Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.11–1.12 Effects and Types of Forces- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.11–1.12 Effects and Types of Forces- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.11–1.12 Effects and Types of Forces- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
1.11 describe the effects of forces between bodies such as changes in speed, shape or direction
1.12 identify different types of force such as gravitational or electrostatic
Effects of Forces
A force is a push or a pull that acts on an object. When forces act between bodies, they can change how an object moves or alter its shape.
The effect of a force depends on its size, direction, and how it acts on the object.
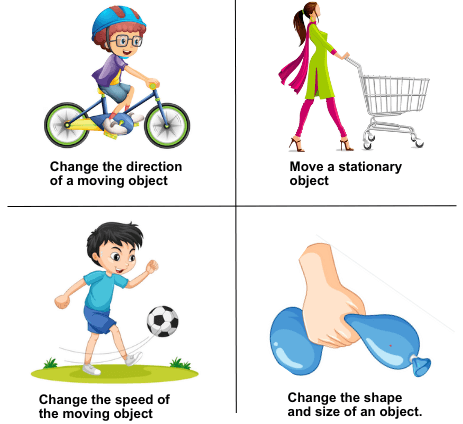
Main Effects of Forces
Forces between bodies can cause the following effects:
- Change in speed
- Change in direction of motion
- Change in shape (deformation)
1. Change in Speed
A force can change the speed of an object by causing it to accelerate or decelerate.
- If a force acts in the direction of motion, the object speeds up.
- If a force acts opposite to the direction of motion, the object slows down.
- If there is no resultant force, speed remains constant.
Examples include a car speeding up when the engine force increases or slowing down due to friction.
2. Change in Direction
A force can change the direction of motion without changing speed.
- This occurs when the force acts at an angle to the motion.
- The object follows a curved or circular path.
- The speed may stay constant, but velocity changes because direction changes.
An example is a ball moving in a circular path when tied to a string.
3. Change in Shape
A force can change the shape of an object by stretching, compressing, or bending it.
- Some objects return to their original shape (elastic deformation).
- Some objects do not return to their original shape (plastic deformation).
Examples include stretching a spring or squeezing a soft object.
Key Idea
- Forces can affect motion and shape.
- More than one effect can occur at the same time.
- The overall effect depends on the resultant force.
Important Points to Remember
- Forces do not always change speed.
- A change in direction is still a change in velocity.
- Contact and non-contact forces can both cause these effects.
Example
A cyclist applies the brakes on a moving bicycle. Describe the effect of the force acting on the bicycle.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The braking force acts opposite to the direction of motion.
This causes the bicycle to slow down, so its speed decreases.
Example
A tennis ball hits a wall and bounces back. Describe the effects of the forces acting on the ball.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The force from the wall changes the direction of the ball.
The ball also briefly changes shape as it is compressed during the collision.
Types of Forces
A force is a push or a pull that acts between objects. There are many different types of forces, but they can be grouped into contact forces and non-contact forces.
Identifying the type of force acting in a situation helps to explain how objects move or interact.
Contact and Non-Contact Forces
- Contact forces act only when objects are touching.
- Non-contact forces act over a distance without direct contact.
Non-Contact Forces
1. Gravitational Force
The gravitational force is an attractive force between masses.
- Acts between any two objects with mass.
- Always attractive.
- Responsible for objects falling to the ground.
- Acts towards the centre of the Earth.
2. Electrostatic Force
The electrostatic force acts between electrically charged objects.
- Acts between positive and negative charges.
- Unlike charges attract; like charges repel.
- Can act over a distance.
3. Magnetic Force
The magnetic force acts between magnets or magnetic materials.
- Acts between north and south poles.
- Like poles repel; unlike poles attract.
- Can act without contact.
Contact Forces
4. Frictional Force
Friction is a force that opposes motion between two surfaces in contact.
- Acts opposite to the direction of motion.
- Occurs when surfaces rub against each other.
- Can slow objects down or prevent motion.
5. Air Resistance (Drag)
Air resistance is a type of friction caused by air.
- Acts on moving objects in air.
- Increases with speed.
- Acts opposite to the direction of motion.
6. Normal Contact Force
The normal contact force is the force between two touching surfaces that prevents them from passing through each other.
- Acts perpendicular to the surface.
- Supports objects resting on surfaces.
Key Idea
- Forces can act with or without contact.
- Different forces can act on an object at the same time.
- The type of force depends on how objects interact.
Important Points to Remember
- Weight is a gravitational force.
- Friction and air resistance are contact forces.
- Electrostatic and magnetic forces act at a distance.
Example
An apple falls from a tree to the ground. Identify the main force causing this motion.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The apple falls due to the gravitational force acting towards the Earth.
Example
A balloon rubbed on a jumper sticks to a wall. Identify the force responsible.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The balloon sticks due to an electrostatic force between charged objects.
