Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.23 Monohybrid Inheritance: Genetic Diagrams- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.23 Monohybrid Inheritance: Genetic Diagrams- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.23 Monohybrid Inheritance: Genetic Diagrams- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
4.23 describe patterns of monohybrid inheritance using a genetic diagram
Monohybrid Inheritance
🌱 Introduction
Monohybrid inheritance studies how a single gene (with two alleles) is inherited.
It shows how alleles are passed from parents to offspring and how they combine to give different phenotypes.
📖 Key Concepts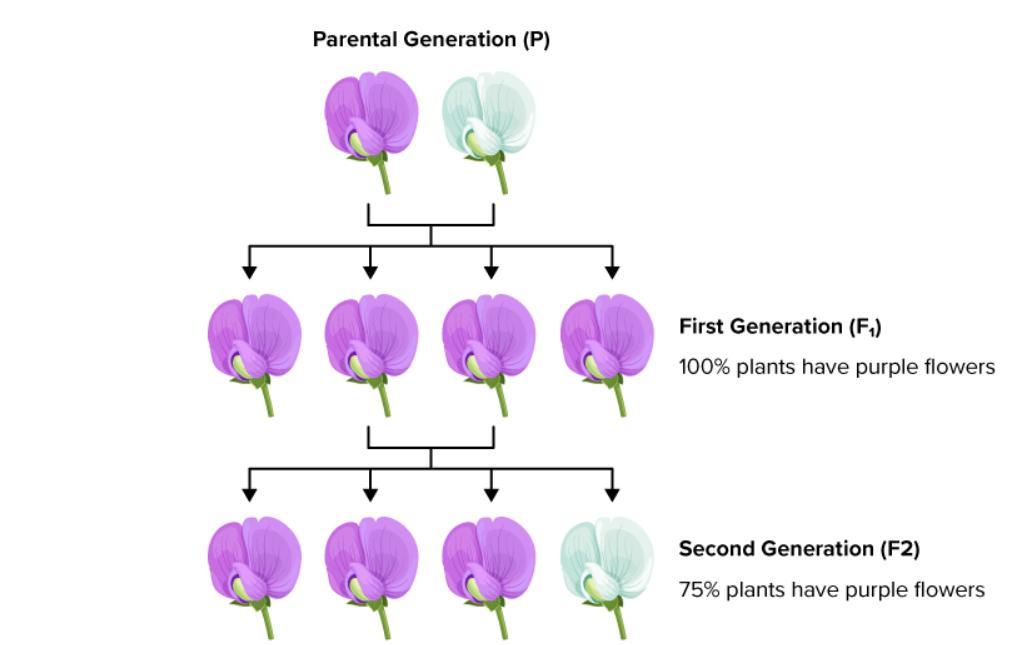
- Gene: A section of DNA controlling a trait (e.g., flower color).
- Allele: Different versions of the same gene (e.g., R = red, r = white).
- Homozygous: Two identical alleles (RR or rr).
- Heterozygous: Two different alleles (Rr).
- Dominant allele: Expressed even if only one copy is present (R).
- Recessive allele: Only expressed if both copies are present (rr).
- Genotype: Genetic makeup (RR, Rr, rr).
- Phenotype: Observable trait (red or white flower).
🌸 Example: Flower Colour
Gene for flower colour → Alleles: R (red, dominant) and r (white, recessive)
1. Cross between Homozygous Red (RR) × Homozygous White (rr)
- Parent Genotypes: RR × rr
- Gametes: R, R × r, r
- F1 Genotypes: All Rr
- F1 Phenotype: All red (since R is dominant).
2. Self-Cross of F1 Generation (Rr × Rr)
- Parent Genotypes: Rr × Rr
- Gametes: R, r × R, r
| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| R | RR | Rr |
| r | Rr | rr |
- Genotype ratio: 1 RR : 2 Rr : 1 rr
- Phenotype ratio: 3 Red : 1 White
📊 Summary Table
| Cross | Genotypes | Phenotypes |
|---|---|---|
| RR × rr | 100% Rr | 100% Red |
| Rr × Rr | 1 RR : 2 Rr : 1 rr | 3 Red : 1 White |
📌 Quick Recap
– Monohybrid inheritance = study of one gene with two alleles.
– Uses Punnett squares to predict outcomes.
– Dominant allele masks recessive.
– Classic F2 ratio (for heterozygote cross) = 3:1 phenotype.
✨ Trick: Mono = One → focus on one gene at a time.
