Edexcel iGCSE Biology-5.7 Food chains, Food webs & Pyramids- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-5.7 Food chains, Food webs & Pyramids- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-5.7 Food chains, Food webs & Pyramids- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
5.7 understand the concepts of food chains, food webs, pyramids of number, pyramids of biomass and pyramids of energy transfer
Food Chains, Food Webs & Ecological Pyramids
Food Chains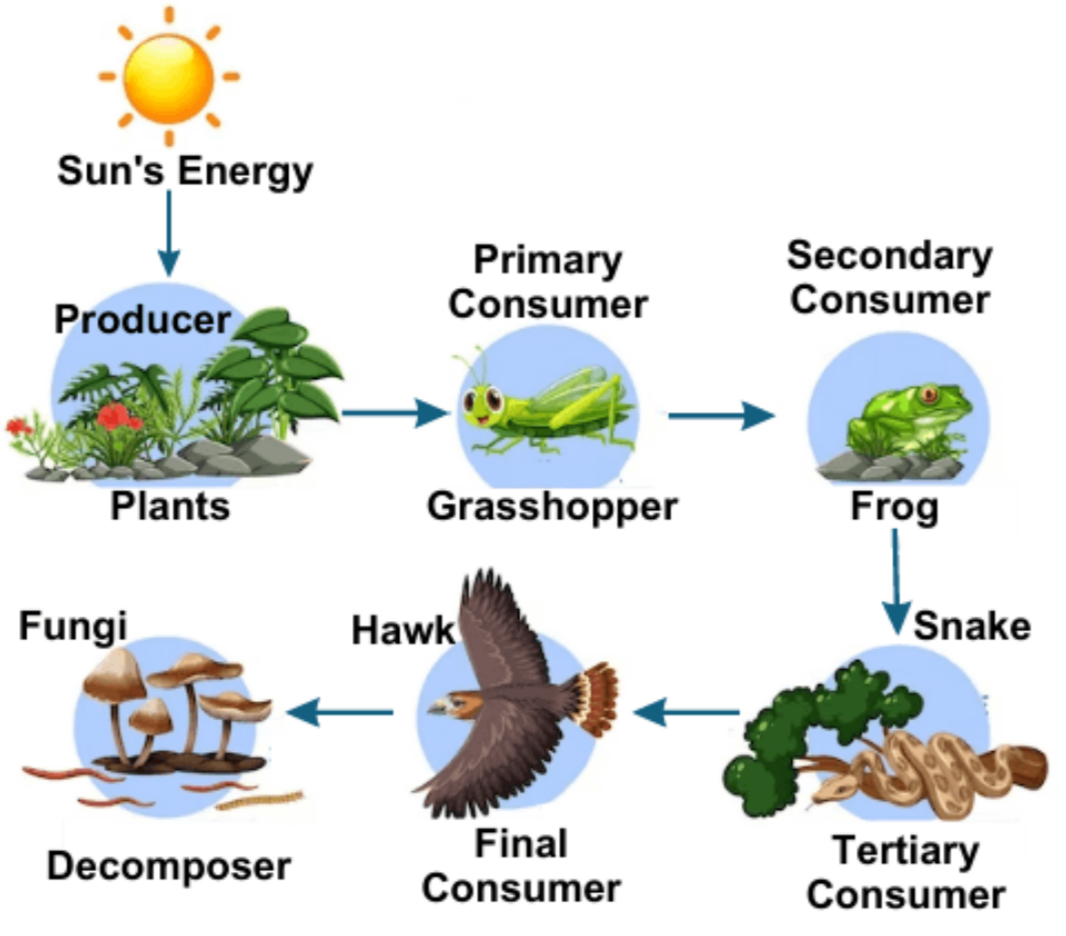
Definition: A simple sequence showing how energy and nutrients flow from one organism to another.
Direction: Always one way (arrow shows “is eaten by”).
Example:
Grass → Rabbit → Fox → Eagle
📌 Key Point: Short, linear. If one link is broken, whole chain is affected.
Food Webs
Definition: A network of interconnected food chains in an ecosystem.
Why important? More realistic than food chains; shows that organisms eat more than one type of food.
Example: Grass eaten by rabbit, deer, insects → eaten by fox, hawk, frog → decomposers recycle nutrients.
📌 Key Point: Provides stability to the ecosystem. If one species disappears, others survive via alternate links.
Pyramids in Ecology
Pyramids represent feeding relationships + energy transfer. Base = producers, top = top carnivores.
1. Pyramid of Numbers
- Definition: Shows number of organisms at each trophic level.
- Shape: Usually upright; can be inverted (e.g., one tree supports thousands of insects).
