Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.19 Alleles- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.19 Alleles- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.19 Alleles- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
4.19 understand how genes exist in alternative forms called alleles which give rise to differences in inherited characteristics
Genes and Alleles – Inherited Characteristics
🌱 Introduction
A gene = a section of DNA that codes for a specific protein and controls a trait (e.g., eye color).
Alleles = different versions of the same gene causing variation in a trait.
Example: Gene for flower color → two alleles: R (red) and r (white).
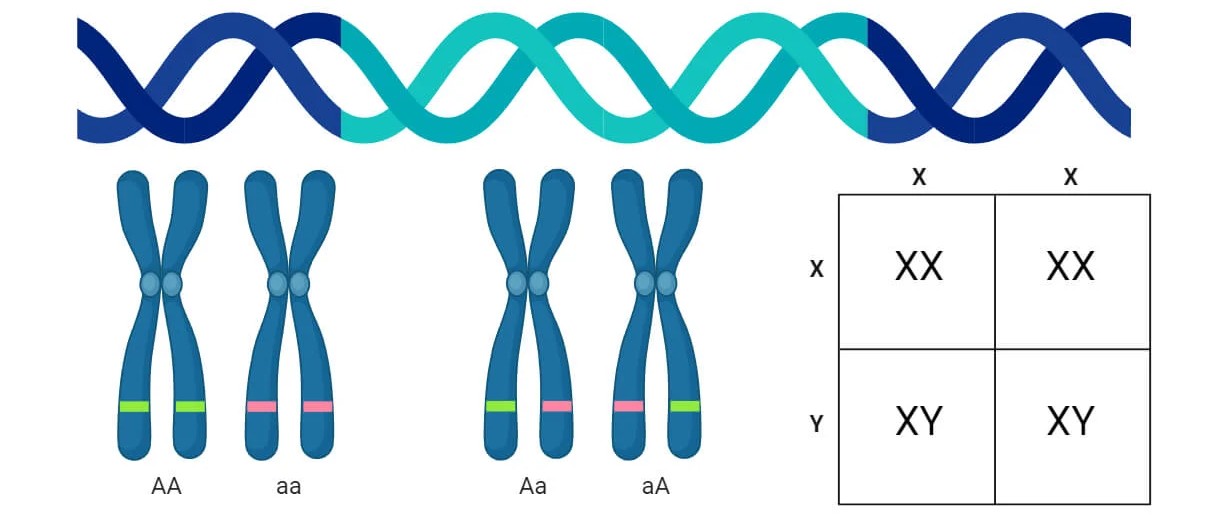
📖 Key Points About Alleles
- Homozygous → both alleles are the same (e.g., RR or rr).
- Heterozygous → alleles are different (e.g., Rr).
- Dominant allele → masks the effect of another allele (capital letter, e.g., R).
- Recessive allele → effect masked by dominant allele (lowercase, e.g., r).
- Alleles are at the same position (locus) on homologous chromosomes.
⚙️ How Alleles Affect Inherited Traits
- Combination of alleles determines the phenotype (observable trait).
- Examples:
- Eye color: B (brown, dominant), b (blue, recessive)
BB → brown eyes, Bb → brown eyes, bb → blue eyes - Seed shape in peas: R (round, dominant), r (wrinkled, recessive)
- Eye color: B (brown, dominant), b (blue, recessive)
- Genotype = genetic makeup (allele combination, e.g., Bb)
- Phenotype = observable characteristic (e.g., brown eyes)
📊 Summary Table
| Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Allele | Alternative form of a gene | R or r for flower color |
| Homozygous | Two identical alleles | RR or rr |
| Heterozygous | Two different alleles | Rr |
| Dominant | Allele that masks another | R |
| Recessive | Allele masked by dominant | r |
| Genotype | Genetic makeup | Bb |
| Phenotype | Observable trait | Brown eyes |
📌 Quick Recap
– Genes can exist in different forms = alleles.
– Allele combinations determine the phenotype.
– Dominant allele shows up if at least one copy is present.
– Recessive allele shows only if both copies are recessive.
– Homozygous = same alleles, Heterozygous = different alleles.
Mnemonic: “Alleles = Alternative, Dominant hides Recessive”
