Edexcel iGCSE Biology-6.10–6.11 Selective Breeding in Plants and Animals- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-6.10–6.11 Selective Breeding in Plants and Animals- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-6.10–6.11 Selective Breeding in Plants and Animals- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
6.10 understand how selective breeding can develop plants with desired characteristics
6.11 understand how selective breeding can develop animals with desired characteristics
Selective Breeding in Plants
🌱 Introduction
Selective breeding (artificial selection) is the process of choosing plants with desirable traits and breeding them over generations to produce offspring with improved characteristics.
Goal: Develop plants that are high-yielding, disease-resistant, or have other useful traits.
⚡ How Selective Breeding Works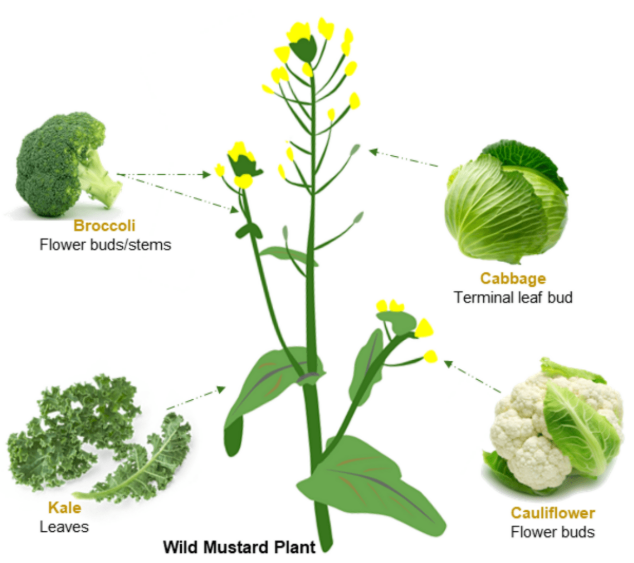
- Identify Desired Trait:
Examples:
– High fruit yield
– Pest or disease resistance
– Drought tolerance
– Faster growth - Select Parent Plants:
Choose plants showing the trait most strongly.
Only these plants are used for reproduction. - Cross-Pollination / Controlled Breeding:
Plants are crossed intentionally to combine desirable traits.
Prevents unwanted traits from spreading. - Repeat Over Generations:
Offspring showing the desired trait are further selected.
Over several generations → trait becomes stable.
🌾 Examples of Selective Breeding
- Wheat & Rice → higher yield and disease resistance
- Tomatoes → larger, juicier fruits
- Maize → drought-tolerant varieties
📊 Summary Table
| Step | Purpose | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Identify trait | Know what to improve | Targeted breeding |
| Select parents | Choose best plants | Strong trait passed on |
| Controlled breeding | Cross desired plants | Combine traits |
| Repeat generations | Stabilize trait | New improved plant variety |
💡 Quick Recap
Selective breeding = choosing best plants + breeding them
Goal: Desired traits → high yield, resistance, quality
Process: Identify → select → breed → repeat
🧠 Mnemonic: “I See Cool Replants” (Identify, Select, Cross, Repeat)
Selective Breeding in Animals
🌱 Introduction
Selective breeding (artificial selection) in animals is the process of choosing individuals with desirable traits and breeding them to produce offspring with improved characteristics.
Goal: Improve productivity, quality, or specific traits useful to humans.
⚡ How Selective Breeding Works
- Identify Desired Trait:
Examples:
– High milk production in cows
– Fast growth in chickens
– Strong, healthy work animals (horses, oxen)
– Disease resistance - Select Parent Animals:
Only individuals showing the strongest expression of the trait are used for breeding. - Controlled Mating:
Animals are bred intentionally to ensure the trait is passed on.
Prevents unwanted traits from spreading. - Repeat Over Generations:
Offspring with desired traits are further selected.
Over several generations → trait becomes stable in population.
🌾 Examples of Selective Breeding
- Cows → higher milk yield
- Chickens → larger eggs or faster growth
- Sheep → thicker wool
- Horses → stronger and faster breeds
📊 Summary Table
| Step | Purpose | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Identify trait | Know what to improve | Targeted breeding |
| Select parents | Choose best animals | Strong trait passed on |
| Controlled mating | Breed desired individuals | Combine traits |
| Repeat generations | Stabilize trait | New improved animal breed |
💡 Quick Recap
Selective breeding = choosing best animals + controlled mating
Goal: Desired traits → productivity, quality, resistance
Process: Identify → select → breed → repeat
🧠 Mnemonic: “I See Clever Reproduce” (Identify, Select, Controlled mating, Repeat)
