Edexcel iGCSE Biology-6.1-6.3 Increasing Crop Yield with Glasshouses, Climate, and Fertilisers- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-6.1-6.3 Increasing Crop Yield with Glasshouses, Climate, and Fertilisers- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-6.1-6.3 Increasing Crop Yield with Glasshouses, Climate, and Fertilisers- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
6.1 describe how glasshouses and polythene tunnels can be used to increase the yield of certain crops
6.2 understand the effects on crop yield of increased carbon dioxide and increased temperature in glasshouses
6.3 understand how the use of fertiliser can increase crop yield
Using Glasshouses and Polythene Tunnels to Increase Crop Yield
🌱 Introduction
Glasshouses (greenhouses) and polythene tunnels are structures used in controlled farming to increase crop yield.
They allow farmers to control environmental conditions like temperature, light, humidity, and pests, ensuring faster growth and better quality crops.
🏠 Glasshouses
- Structure
Made of glass walls and roof.
Transparent → allows sunlight to enter.
Traps heat inside, creating a warm environment. - How They Increase Yield
Warmer temperature → faster photosynthesis → faster plant growth.
Protect plants from cold weather, frost, and wind.
Humidity control → reduces water loss through transpiration.
Easier to control pests and diseases using nets or sprays.
Crops can be grown all year round, not just in a season.
🛖 Polythene Tunnels
- Structure
Long tunnels made of metal hoops and polythene sheets.
Lightweight and cheaper than glasshouses.
Can cover rows of crops. - How They Increase Yield
Traps heat inside → warmer microclimate for crops.
Protects from rain, frost, and strong winds.
Reduces pest attack by creating a physical barrier.
Maintains humidity → reduces water stress on plants.
Useful for vegetables and fruits grown out of season.
📊 Comparison Table
| Feature | Glasshouse | Polythene Tunnel |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Glass | Polythene sheet |
| Cost | Expensive | Cheaper |
| Structure | Rigid, permanent | Flexible, semi-permanent |
| Temperature control | Excellent | Good |
| Humidity control | Very good | Good |
| Pest control | Easy | Moderate |
| Crops grown | Fruits, flowers, vegetables | Vegetables, strawberries, early crops |
| Seasonal growth | All year | Mostly early or off-season crops |
💡 Benefits of Both
- Faster growth → earlier harvest
- Protection from weather extremes
- Reduced pest and disease damage
- Higher yield and better quality crops
- Can grow out-of-season crops
📘 Quick Recap
Glasshouses & polythene tunnels = controlled environment farming
Warm + humid + protected → faster photosynthesis → more yield
All-year or off-season crop growth
Pest and frost protection
🧠 Mnemonic: “Trap Heat → Grow Sweet → Yield Complete”
Effects of Increased Carbon Dioxide and Temperature on Crop Yield in Glasshouses
🌱 Introduction
Glasshouses allow control of environmental factors such as CO₂ levels and temperature to enhance plant growth and crop yield.
Two key factors that can be manipulated in glasshouses:
- Carbon dioxide concentration
- Temperature
🌡️ Effect of Increased Carbon Dioxide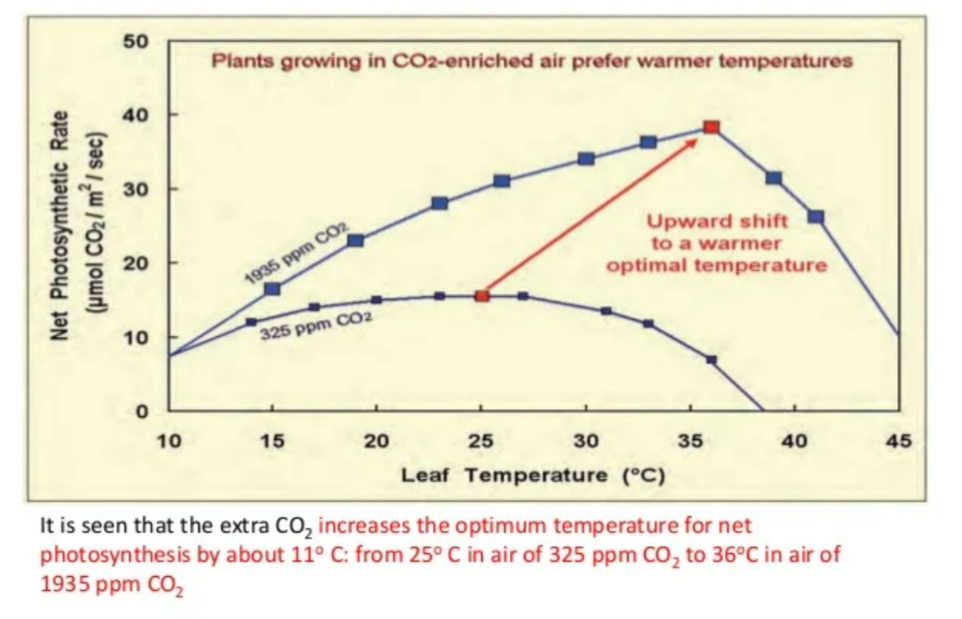
- CO₂ is a raw material for photosynthesis.
