Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.22 Polygenic Inheritance- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.22 Polygenic Inheritance- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.22 Polygenic Inheritance- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
4.22 understand that most phenotypic features are the result of polygenic inheritance rather than single genes
Polygenic Inheritance
🧬 Introduction
Not all traits are controlled by a single gene.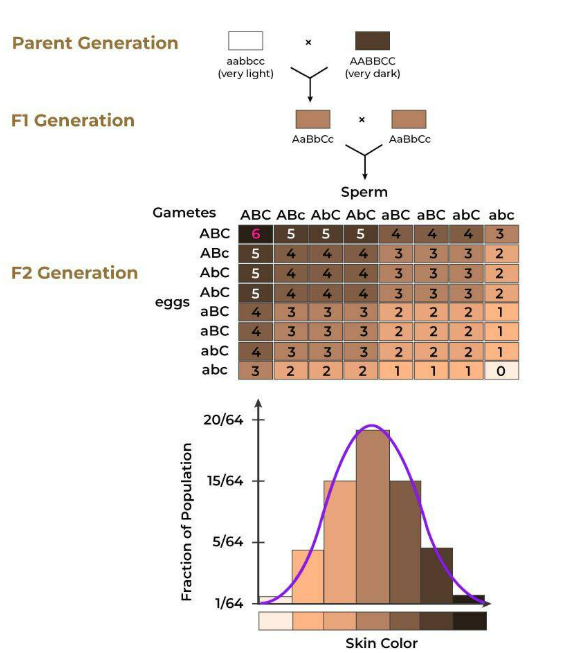 Many important characteristics are influenced by multiple genes working together.
Many important characteristics are influenced by multiple genes working together.
This type of inheritance is called polygenic inheritance.
📖 Key Points
- Definition: Polygenic inheritance = when a characteristic is controlled by two or more genes (often located on different chromosomes).
- Each gene may have two or more alleles, and their combined effect influences the phenotype.
- Unlike single-gene traits (e.g., flower color in peas), polygenic traits show a wide range of variation (continuous variation).
🌸 Examples of Polygenic Traits in Humans
- Height – influenced by many genes + environment (nutrition).
- Skin color – controlled by several genes affecting melanin production.
- Eye color – multiple genes interact to give a range of colors.
- Weight – combination of genes + lifestyle (diet/exercise).
📊 Difference Between Single-Gene vs Polygenic Traits
| Feature | Single-Gene (Monogenic) | Polygenic |
|---|---|---|
| Number of genes | Controlled by 1 gene | Controlled by many genes |
| Variation | Discrete (clear categories) | Continuous (range of values) |
| Examples | Blood group (A, B, AB, O) | Height, skin color, eye color |
| Graph | Bar chart with distinct groups | Bell-shaped curve (normal distribution) |
📈 Continuous Variation in Polygenic Traits
Polygenic traits show gradual differences in phenotype.
Example: Height → ranges from very short to very tall, with many intermediate values.
If graphed, produces a bell-shaped curve (normal distribution).
📌 Quick Recap
– Polygenic inheritance = many genes control one trait.
– Produces continuous variation (smooth range, not categories).
– Examples: height, skin color, weight, eye color.
– Contrast: Monogenic inheritance → single gene, discrete categories (like blood groups).
✨ Trick: Poly = Many → Polygenic = Many genes for one trait.
