Edexcel iGCSE Biology-5.8 & 5.9 Transfers Along a Food Chain- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-5.8 & 5.9 Transfers Along a Food Chain- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-5.8 & 5.9 Transfers Along a Food Chain- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
5.8 understand the transfer of substances and energy along a food chain
5.9 understand why only about 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next
Transfer of Substances & Energy in Food Chains
🔹 Introduction
In ecosystems, energy and substances (nutrients) move from one organism to another through feeding relationships.
This is called energy flow and material cycling.
📌 Transfer of Substances
Substances include: water, minerals, organic matter (carbohydrates, proteins, fats).
How transferred:
- Producers: Absorb minerals from soil/water & make organic molecules via photosynthesis.
- Primary consumers: Eat producers → gain substances (glucose, amino acids).
- Secondary & tertiary consumers: Eat lower consumers → substances transferred along food chain.
- Decomposers: Break down dead organisms → release minerals back into soil for producers.
Key point: Substances recycle in ecosystem → unlike energy, they are not lost.
📌 Transfer of Energy
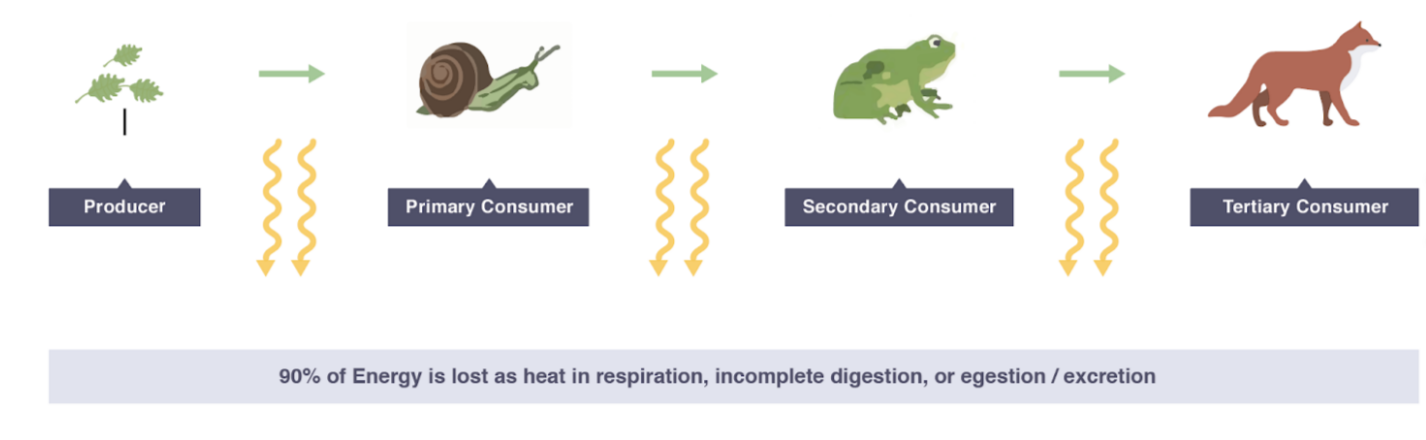
Energy source: Sun ☀️
Flow: Sun → Producers → Primary Consumers → Secondary Consumers → Tertiary Consumers → Decomposers
10% Rule: Only ~10% of energy passes to the next trophic level. Rest lost as:
- Heat (respiration)
- Movement & activity
- Waste products
Example:
Grass (10,000 J) → Grasshopper (1,000 J) → Frog (100 J) → Snake (10 J) → Decomposer recycles nutrients.
Key Point: Energy flow is one-way, unlike substances which recycle.
