nucleus
🌱 Introduction
The nucleus = control center of the cell.
It contains chromosomes, which carry genetic information in the form of DNA.
Genes are located on these chromosomes and they control traits and functions of the organism.
📖 Chromosomes
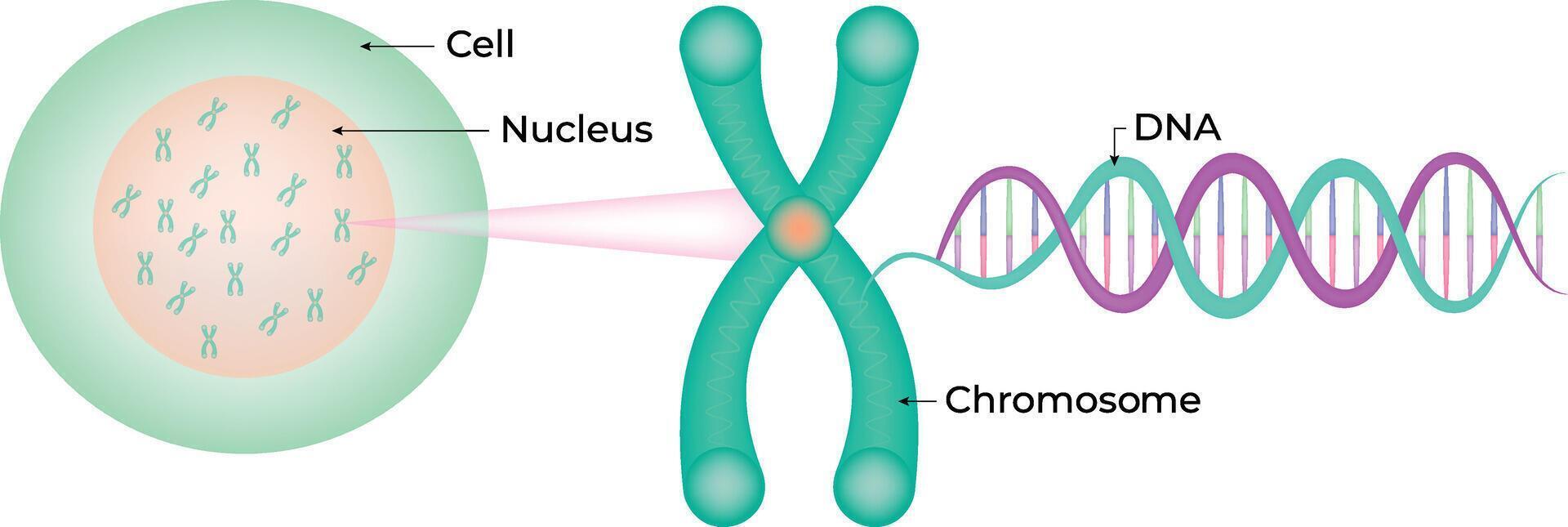
- Definition: Long, coiled molecules of DNA wrapped around proteins (histones).
- Found inside the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
- Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) in each body cell.
- During cell division, chromosomes become more visible as distinct structures.
📖 Genes
- Definition: Specific segments of DNA located on chromosomes.
- Each gene codes for a particular protein.
- Proteins control cell activities, structure, and traits.
- Examples:
- Hemoglobin gene → makes hemoglobin protein
- Eye color gene → controls pigment production
⚙️ Relationship (Nucleus → Chromosome → Gene)
- Nucleus: contains chromosomes
- Chromosomes: made of DNA
- Genes: sections of DNA on chromosomes
- Genes → Proteins → Traits: proteins determine cell function and organism characteristics
📊 Summary Table
| Level | Structure | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Control center of the cell | Stores chromosomes | Animal & plant cells |
| Chromosome | DNA wrapped around proteins | Carries many genes | Chromosome 11 → insulin gene |
| Gene | Segment of DNA | Codes for a specific protein | Gene for blood group |
📌 Quick Recap
– Nucleus = cell’s control room.
– Chromosomes = DNA packages inside the nucleus.
– Genes = instructions on DNA coding for proteins.
– Genes → Proteins → Traits.
– Mnemonic: “Nucleus → Contains Chromosomes → Carry Genes”
