Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.7 Asexual Plant Reproduction- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.7 Asexual Plant Reproduction- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-4.7 Asexual Plant Reproduction- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
4.7 understand that plants can reproduce asexually by natural methods (illustrated by runners) and by artificial methods (illustrated by cuttings)
Asexual Reproduction in Plants
🌟 Introduction
Asexual reproduction = production of new plants without gametes.
Offspring are genetically identical (clones) to the parent.
Advantage → quick, reliable, no need for pollinators.
Disadvantage → no genetic variation (less adaptability).
🌿 1. Natural Method → Runners 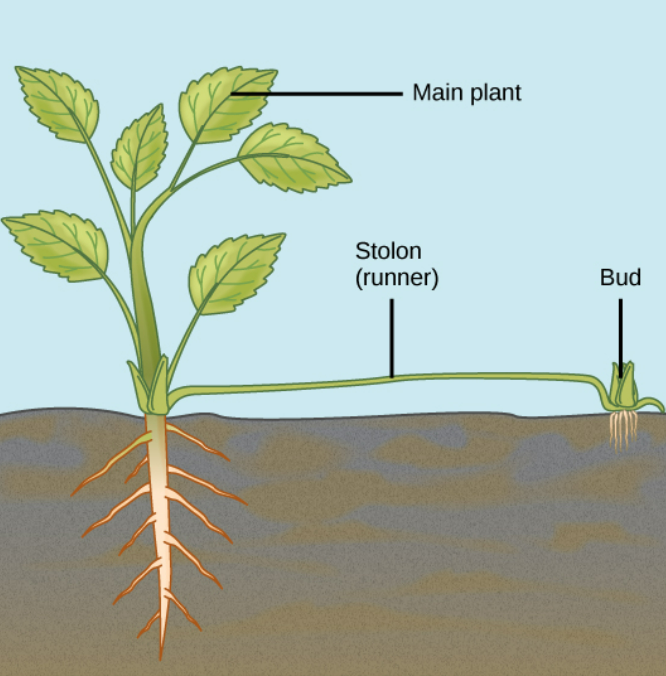
- Runner = a horizontal stem that grows along the surface of the soil.
- Example: strawberry plant
Process:
- Parent plant grows a runner (stolon) sideways.
- Runner touches soil → forms roots & shoots at nodes.
- These develop into new independent plants.
- Each plant is a clone of the parent.
Advantage: rapid spread of plants across an area.
🌱 2. Artificial Method → Cuttings
- Cutting = a piece of stem/leaf taken from a plant and grown into a new one.
- Examples: coleus, geranium, money plant
Process:
- A healthy stem cutting is taken.
- Planted in moist soil (sometimes dipped in rooting hormone).
- Cutting develops roots and grows into a new plant.
- Offspring = genetically identical to parent.
Advantage: easy way for gardeners to produce many plants quickly.
📊 Summary Table
| Method | Example | Process | Key Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural – Runners | Strawberry | Runners grow sideways, root at nodes | Spreads naturally |
| Artificial – Cuttings | Coleus, Geranium | Stem cutting grows roots in soil | Used in horticulture |
📌 Quick Recap
– Asexual reproduction = no gametes, offspring are clones.
– Natural method (runner) → strawberry spreads by stolons.
– Artificial method (cutting) → stem pieces grow roots to form new plants.
– Both methods are fast but lack variation.
