Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.28 Mitosis- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.28 Mitosis- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.28 Mitosis- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
4.28 understand how division of a diploid cell by mitosis produces two cells that contain identical sets of chromosomes
Mitosis – Producing Identical Cells
🌱 Introduction
Mitosis = a type of cell division.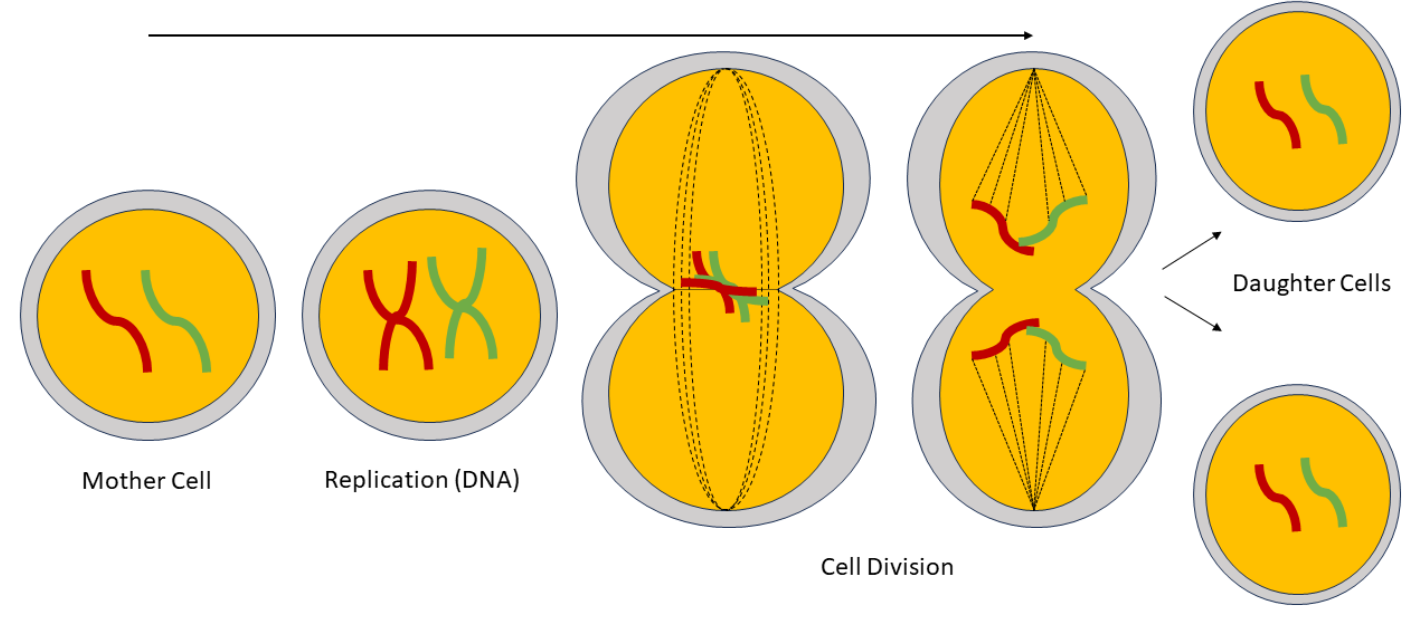
Happens in diploid cells (cells with full set of chromosomes).
Produces two genetically identical diploid daughter cells.
Essential for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction.
📌 Key Features of Mitosis
- Diploid → Diploid (chromosome number stays the same).
- Each new cell has identical DNA to the parent cell.
- Ensures genetic stability in tissues and organisms.
🔄 Stages of Mitosis
| Stage | What Happens | Easy Note |
|---|---|---|
| Interphase | DNA is replicated, chromosomes become double-stranded (sister chromatids). | Prep stage |
| Prophase | Chromosomes condense, spindle fibers form, nuclear envelope breaks down. | “Packaging” |
| Metaphase | Chromosomes line up along the cell equator. | “Middle” |
| Anaphase | Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles. | “Apart” |
| Telophase | New nuclear membranes form around sets of chromosomes. | “Two nuclei” |
| Cytokinesis | Cytoplasm divides → 2 identical cells formed. | Cell splits |
🎯 Outcome
- Two daughter cells produced.
- Both are diploid (2n) and genetically identical to the parent cell.
- Chromosome number is conserved.
📚 Importance of Mitosis
- Growth → more body cells.
- Repair → replaces damaged cells.
- Asexual reproduction → e.g., in plants (cuttings, runners).
- Genetic stability → no variation introduced.
📌 Quick Recap
Mitosis = 1 division → 2 identical diploid cells.
Maintains chromosome number.
Key uses: growth, repair, asexual reproduction.
Stages in order: IPMATC (Interphase → Prophase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase → Cytokinesis).
💡 Mnemonic for stages: Interesting People Meet At The Café
