Edexcel iGCSE Biology-6.14 Manufacturing Human Insulin- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-6.14 Manufacturing Human Insulin- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Biology-6.14 Manufacturing Human Insulin- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
6.14 understand how large amounts of human insulin can be manufactured from genetically modified bacteria that are grown in a fermenter
Human Insulin Production Using GM Bacteria
📌 Introduction
Before biotechnology, diabetic patients depended on insulin extracted from animals (like pigs and cows).
Now, human insulin is produced safely and in large quantities using genetically modified (GM) bacteria grown in industrial fermenters.
This method is efficient, ethical, and produces insulin identical to human insulin.
🧩 Step-by-Step Process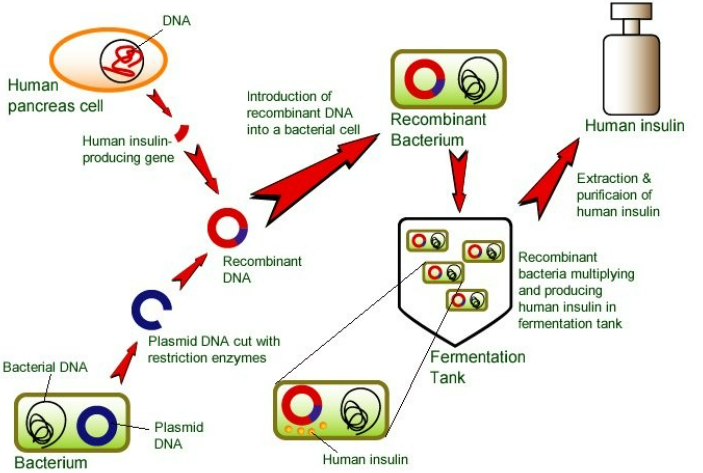
- Identify and Isolate the Human Insulin Gene
Scientists locate the insulin-producing gene on human DNA.
This gene is cut out using a restriction enzyme (acts like molecular scissors). - Prepare the Plasmid Vector
A plasmid (small circular DNA from bacteria) is removed.
The same restriction enzyme is used to cut open the plasmid at a specific site. - Insert the Human Gene into the Plasmid
The insulin gene is inserted into the plasmid DNA using the enzyme ligase (DNA glue).
The result is recombinant DNA (rDNA) – a combination of human and bacterial DNA. - Insert Recombinant Plasmid into Bacterium
The recombinant plasmid is placed back into a bacterial cell (usually E. coli).
The bacterium now becomes genetically modified (GM) because it carries a human gene. - Grow GM Bacteria in a Fermenter
These bacteria are grown in large stainless steel fermenters under controlled conditions:
- Identify and Isolate the Human Insulin Gene
| Condition | Importance |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Optimum for bacterial enzyme activity |
| pH | Kept steady for best growth |
| Oxygen | Needed for aerobic respiration |
| Nutrients | Glucose + minerals for energy and growth |
| Agitation | Keeps mixture even and oxygen well distributed |
As the bacteria multiply, they produce human insulin as one of their proteins.
Extraction and Purification of Insulin
The insulin is collected from the fermenter mixture, then Filtered, Purified, and Prepared for medical use in diabetic patients.
🌿 Advantages of GM Bacterial Insulin
- Identical to human insulin → no allergic reactions.
- Cheaper and faster production.
- No animal sources required → ethical.
- Can be produced in unlimited amounts.
- Stable and reliable — same quality every batch.
🧠 Mnemonic Trick
“I Picked In Intelligent Bacteria” → Isolate → Prepare plasmid → Insert gene → Into bacteria → Bacteria produce insulin
📊 Summary Table
| Step | Process | Enzyme/Tool Used | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Isolate insulin gene | Restriction enzyme | Human insulin gene obtained |
| 2 | Cut open plasmid | Same restriction enzyme | Opening for insertion |
| 3 | Insert gene | Ligase enzyme | Recombinant plasmid formed |
| 4 | Transform bacteria | – | GM bacteria created |
| 5 | Grow in fermenter | Controlled environment | Insulin produced |
| 6 | Extract and purify | – | Ready-to-use insulin |
⚙️ Fermenter Diagram 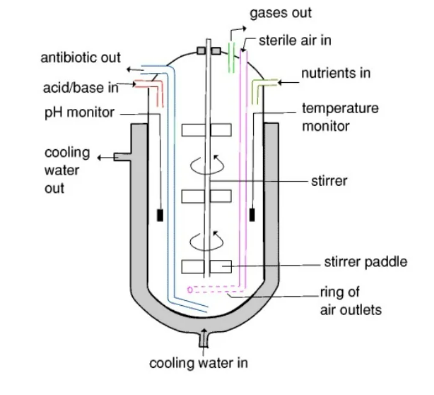
- A large steel tank with:
- Stirrer → keeps mixture even
- Air inlet → supplies oxygen
- pH & temperature sensors → automatic control
- Outlet → for extracting insulin
💡 Quick Recap
Human insulin gene → cut by restriction enzyme
Inserted into bacterial plasmid → ligase joins → recombinant DNA
GM bacteria grown in fermenter → produce insulin
Insulin is purified for human use
Advantages → cheap, ethical, pure, reliable