- Increasing CO₂ concentration (e.g., from 0.04% to 0.1%) → faster photosynthesis rate → higher growth.
- Leads to larger leaves, faster fruit development, and higher yield.
- CO₂ enrichment is especially useful for tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers.
Tip: “More CO₂ → More Sugar → More Crop”
🔥 Effect of Increased Temperature
- Most crops have an optimal temperature range for growth.
- Slight increase in temperature:
- Faster enzyme activity → faster photosynthesis and respiration → quicker growth.
- Can shorten the time to harvest.
- Too high temperature:
- Enzyme denaturation → slowed photosynthesis → reduced growth.
- Water loss through transpiration increases, causing stress.
Key: Temperature must be controlled carefully in glasshouses.
🌾 Combined Effect on Crop Yield
| Factor | Effect on Crop Growth | Effect on Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Increased CO₂ | Faster photosynthesis, bigger leaves | Higher yield, better fruits/vegetables |
| Increased temperature (optimal) | Enzyme activity increases | Faster growth, early harvest |
| Too high temperature | Enzymes damaged, water stress | Lower yield, poor quality crops |
💡 Additional Points
- Glasshouse management often uses CO₂ burners and heating systems to maintain optimal conditions.
- Crop yield increases only if water, nutrients, and light are sufficient.
- Monitoring ensures no stress conditions like overheating or CO₂ toxicity.
📘 Quick Recap
CO₂ ↑ → Photosynthesis ↑ → Yield ↑
Temperature optimal → Growth faster → Early harvest
Too high temperature → Stress → Yield ↓
🧠 Mnemonic: “CO₂ feeds, Heat speeds, Too much bleeds”
How Fertilisers Increase Crop Yield
🌱 Introduction
Fertilisers are substances added to soil or plants to provide essential nutrients for growth.
They are important because crops remove nutrients from the soil during growth, and without replacement, soil fertility decreases, limiting crop yield.
⚡ Role of Fertilisers
- Supply essential mineral nutrients like:
- Nitrogen (N) → promotes leaf and stem growth
- Phosphorus (P) → supports root growth, flowering, and fruiting
- Potassium (K) → improves disease resistance, water regulation, and fruit quality
- Can be organic (manure, compost) or inorganic (chemical fertilisers like NPK mix).
🌾 How Fertilisers Increase Yield
- Improved Growth: Adequate nutrients → larger leaves, stronger stems → more photosynthesis → higher yield.
- Faster Development: Fertilisers ensure no nutrient limitation, allowing crops to reach maturity quickly.
- Better Quality Produce: Balanced nutrients → bigger fruits, healthier vegetables, higher protein in grains.
- Multiple Cropping: Fertilisers replenish soil → support repeated cropping → more produce per year.
📊 Summary Table
| Nutrient | Role in Plant | Effect on Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | Leaf & stem growth | More photosynthesis → larger plants → higher yield |
| Phosphorus (P) | Roots, flowers, fruits | Strong roots & better fruiting → better quality & quantity |
| Potassium (K) | Water balance, disease resistance | Healthier plants → less loss & higher harvest |
⚠️ Important Notes
- Excess fertiliser → leaching, water pollution, eutrophication → environmental damage.
- Fertilisers must be applied in correct amount and ratio.
- Often combined with good irrigation and pest control for maximum yield.
📘 Quick Recap
Fertilisers = nutrient boosters → more growth, better quality, faster development
N → leaves & stem, P → roots & fruit, K → health & quality
Balanced fertiliser use → higher crop yield
🧠 Mnemonic: “N for Leaf, P for Root, K for Health → Yield Boost”
