Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.29 Meiosis- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.29 Meiosis- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.29 Meiosis- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
4.29 understand that mitosis occurs during growth, repair, cloning and asexual reproduction
Mitosis in Growth, Repair, Cloning & Asexual Reproduction
🔹 Introduction
Mitosis = type of cell division that produces two identical diploid daughter cells.
It is not just for multiplication, but also essential in many life processes.
📌 Where Mitosis Happens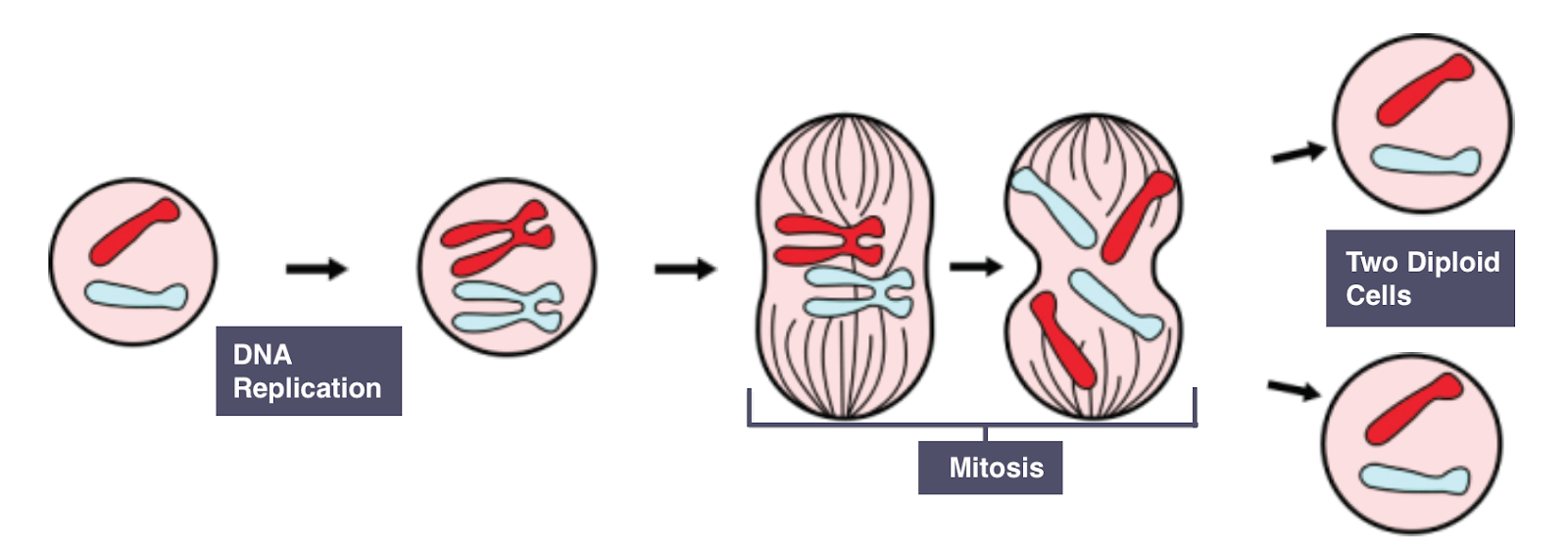
- Growth → to increase number of cells in an organism.
- Repair → to replace damaged or dead cells.
- Cloning → to produce genetically identical organisms.
- Asexual reproduction → in some organisms, it’s the method of making new individuals.
🧬 Roles of Mitosis
Growth
A fertilised egg (zygote) → divides repeatedly by mitosis → multicellular organism.
All cells have identical DNA, so body cells remain genetically stable.
Repair
Wounds heal by mitosis of nearby healthy cells.
Example: skin regeneration after a cut.
Cloning
Artificial cloning uses mitosis to produce identical copies.
Example: Dolly the sheep → nucleus from body cell (with diploid DNA) used for cloning.
Asexual Reproduction
Organisms like bacteria, Hydra, yeast, and some plants reproduce by mitosis.
Offspring are clones (genetically identical to parent).
📊 Summary Table
| Role of Mitosis | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Growth | Increases number of cells | From zygote → adult |
| Repair | Replaces damaged cells | Skin healing |
| Cloning | Produces identical organisms | Dolly the sheep |
| Asexual reproduction | Offspring formed without gametes | Hydra budding, bacteria |
📝 Quick Recap
Mitosis → produces 2 identical diploid cells.
Roles: Growth, Repair, Cloning, Asexual reproduction.
Growth → more cells; Repair → healing; Cloning → identical copies; Asexual reproduction → offspring without gametes.
Offspring / new cells are genetically identical.
