Edexcel iGCSE Biology-5.11B Nitrogen Cycle- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-5.11B Nitrogen Cycle- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-5.11B Nitrogen Cycle- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
5.11B describe the stages in the nitrogen cycle, including the roles of nitrogen fixing bacteria, decomposers, nitrifying bacteria and denitrifying bacteria (specific names of bacteria are not required)
Nitrogen Cycle
🔹 Introduction
Nitrogen is essential for life – used in amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids, and other nitrogen-containing compounds.
Atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) = ~78% of air, but unusable directly by most organisms.
Nitrogen cycles through soil, plants, animals, decomposers, and atmosphere, ensuring a constant supply for living organisms.
📌 Stages of the Nitrogen Cycle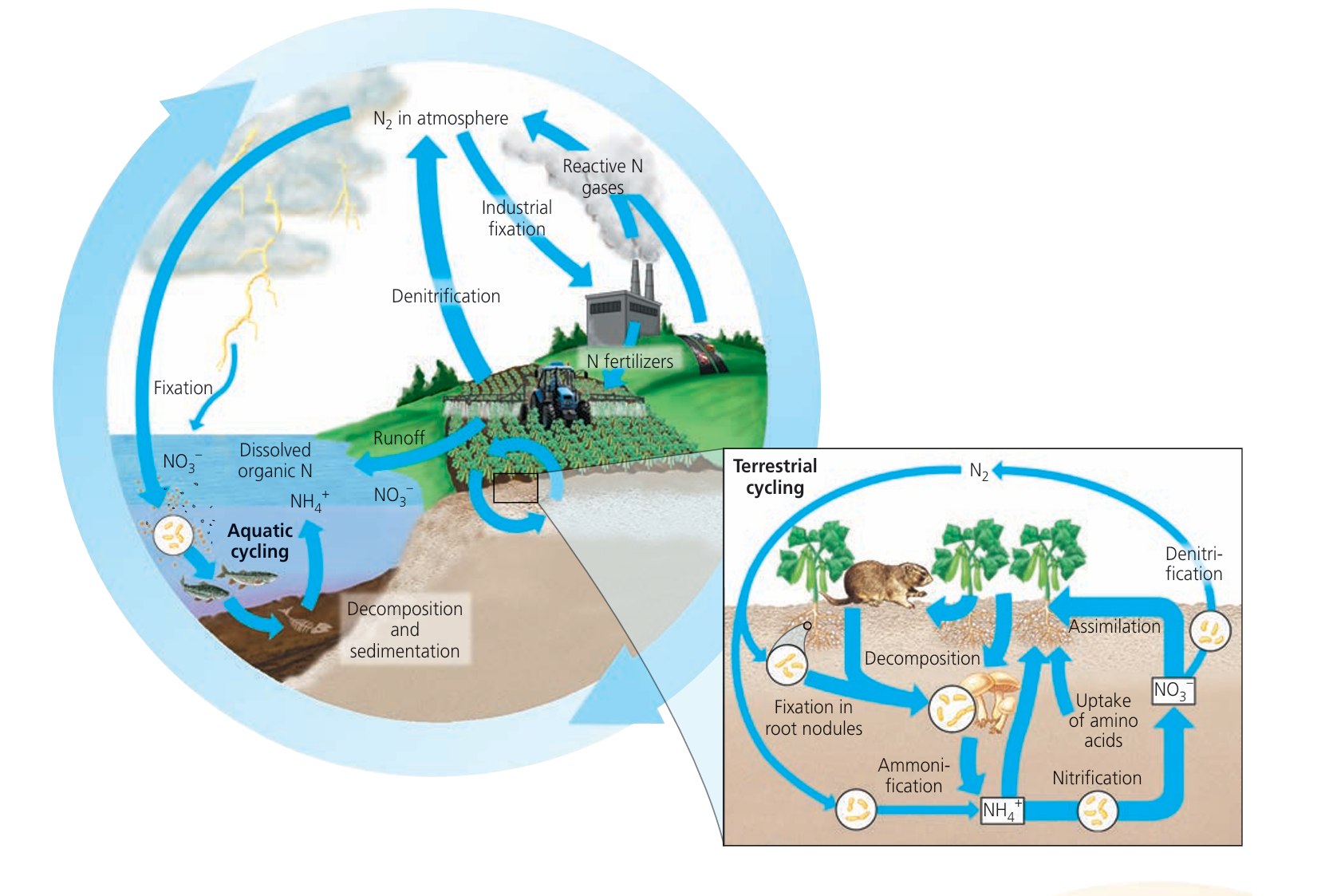
- Nitrogen Fixation
Conversion of atmospheric N₂ → ammonium (NH₄⁺) usable by plants.
How: Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in soil/root nodules of legumes capture N₂ and convert → NH₄⁺.
Importance: Introduces nitrogen into the ecosystem for plant growth.
Example: Beans, peas with root nodules. - Nitrification
Conversion of NH₄⁺ → NO₂⁻ → NO₃⁻ in soil.
Role: Nitrifying bacteria make nitrogen available in forms plants can absorb.
Importance: Provides nitrates for amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids. - Assimilation
Plants absorb nitrates → convert to amino acids → proteins → nucleic acids.
Animals obtain nitrogen by consuming plants or other animals.
Importance: Moves nitrogen through the food chain, supporting growth, repair, reproduction. - Ammonification
Organic nitrogen from dead matter/waste → NH₄⁺.
Role: Decomposers (bacteria & fungi) recycle nitrogen back into soil.
Importance: Maintains soil fertility, closes nitrogen cycle loop. - Denitrification
Nitrates (NO₃⁻) → N₂ in anaerobic conditions.
Role: Denitrifying bacteria return nitrogen to atmosphere.
Importance: Prevents excess nitrogen accumulation, maintains ecosystem balance.
📊 Summary Table – Stages & Roles
| Stage | Process | Role of Organisms/Agents | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen Fixation | N₂ → NH₄⁺ | Nitrogen-fixing bacteria | Introduces usable nitrogen into ecosystem |
| Nitrification | NH₄⁺ → NO₂⁻ → NO₃⁻ | Nitrifying bacteria | Makes nitrogen available to plants |
| Assimilation | NO₃⁻ → amino acids/proteins | Plants absorb, animals eat | Moves nitrogen through food chain |
| Ammonification | Organic N → NH₄⁺ | Decomposers (bacteria & fungi) | Recycles nitrogen back to soil |
| Denitrification | NO₃⁻ → N₂ | Denitrifying bacteria | Returns nitrogen to atmosphere |
📝 Quick Recap
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria → N₂ → NH₄⁺ (usable for plants).
Nitrifying bacteria → NH₄⁺ → NO₂⁻ → NO₃⁻ (plants absorb).
Decomposers → dead matter/waste → NH₄⁺ (recycles nitrogen).
Denitrifying bacteria → NO₃⁻ → N₂ (returns nitrogen to air).
Nitrogen cycles continuously through soil, plants, animals, decomposers, and atmosphere, maintaining ecosystem balance.
