Edexcel iGCSE Biology-5.10 Carbon Cycle- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-5.10 Carbon Cycle- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-5.10 Carbon Cycle- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
5.10 describe the stages in the carbon cycle, including respiration, photosynthesis, decomposition and combustion
Carbon Cycle
🔹 Introduction
The carbon cycle describes how carbon moves between living organisms, atmosphere, oceans, soil, and rocks.
Carbon is essential for carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Carbon cycles continuously through producers, consumers, decomposers, and the environment.
📌 Stages of the Carbon Cycle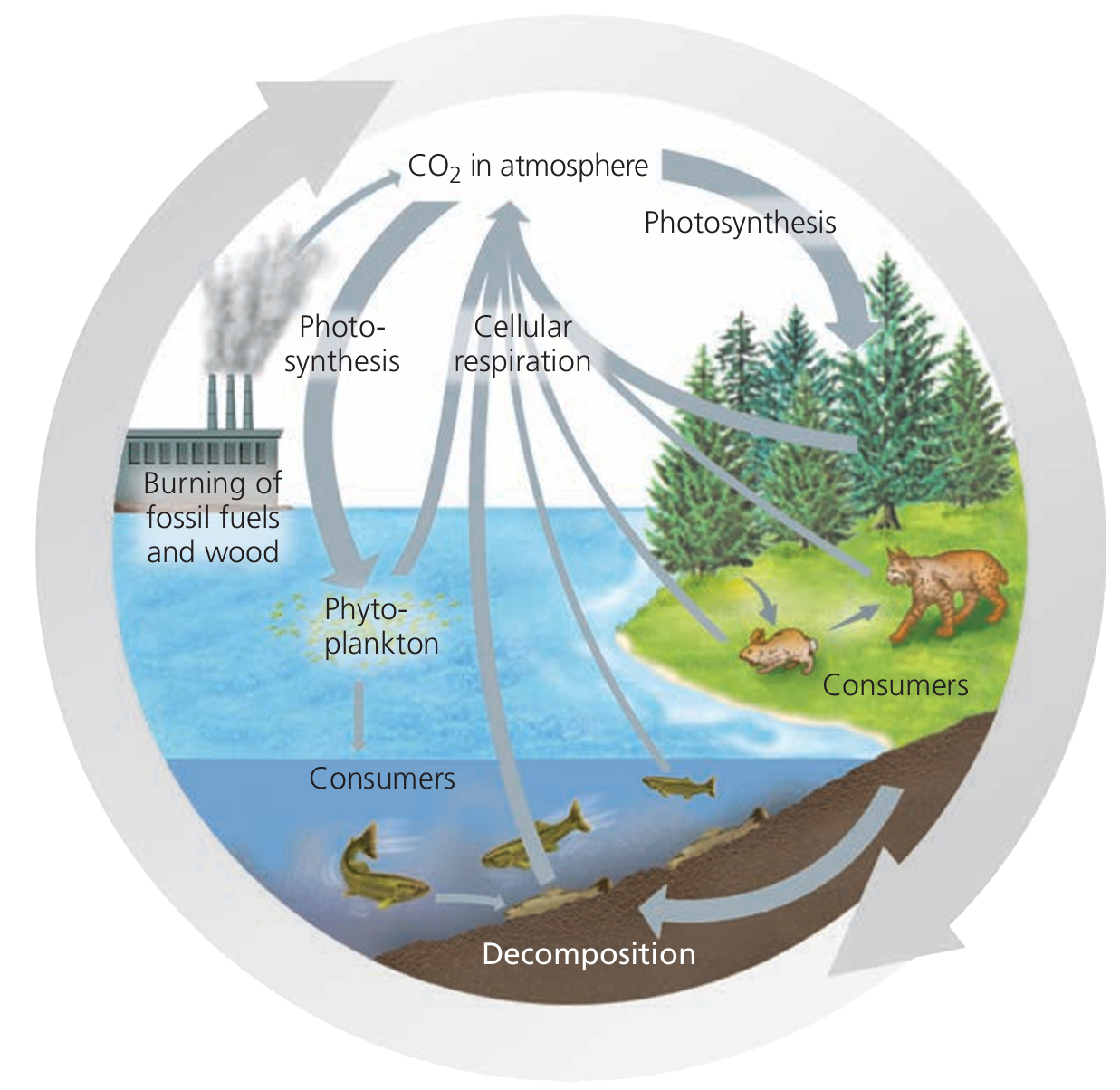
- Photosynthesis
Plants and algae absorb CO₂ and convert it into glucose using sunlight.
Equation: CO₂ + H₂O → (Sunlight) → C₆H₁₂O₆ + O₂
Role: Removes carbon from atmosphere, stores in plant biomass.
Importance: Basis of food chains, provides energy to all consumers. - Respiration
All organisms release CO₂ during cellular respiration.
Equation: C₆H₁₂O₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O + Energy
Role: Returns carbon to atmosphere, releases energy for life processes. - Decomposition
Dead plants, animals, and waste broken down by decomposers.
Organic carbon → CO₂ released to atmosphere or remains in soil.
Role: Recycles carbon, maintains soil fertility. - Combustion
Burning fossil fuels or organic matter releases CO₂.
Examples: Coal, oil, natural gas, forest fires, wood.
Role: Adds CO₂ to atmosphere, can increase global warming. - Other Carbon Movements
Sedimentation & Fossilization → carbon stored in rocks/fossil fuels over millions of years.
Ocean Absorption → CO₂ dissolves → forms carbonates → used by marine life.
📊 Summary Table
| Stage | Process | Role of Organisms/Process |
|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis | CO₂ → glucose | Plants/algae capture carbon, store in biomass |
| Respiration | Glucose → CO₂ + energy | All organisms release CO₂, provide energy |
| Decomposition | Organic matter → CO₂ | Decomposers recycle carbon to soil & atmosphere |
| Combustion | Fossil fuels/organic matter → CO₂ | Human activity & fires release CO₂ |
| Ocean absorption & sedimentation | CO₂ → carbonates/fossil fuels | Long-term storage of carbon |
📝 Quick Recap
Photosynthesis → removes CO₂ from atmosphere, stores in plants.
Respiration → returns CO₂ from all organisms to atmosphere.
Decomposition → recycles carbon from dead matter via decomposers.
Combustion → releases CO₂ from fuels & fires.
Cycle is continuous → maintains carbon balance on Earth.