- Example: Grass (1000) → Grasshoppers (500) → Frogs (50) → Snakes (5)
2. Pyramid of Biomass
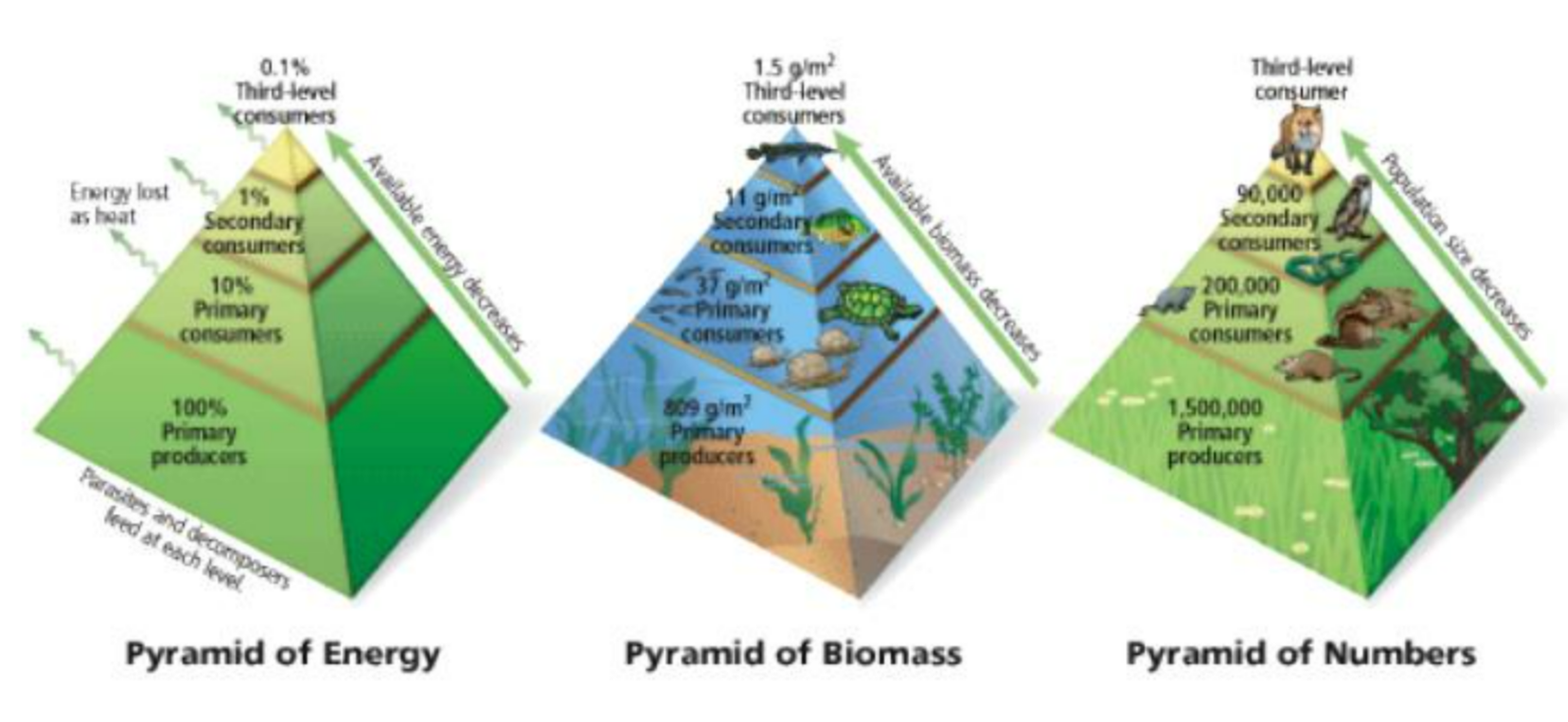
- Definition: Shows total dry mass of organisms at each trophic level.
- Shape: Usually upright; can be inverted in aquatic ecosystems.
- Example: Grass (2000 kg) → Cows (500 kg) → Humans (50 kg)
3. Pyramid of Energy Transfer
- Definition: Shows energy available at each trophic level per unit area/time.
- Shape: Always upright (energy decreases step by step).
- Rule: Only ~10% energy passed on; rest lost as heat, respiration, movement.
- Example: Grass (10,000 J) → Grasshopper (1,000 J) → Frog (100 J) → Snake (10 J)
📊 Summary Table
| Concept | Definition | Shape | Example / Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Chain | Linear energy flow | – | Grass → Rabbit → Fox |
| Food Web | Network of food chains | – | Grass eaten by many herbivores |
| Pyramid of Numbers | Number of organisms | Upright / Inverted | Tree → Insects |
| Pyramid of Biomass | Dry mass at each level | Upright / Inverted (aquatic) | Grassland vs pond |
| Pyramid of Energy | Energy flow (per area/time) | Always Upright | 10% rule |
📝 Quick Recap
Food chain = single pathway, food web = network.
Pyramids:
• Numbers → count of organisms.
• Biomass → total dry mass.
• Energy → energy transfer, always upright.
Energy flow = one way obeys 10% rule.
Food webs = more stable than chains.
