Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.38 Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.38 Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.38 Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
4.38 explain Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection
Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
🔹 Introduction
Evolution = change in inherited characteristics of a species over time.
Charles Darwin (1809–1882) proposed that evolution occurs via natural selection.
Explains how species adapt and survive in changing environments.
📌 Key Points of Natural Selection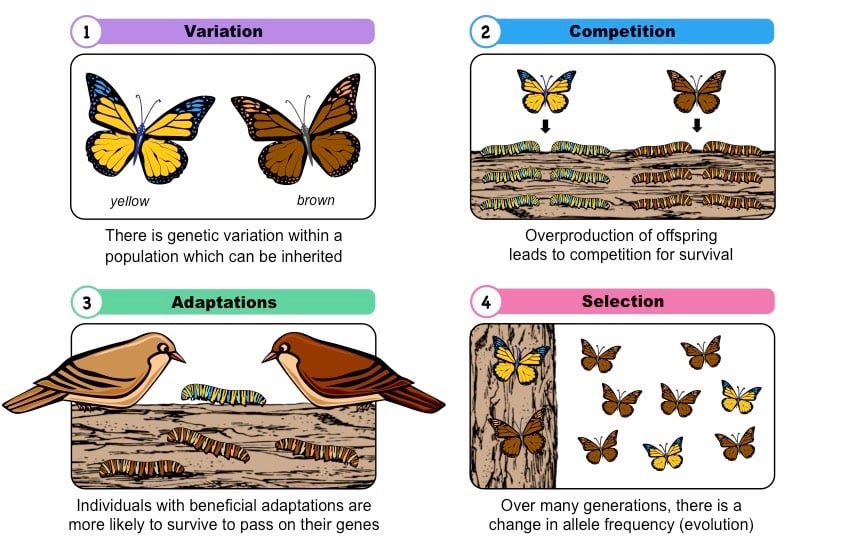
- Variation exists within a species: Individuals differ in traits (genetic & environmental).
Example: some beetles are green, some brown. - Overproduction of offspring: More offspring are born than can survive → competition for resources (food, shelter, mates).
- Survival of the fittest: Individuals with favourable traits are more likely to survive & reproduce. Traits improving survival = adaptations.
- Inheritance of favourable traits: Survivors pass advantageous traits to offspring → traits become more common over generations.
- Evolution over time: Gradual accumulation of changes → new species can form.
🧬 Example:
Peppered moths during Industrial Revolution:
Light moths → visible on soot-covered trees → eaten by birds
Dark moths → camouflage → survive & reproduce
Over time → population mostly dark moths
📊 Summary Table
| Step | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Variation | Differences in traits | Light vs dark moths |
| Overproduction | More offspring than resources | Many moths born |
| Selection | Favourable traits survive | Dark moths survive |
| Inheritance | Traits passed to next generation | Dark colour in offspring |
| Evolution | Population changes over time | Majority dark moths |
📝 Quick Recap
Natural selection = key mechanism of evolution.
Requires: variation + overproduction + survival of the fittest + inheritance.
Leads to adaptation and sometimes new species.
Famous example: Peppered moths.