📊 Summary Table
| Aspect | How It Works | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| Substances | Minerals & organic compounds pass via feeding; decomposers recycle | Recycled, not lost |
| Energy | Sun → producers → consumers → decomposers | One-way, 10% transferred |
📝 Quick Recap
Substances: recycled → soil → plants → consumers → decomposers → soil
Energy: one-way → Sun → producers → consumers → decomposers
Only ~10% energy passes to next level; rest lost as heat, movement, waste
Energy Transfer Between Trophic Levels
🔹 Introduction
Energy flows from Sun → producers → consumers → top predators.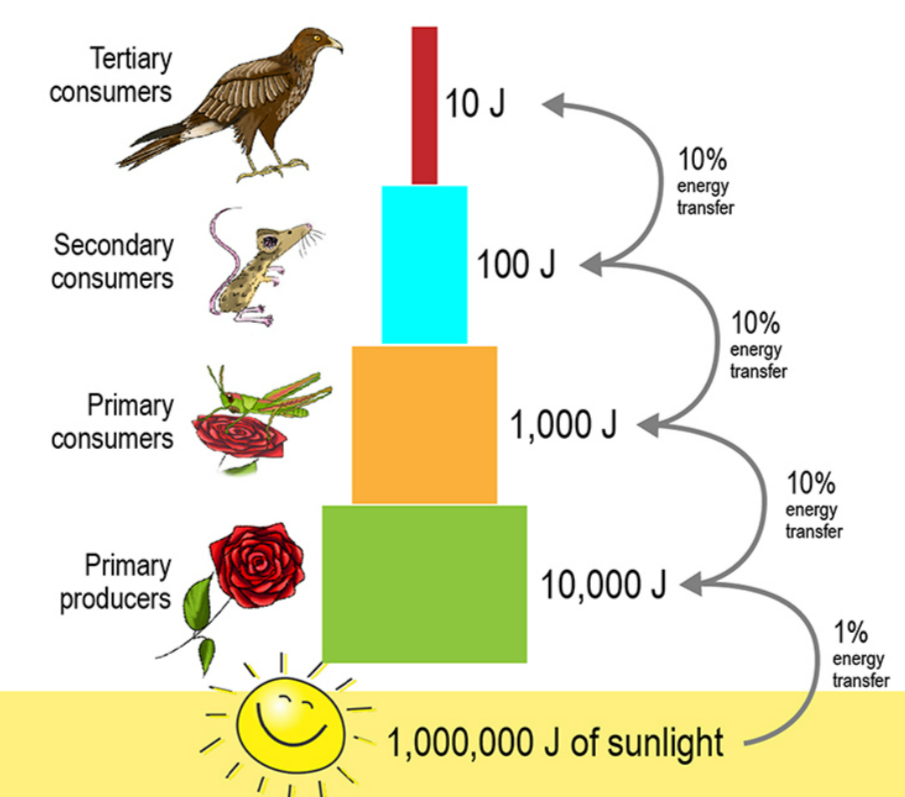
Only about 10% of energy is transferred to the next trophic level.
Rest of the energy is lost, explaining why energy pyramids always decrease upwards.
📌 Reasons for Energy Loss
- Respiration & Heat Loss: Organisms use energy for movement, growth, reproduction. Most energy lost as heat during respiration.
- Incomplete Consumption: Not all parts of food are eaten (e.g., bones, roots, shells). Energy in these uneaten parts is not passed on.
- Indigestible Materials: Some eaten food cannot be digested (cellulose, hair). Energy in indigestible parts is excreted as waste.
- Energy Used for Maintenance: Energy used for keeping the body alive (e.g., repairing cells, pumping blood) is not stored.
📊 Summary Table
| Reason | Example / Explanation |
|---|---|
| Respiration & Heat Loss | Movement, keeping warm, metabolic activity |
| Incomplete Consumption | Roots, bones, tough leaves not eaten |
| Indigestible Material | Cellulose, hair, feathers → excreted |
| Maintenance Energy | Cell repair, circulation, nerve impulses |
📝 Quick Recap
Only ~10% of energy passes to next level → rest lost as:
– Heat via respiration
– Uneaten food parts
– Indigestible waste
– Energy for maintenance
