Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.17B RNA Structure- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.17B RNA Structure- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.17B RNA Structure- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
4.17B understand that an RNA molecule is single stranded and contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T)
RNA Molecule – Structure, Bases, and Function
🌱 Introduction
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) is a nucleic acid involved in protein synthesis.
Unlike DNA, RNA is shorter, single-stranded, and not a long-term storage molecule.
It transfers genetic information from DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm for making proteins.
🧬 Structure of RNA
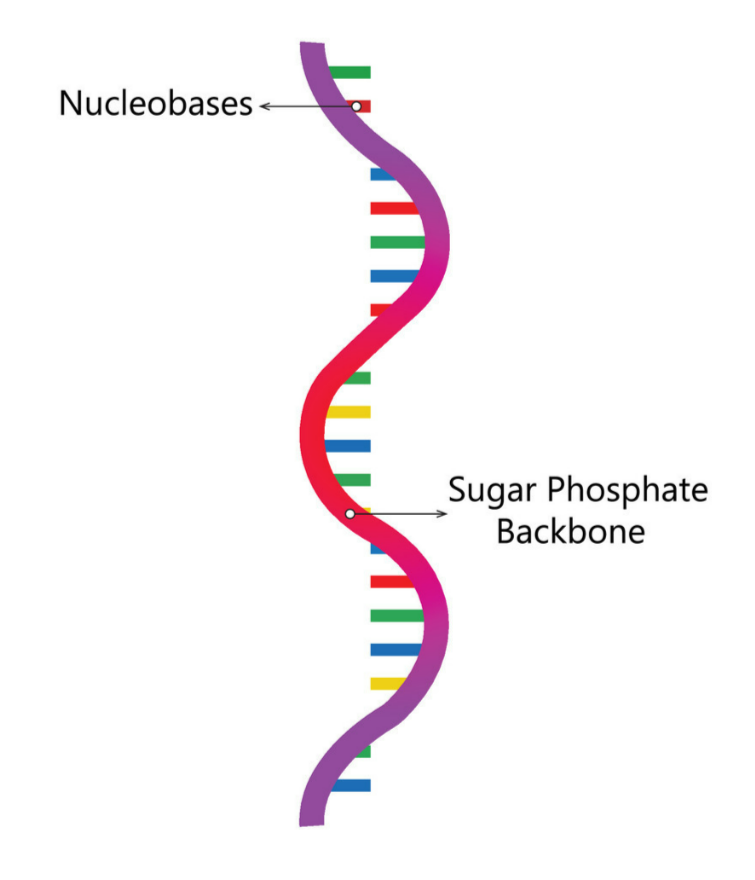
- Strand: Single-stranded, unlike DNA’s double helix.
Allows folding into complex 3D shapes for specific functions (e.g., tRNA). - Nucleotide Components:
- Sugar: ribose (one extra oxygen than DNA)
- Phosphate group: backbone of the strand
- Nitrogenous bases: A, U (replaces T in DNA), C, G
Sugar-phosphate backbone = “rails”, bases = “rungs” when folded.
- Base Pairing:
- Mostly single-stranded, but complementary pairing in folded regions:
- A ↔ U
- C ↔ G
- Helps tRNA and rRNA fold into functional shapes.
- Mostly single-stranded, but complementary pairing in folded regions:
🧩 Types of RNA & Functions
| Type of RNA | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| mRNA (messenger RNA) | Linear single strand | Carries genetic code from DNA to ribosomes |
| tRNA (transfer RNA) | Cloverleaf folded single strand | Transfers amino acids to ribosome during protein synthesis |
| rRNA (ribosomal RNA) | Part of ribosome | Forms ribosomes and catalyzes protein formation |
⚡ Key Differences: DNA vs RNA
| Feature | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
| Strands | Double-stranded | Single-stranded |
| Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Bases | A, T, C, G | A, U, C, G |
| Stability | Stable, long-term | Less stable, temporary |
| Function | Stores genetic info | Transfers & translates info into proteins |
🌞 Importance of RNA
- Temporary copy of the genetic code for protein synthesis.
- Ensures correct amino acids are added in the right order to make functional proteins.
- Supports rapid cellular responses, unlike DNA which is static storage.
📌 Quick Recap
– RNA = single-stranded, sugar = ribose, base U replaces T.
– Main function → transfer & translation of genetic code into proteins.
– Types: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA with specific roles.
– Less stable than DNA → temporary information transfer.
Mnemonic: “RNA = Single strand, U stands for You, helps make Proteins too.”
